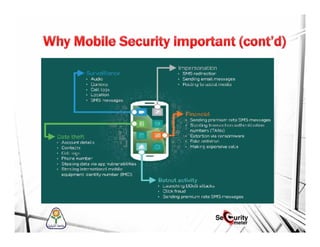
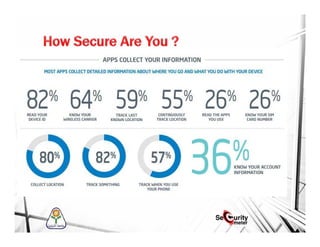
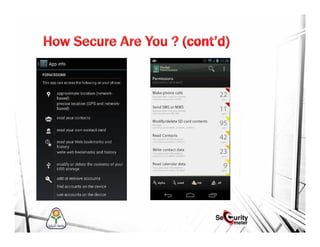
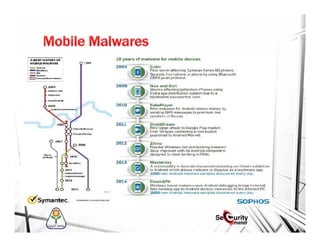
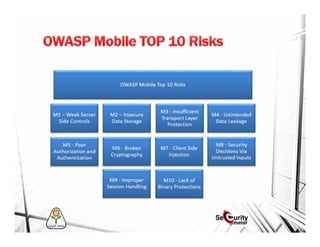
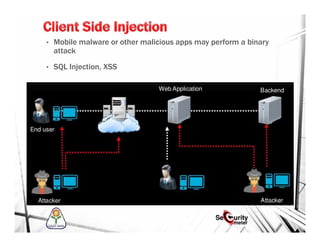
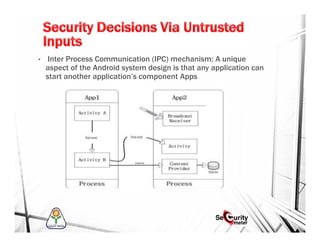
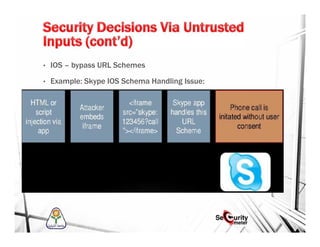
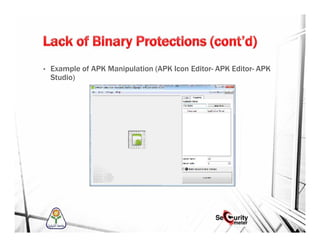
This document discusses mobile security and vulnerabilities. It begins with definitions of security concepts like assets, vulnerabilities, threats, and risks. It then covers why mobile security is important and provides an overview of common mobile security issues like malware, insecure data storage, data leakage, and insecure communication channels. Specific vulnerabilities discussed include SQL injection, cross-site scripting, insecure authentication, cryptographic weaknesses, and insecure permissions. The document emphasizes that mobile apps must not store sensitive data locally and must implement secure protocols like HTTPS. It also notes that mobile devices are susceptible to malware and reverse engineering attacks.



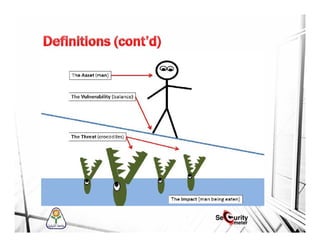
![• Asset [People, property, information, source code, DB]
• Vulnerability
• SQL Injection [embedding untrusted input into raw SQL statements]
• XSS [inject Java Script to untrusted input ]
• Exploit
• Threat [Anything that can exploit a vulnerability, intentionally or
accidentally, and obtain, damage, or destroy an asset]
• Risk = Asset * Threat * Vulnerability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15d56423-a81f-4482-bf8d-58a9cd3dd5cf-151118145228-lva1-app6892/85/Menofia-UN-Mobile-Security-4-320.jpg)
![• [BYOD] Bring Your Own Device
• Refers to the policy of permitting employees to bring personally
owned mobile devices (laptops, tablets, and smart phones) to
their workplace](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/15d56423-a81f-4482-bf8d-58a9cd3dd5cf-151118145228-lva1-app6892/85/Menofia-UN-Mobile-Security-6-320.jpg)