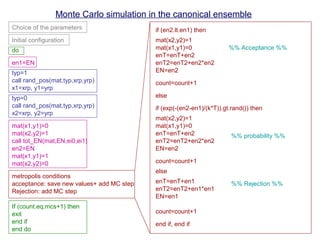
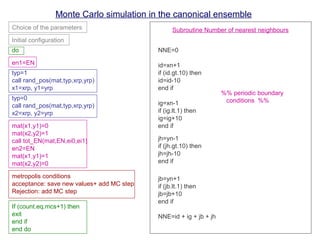
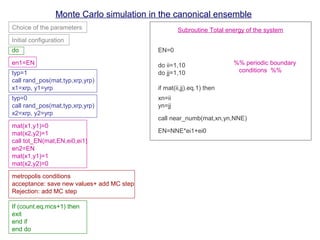
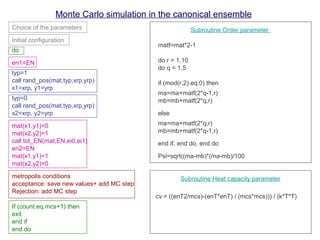
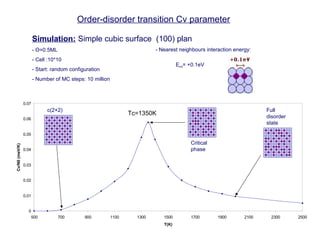
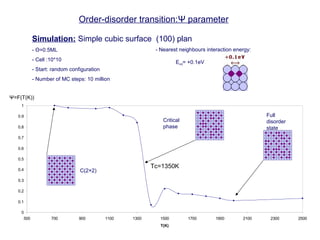
The document discusses Monte Carlo methods for simulating systems in statistical mechanics, focusing on the Metropolis algorithm for sampling configurations in the canonical ensemble. It details the step-by-step process of generating new configurations, calculating energy changes, and using acceptance criteria based on these energy differences. Additionally, it covers related topics such as ergodicity, heat capacity, and order-disorder transitions, emphasizing the need for periodic boundary conditions in simulations.
![Monte Carlo Methods:
- Markov Chain
Random movements, one follow another
- Importance sampling
To sample many points in the region where the Boltzmann
factor is large and few elsewhere
- Ergodicity (ensemble average)
Such an average over all possible quantum states of a system
- Detailed Balance
?
?
Metropolis Method:
]/)(exp[yprobabilithaccept wit:
accept:
TKEEEE
EE
Bonon
on
−−>
<](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mcprogram-160126163104/75/Monte-Carlo-Simulation-Methods-1-2048.jpg)
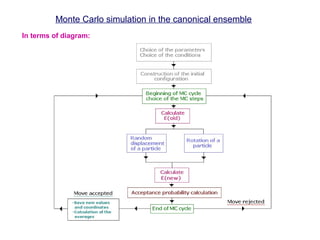
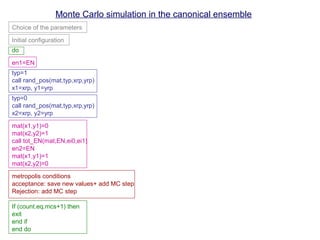
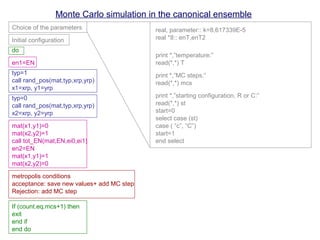
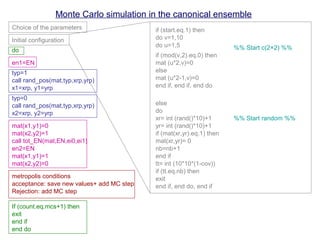
![In terms of words:
- Canonical ensemble: N,V,T constant
- Metropolis method: To generate a new configuration with probabilities
Monte Carlo simulation in the canonical ensemble
0. Generate the initial configuration (random or c(2×2))
Beginning of the MC cycle
1. Calculate Eold
2. Randomly select a particle
3. Random displacement (or rotation)
4. Calculate Enew
5. Accept the move with probability (Metropolis method)
En<Eo accept (the move)
En>Eo accept with probability exp[-(En-Eo)/kT]
(Periodic boundary conditions)
End of MC cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mcprogram-160126163104/85/Monte-Carlo-Simulation-Methods-2-320.jpg)