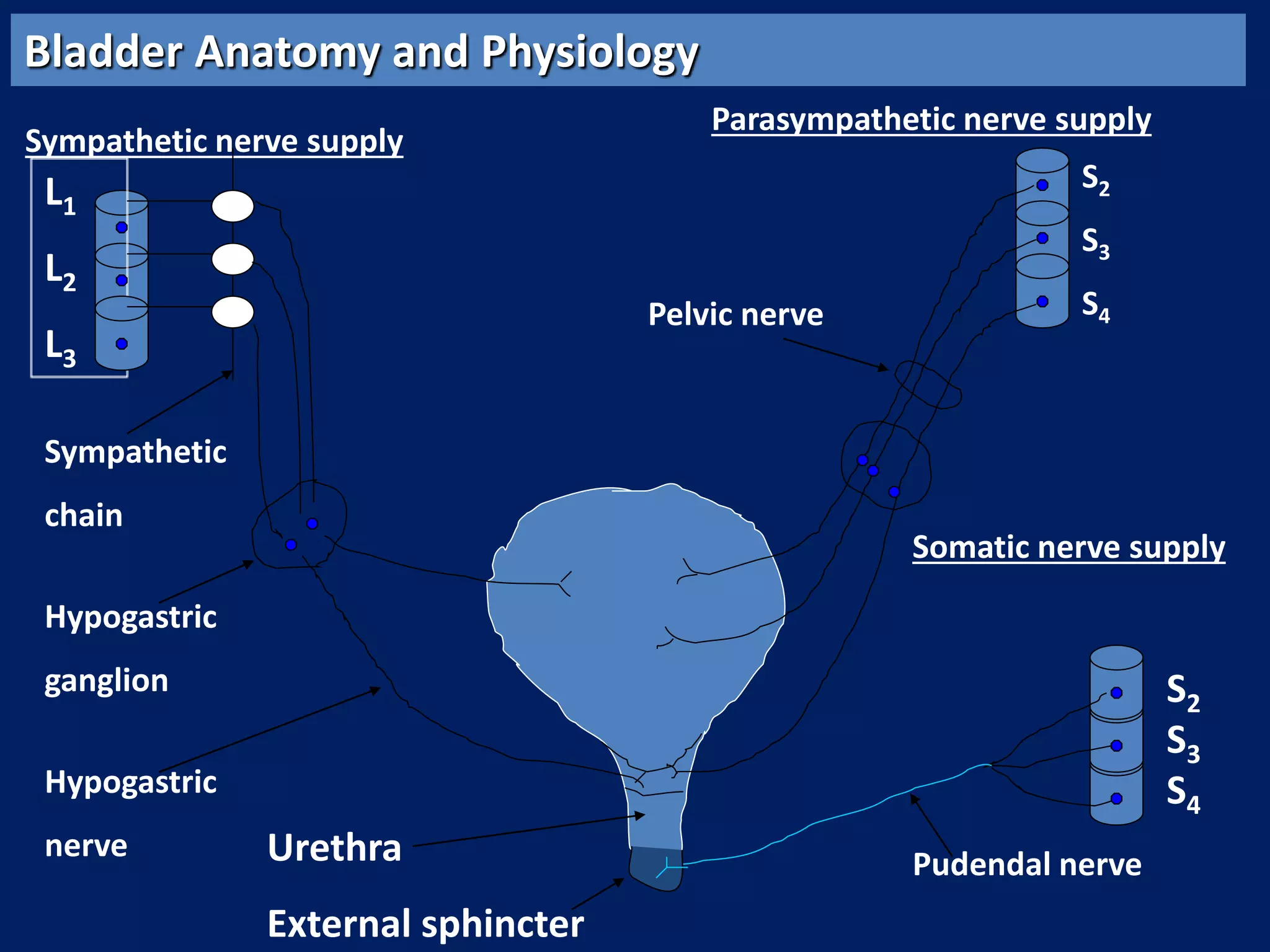
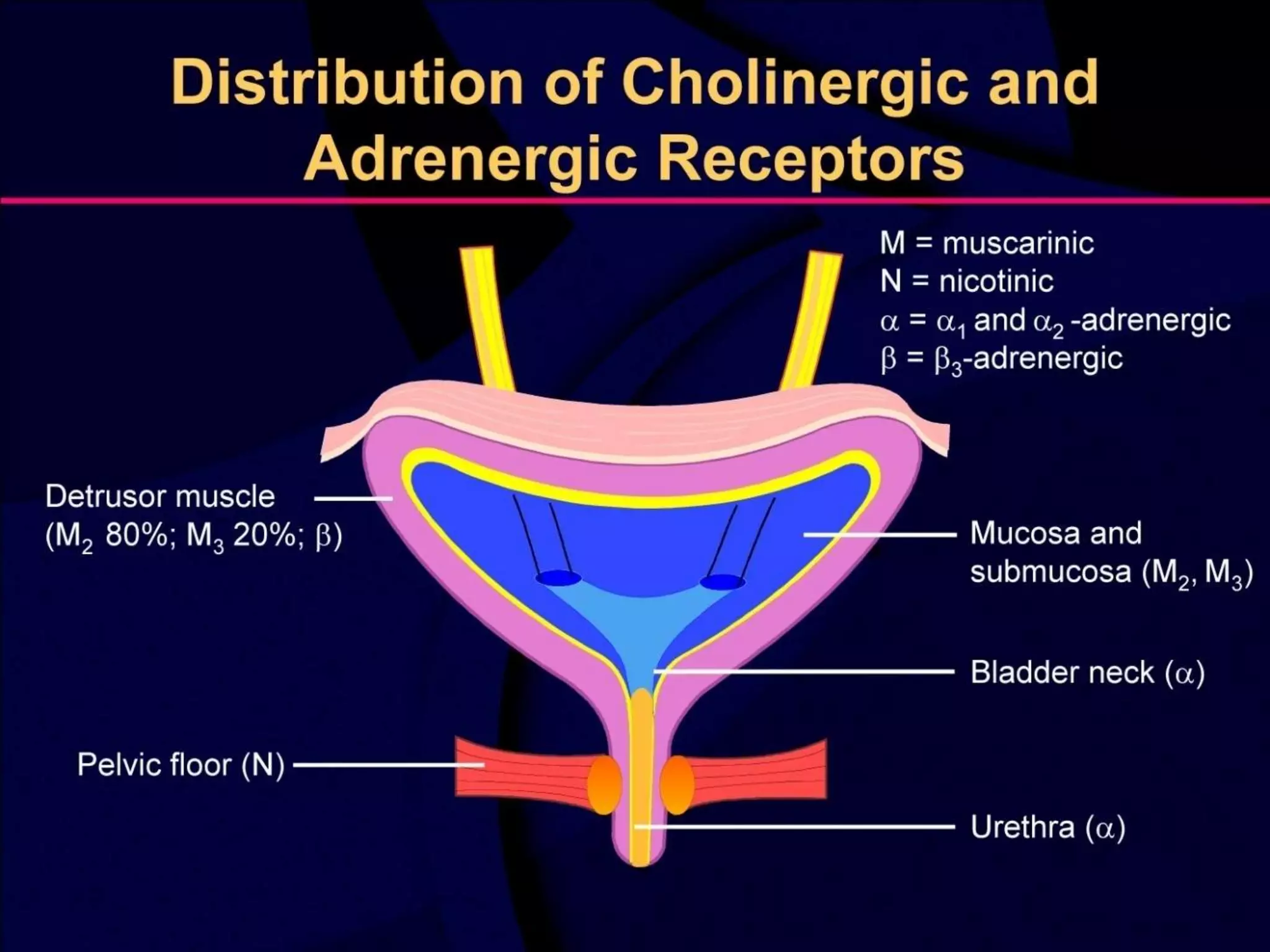
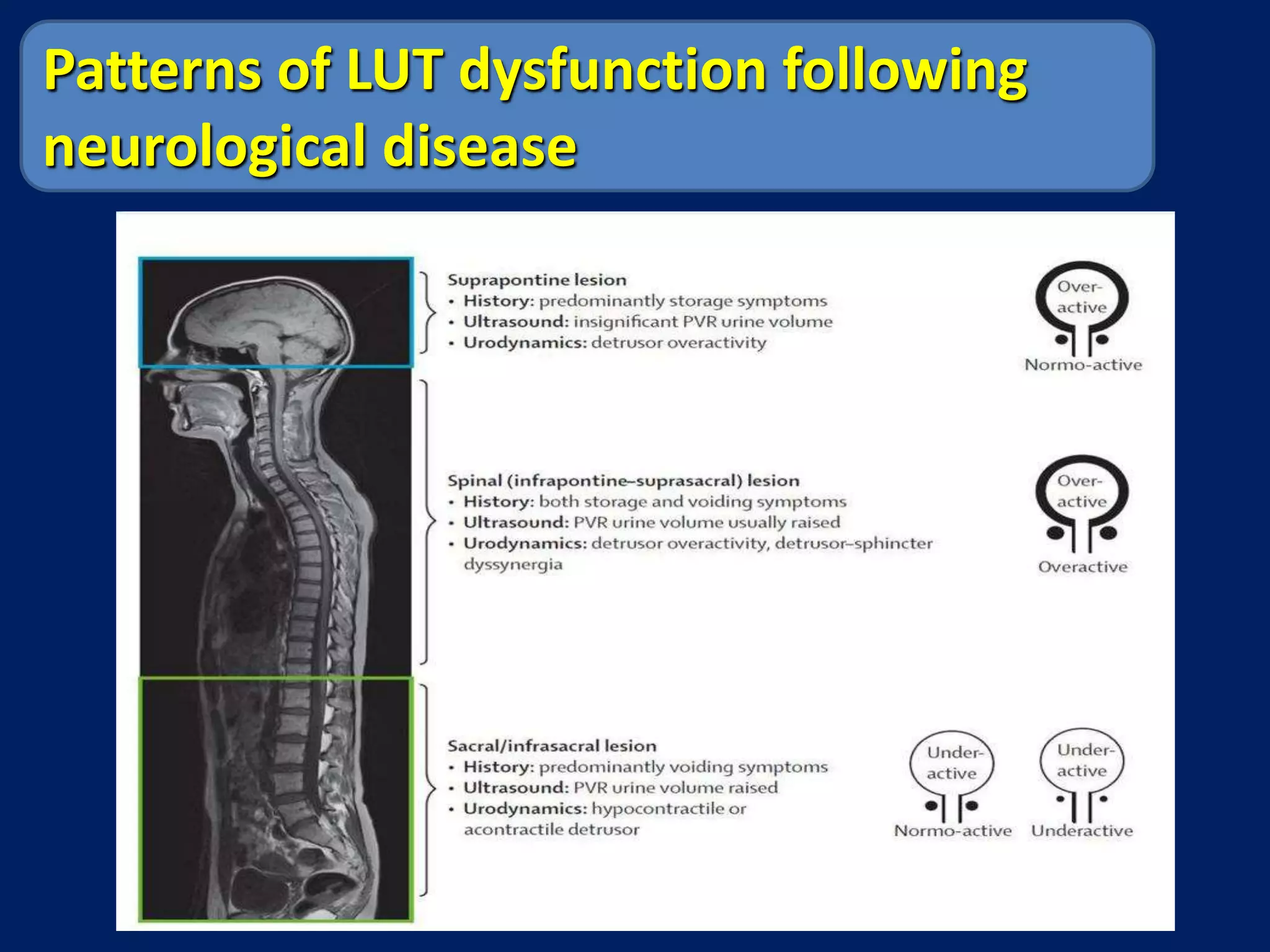
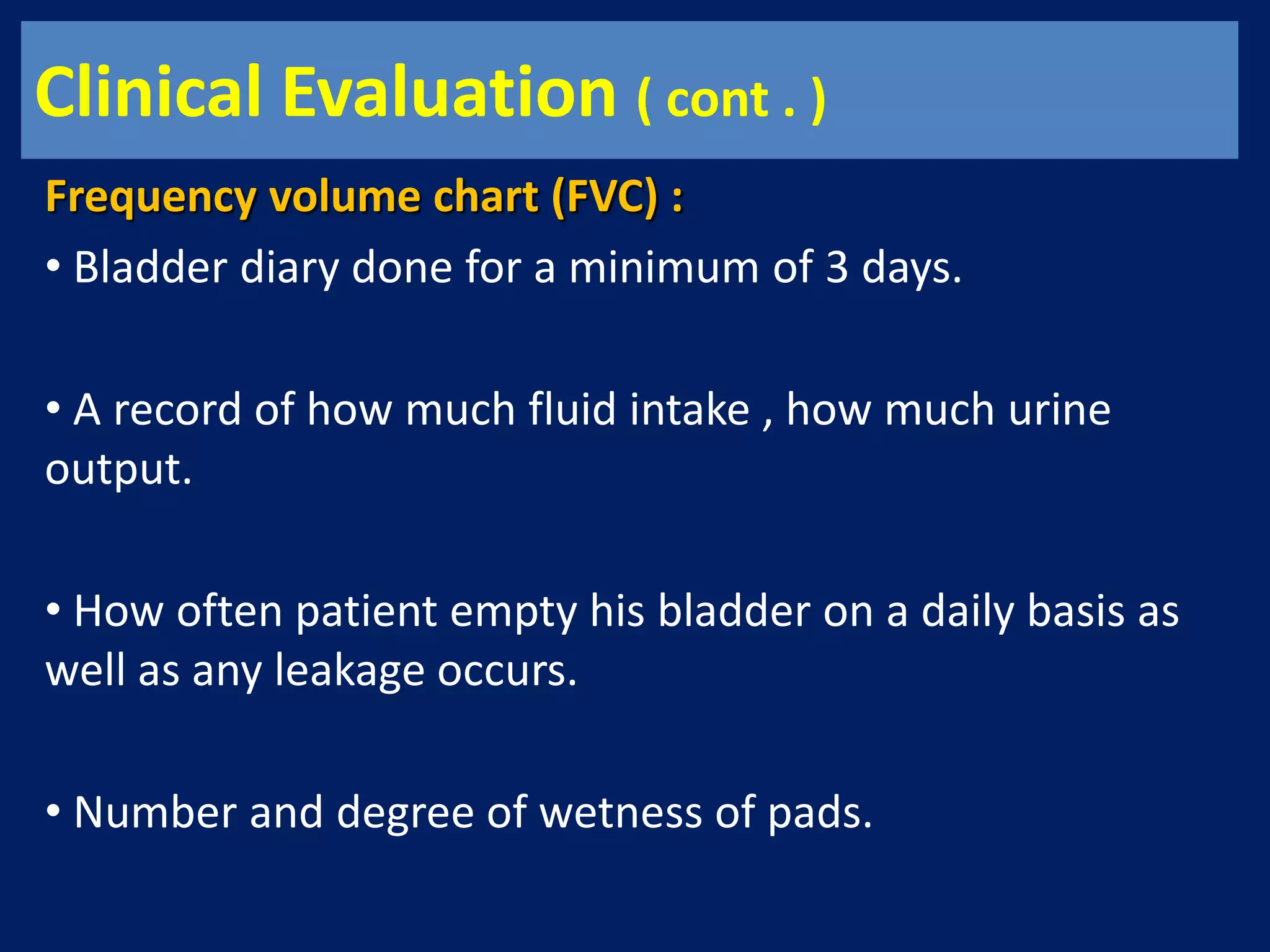
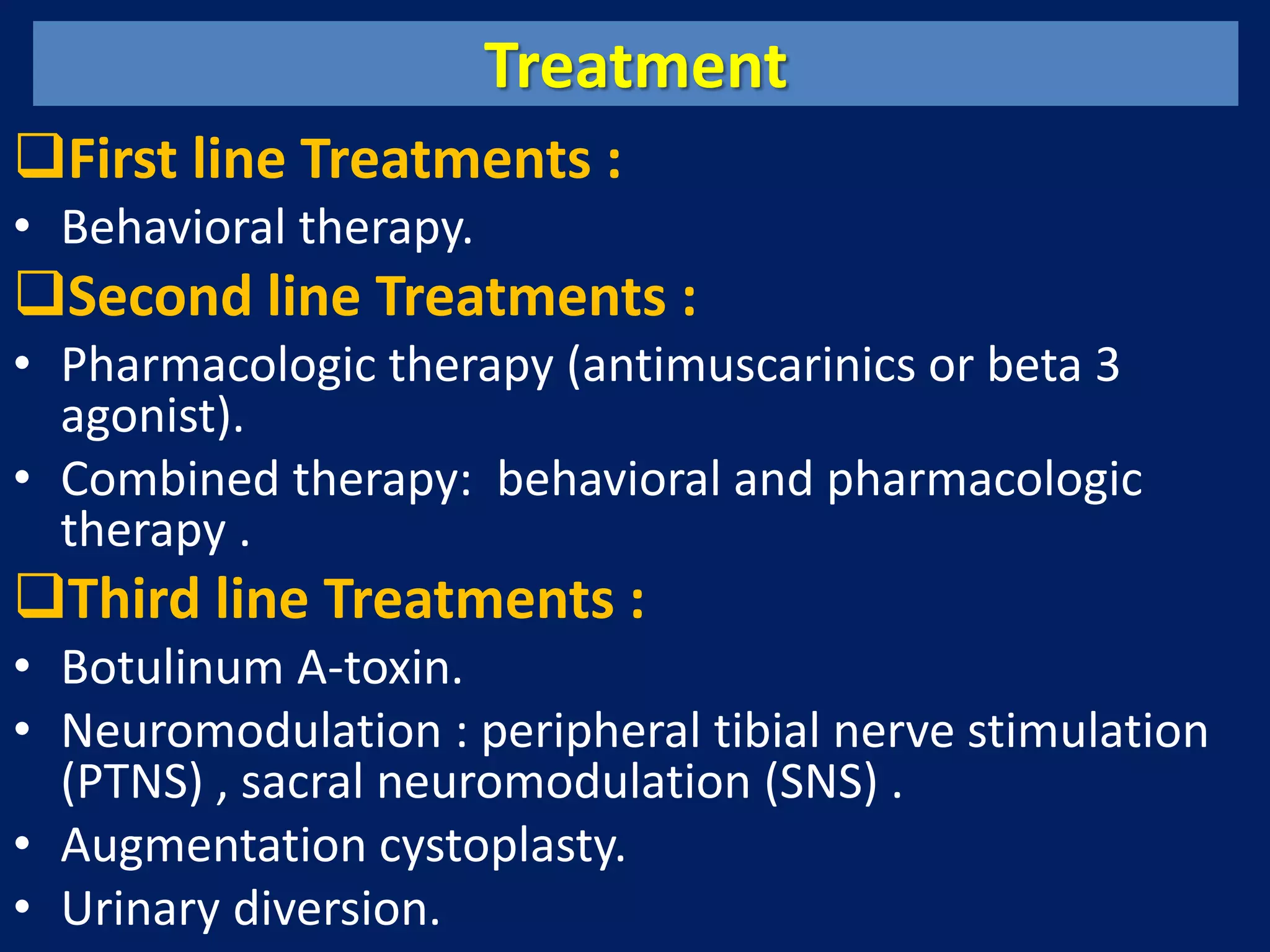
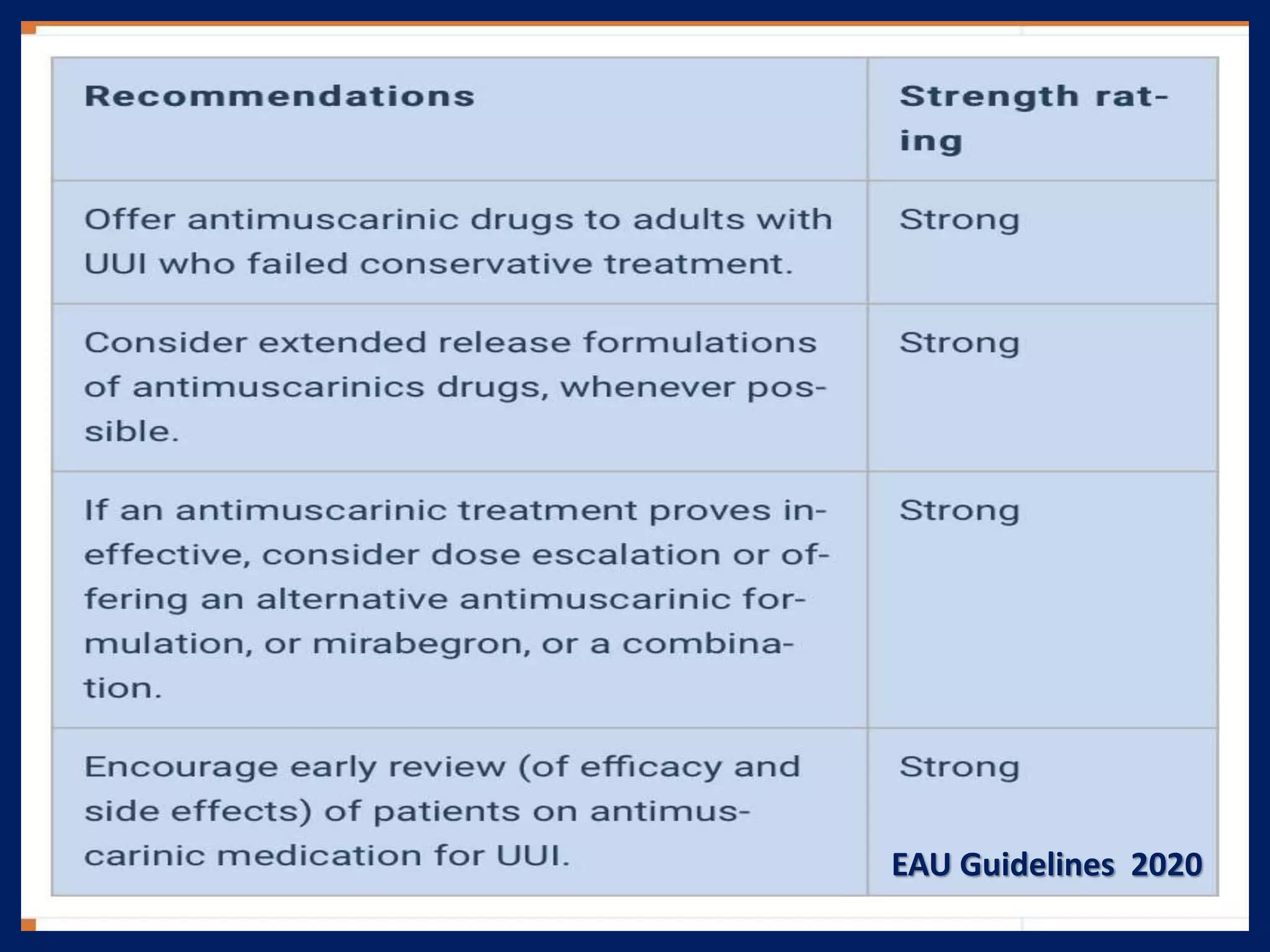
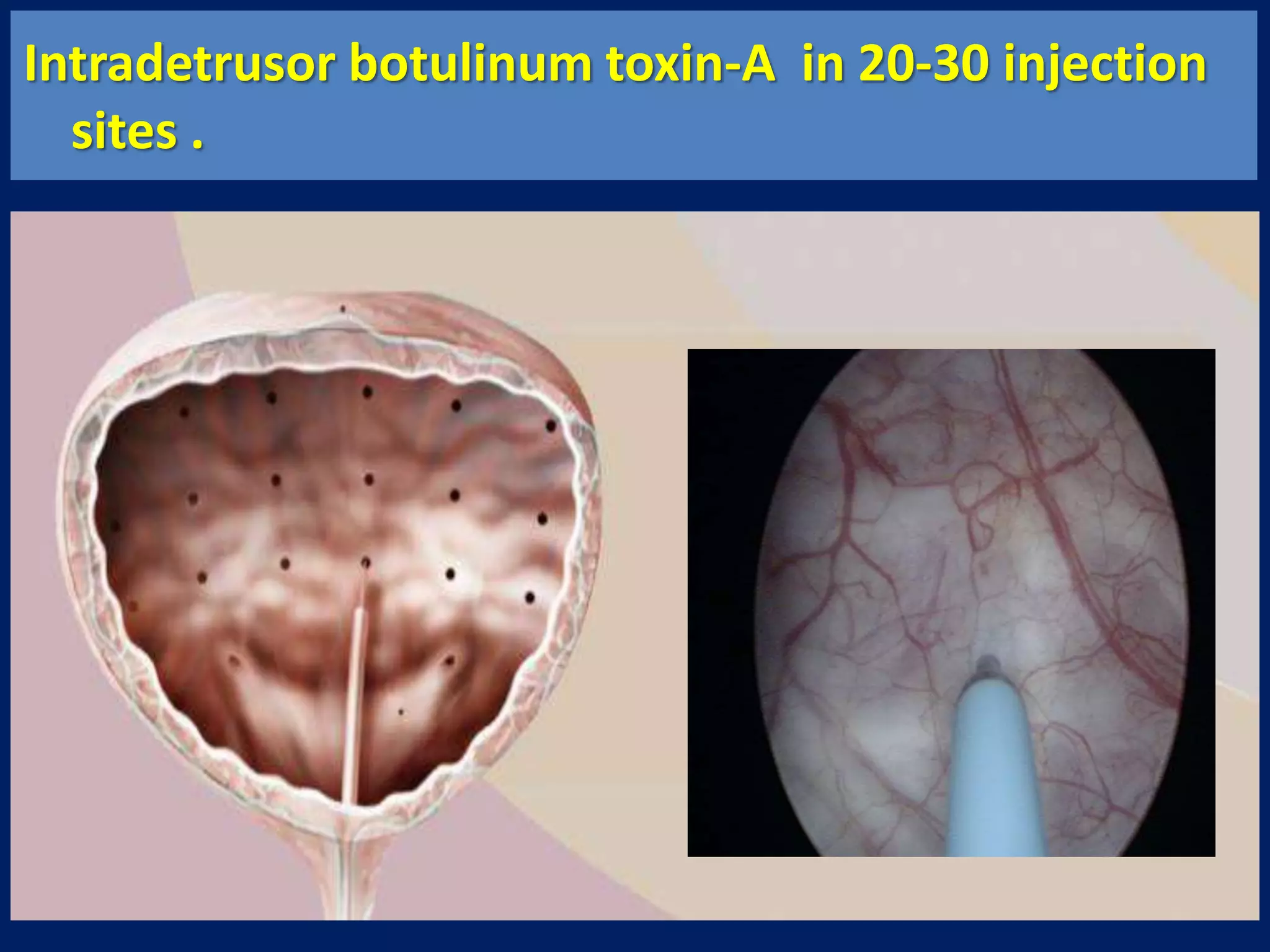
The document discusses overactive bladder (OAB), defining it as urinary urgency with or without incontinence and noting its prevalence rates of 16.9% in women and 16.2% in men, increasing with age. It covers the clinical evaluation, which includes a detailed history and physical exams, as well as treatment options ranging from behavioral therapies to advanced surgical interventions. Key treatment approaches include pharmacologic therapies such as antimuscarinics and beta-3 agonists, along with third-line options like botulinum toxin injections and neuromodulation techniques.