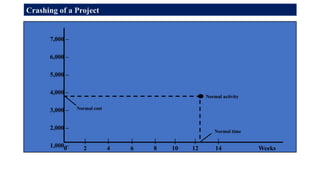
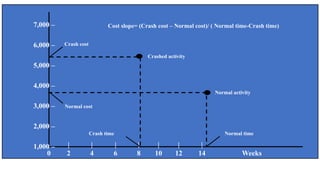
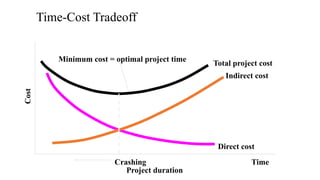
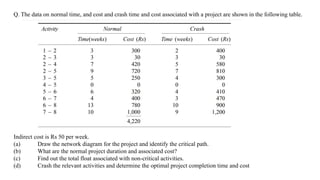
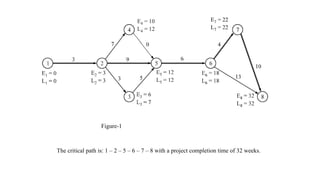
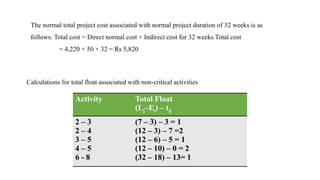
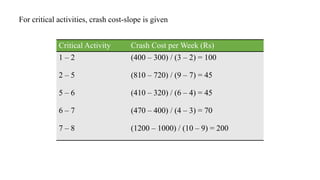
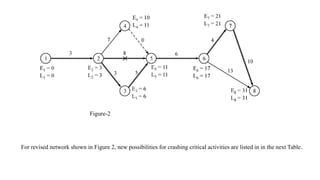
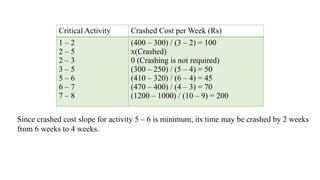
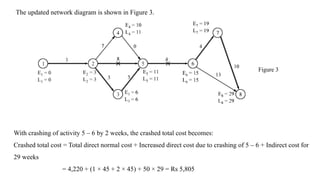
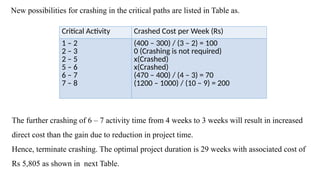
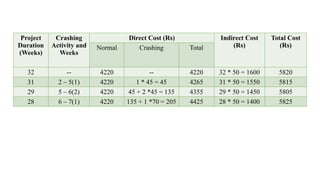
The document discusses the process of crashing a project to reduce its duration by analyzing costs associated with materials, labor, and expenses. It outlines steps to compute cost slopes, identify critical activities, and determine the optimal project completion time and cost. The analysis concludes with calculations showing the normal project duration of 32 weeks and potential cost reductions through strategic crashing of activities.