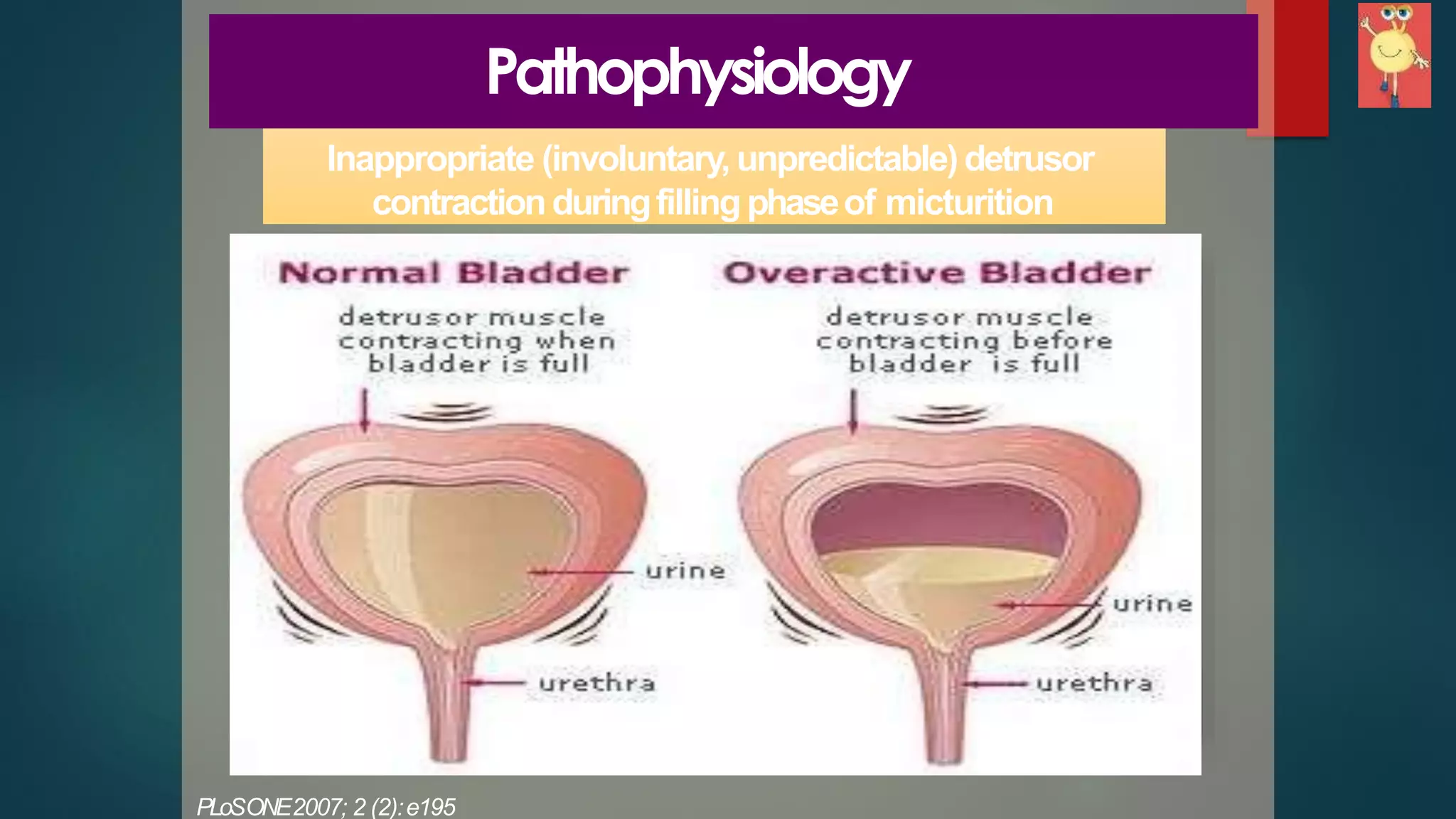
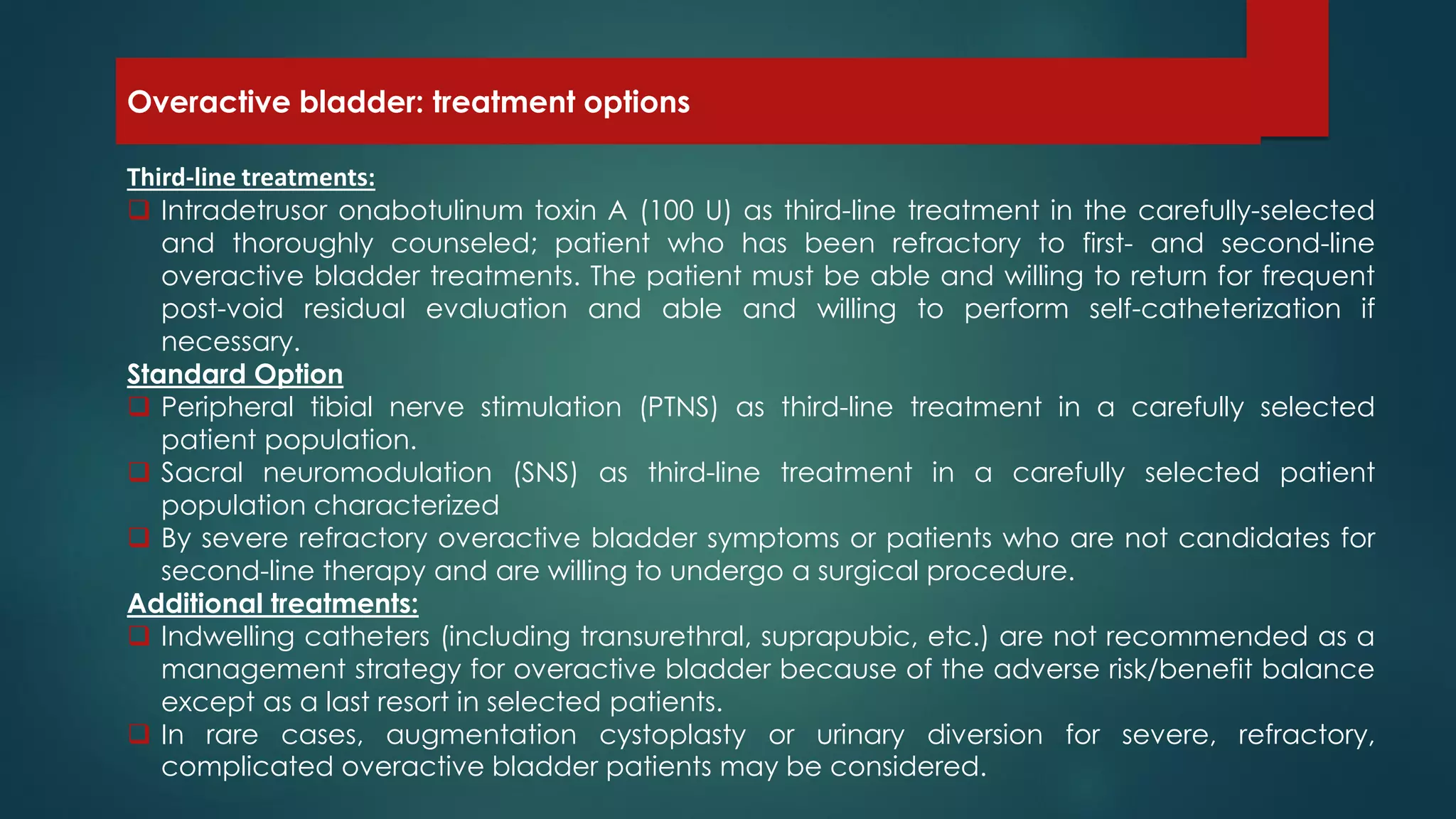
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a prevalent symptom affecting quality of life, particularly in the aging population, characterized by urgency and urge incontinence. Treatment options range from first-line behavioral therapies to pharmacologic management with antimuscarinic agents, which are effective but may have side effects. For refractory cases, third-line treatments include onabotulinum toxin A injections or surgical options such as sacral neuromodulation.