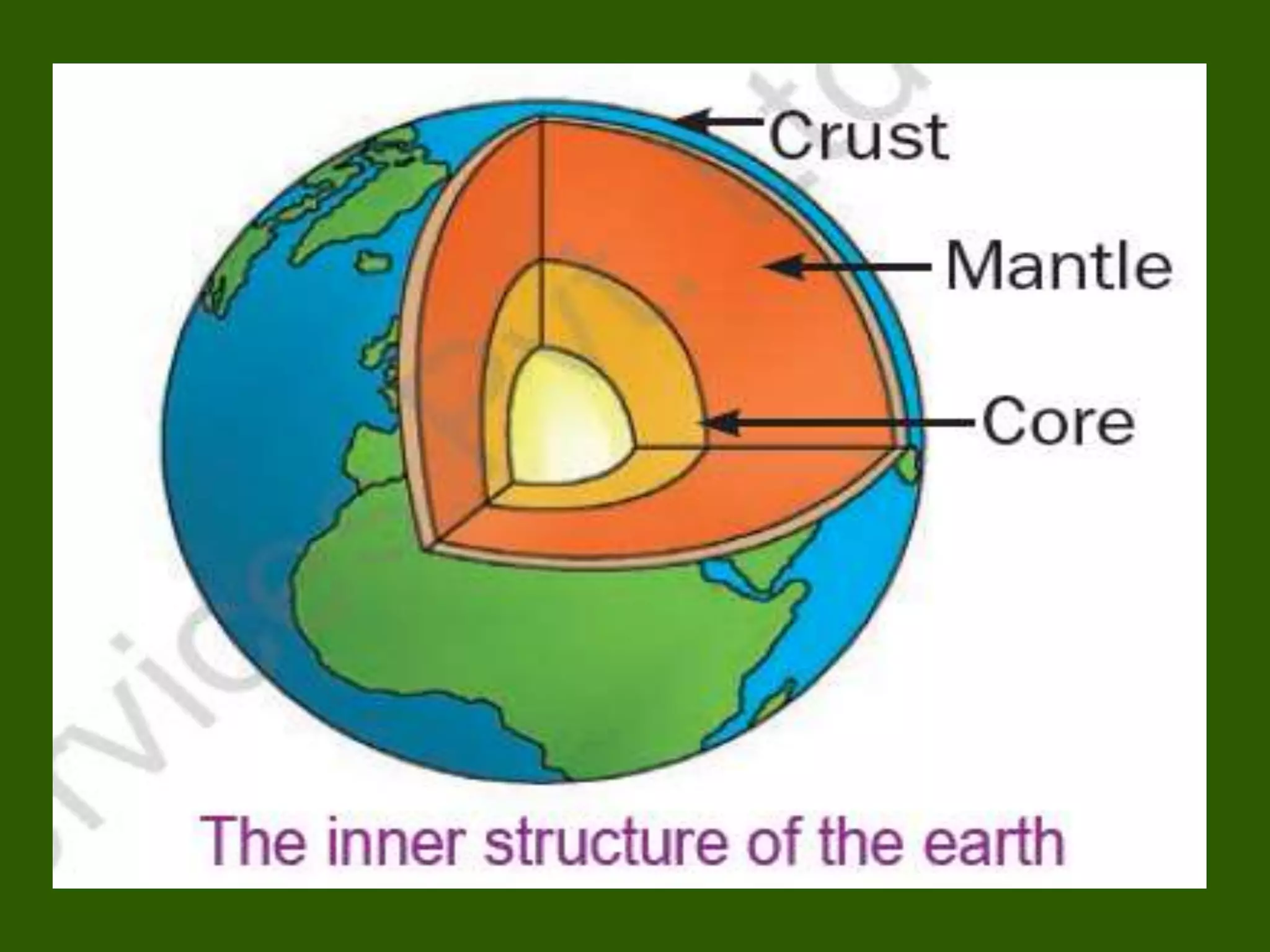
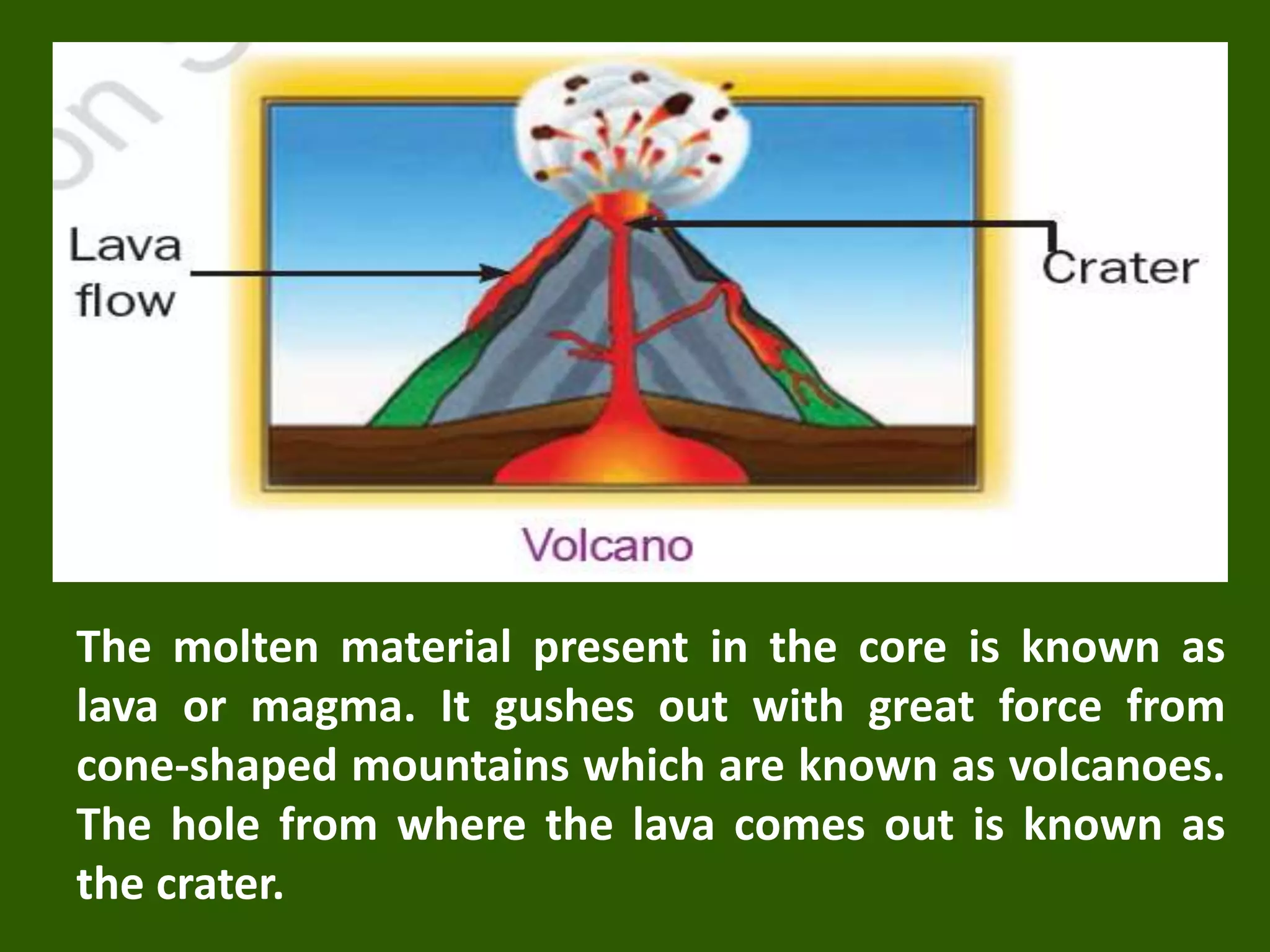
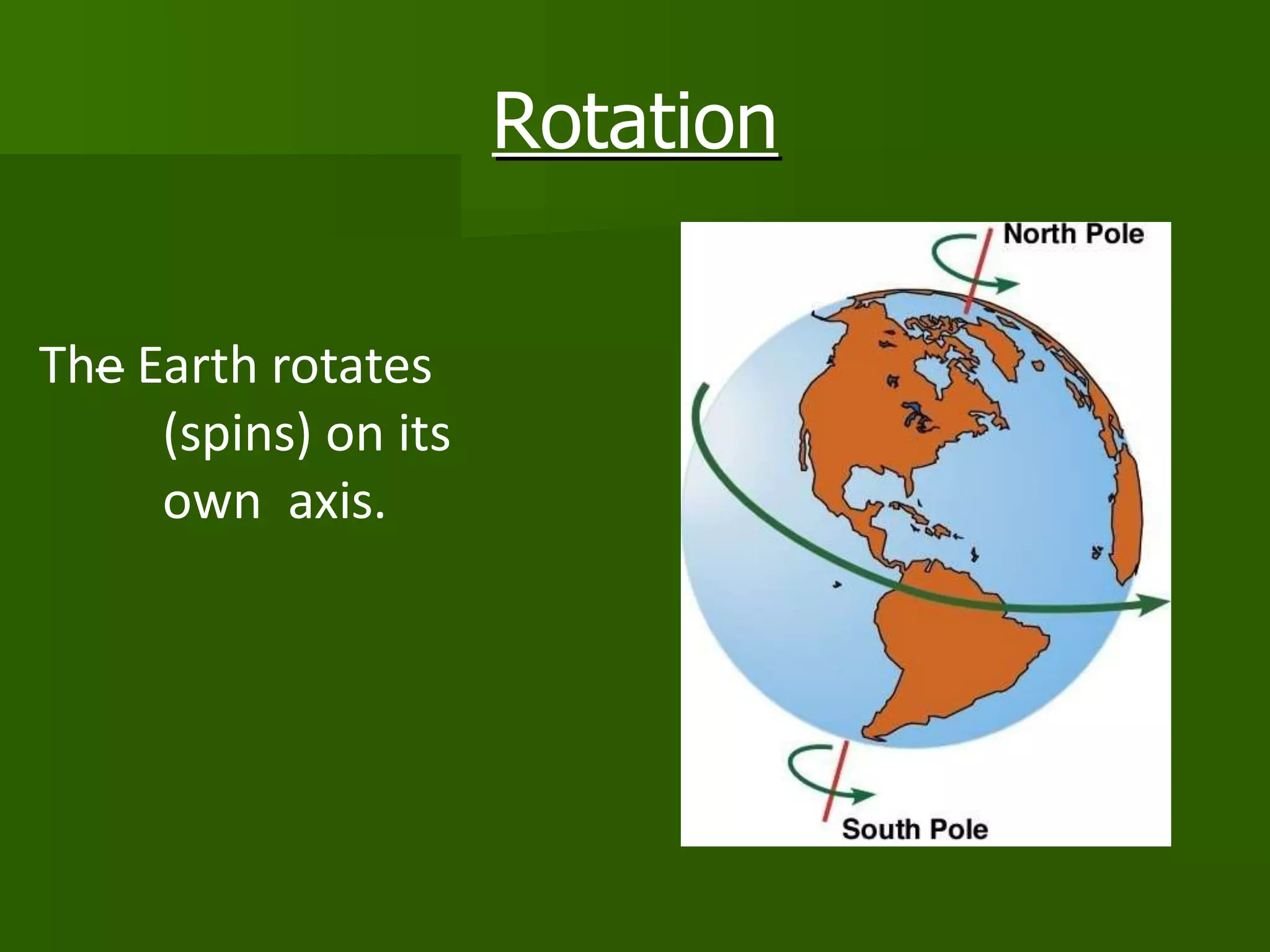
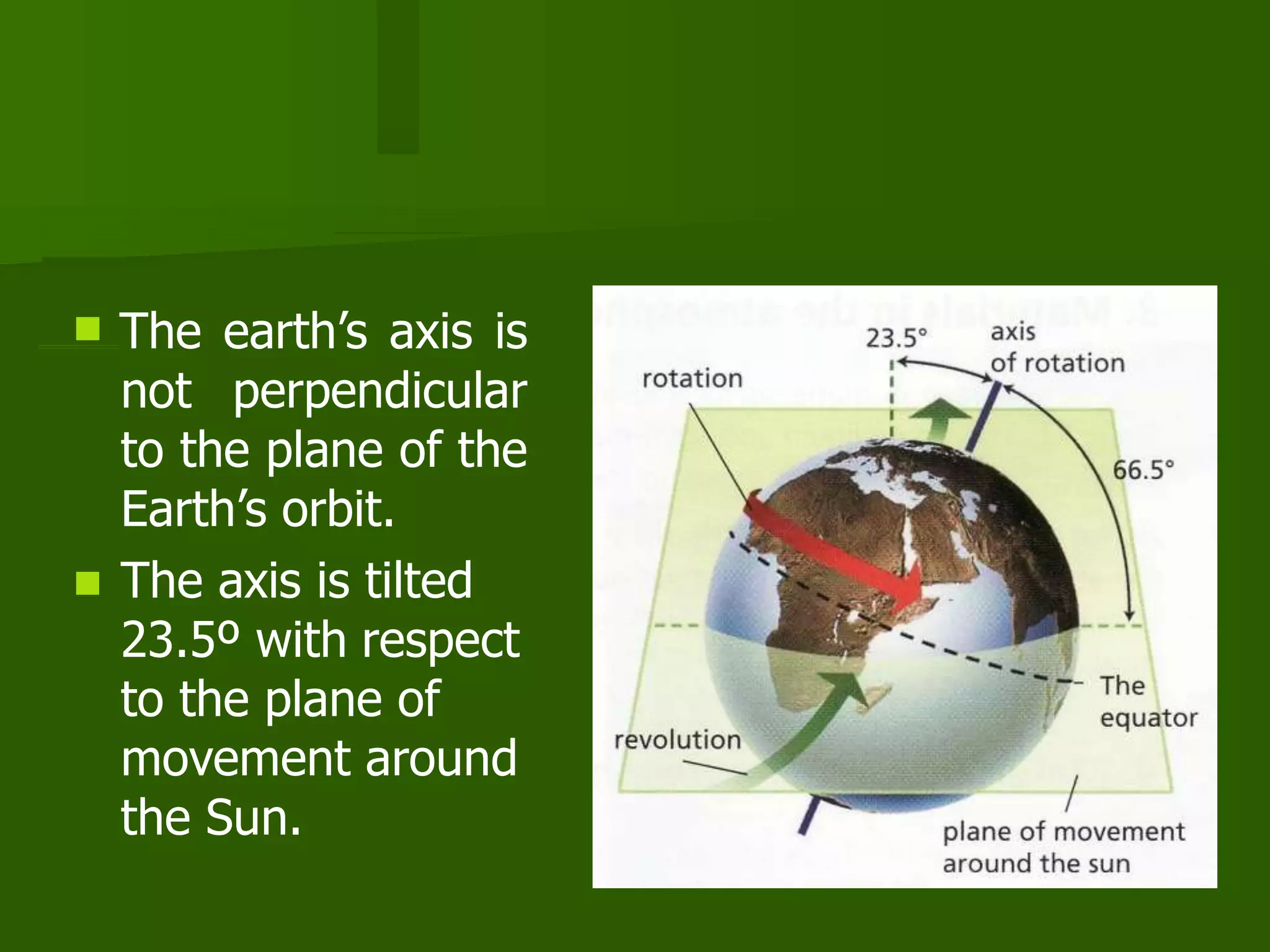
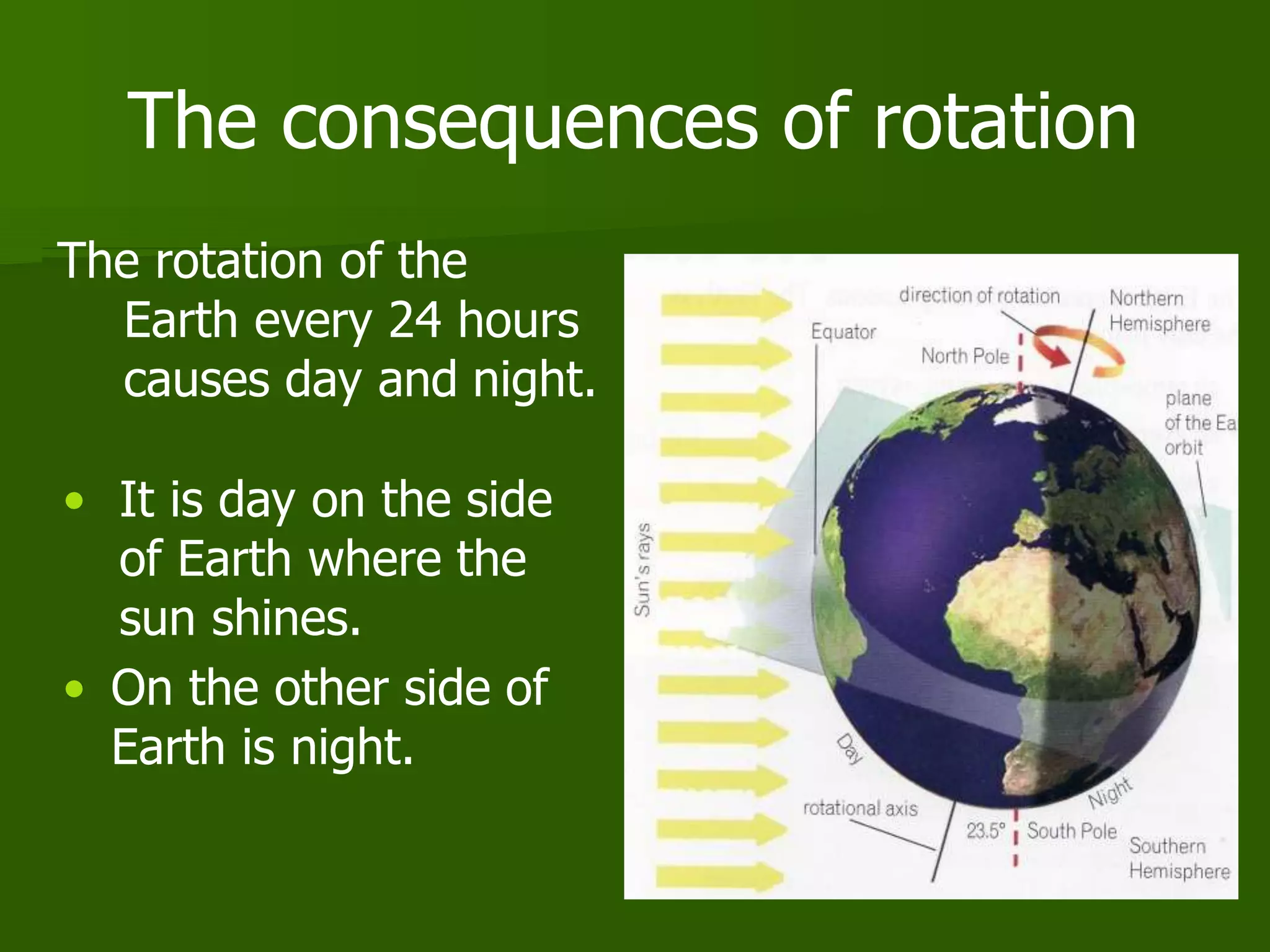
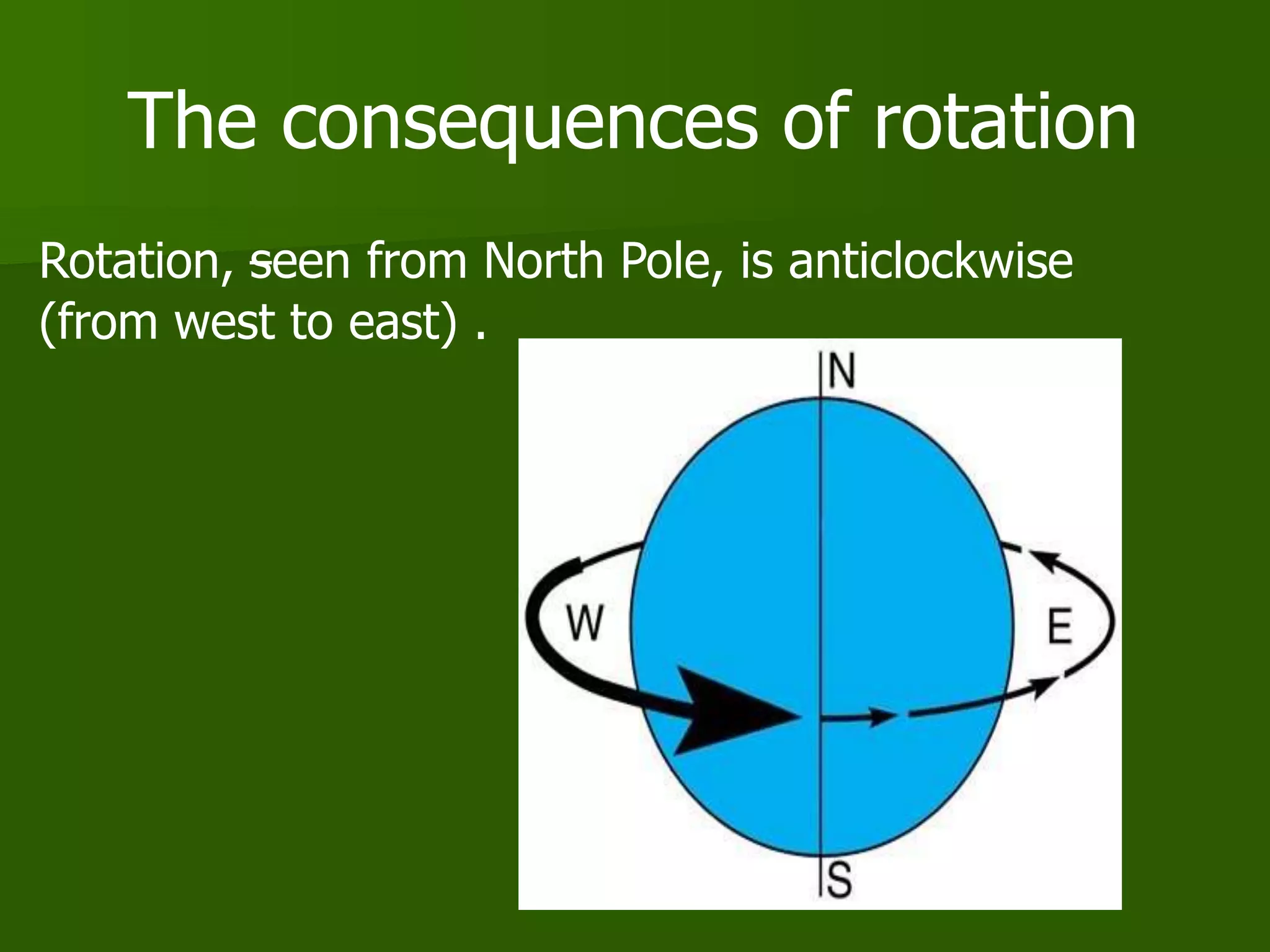
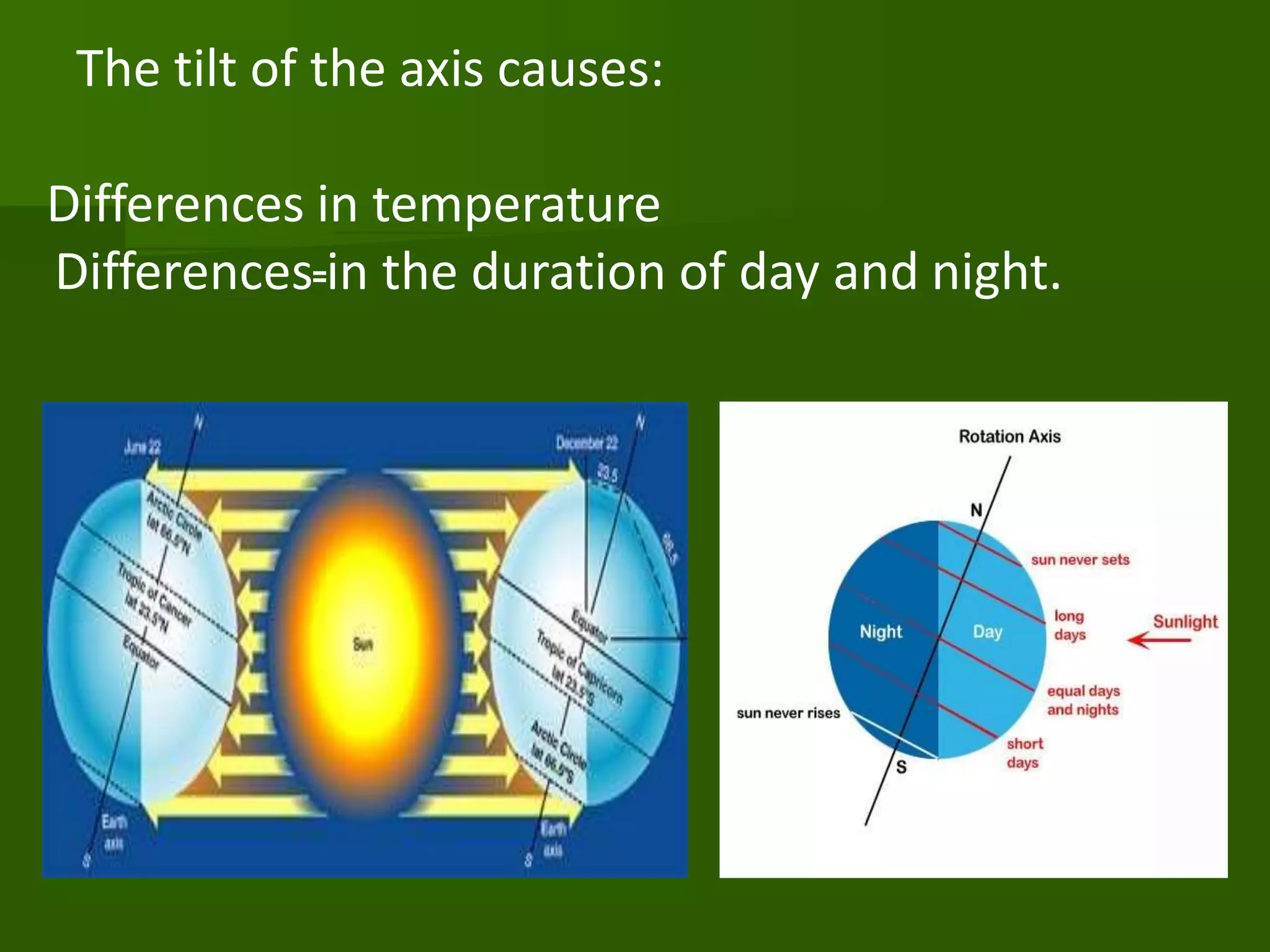
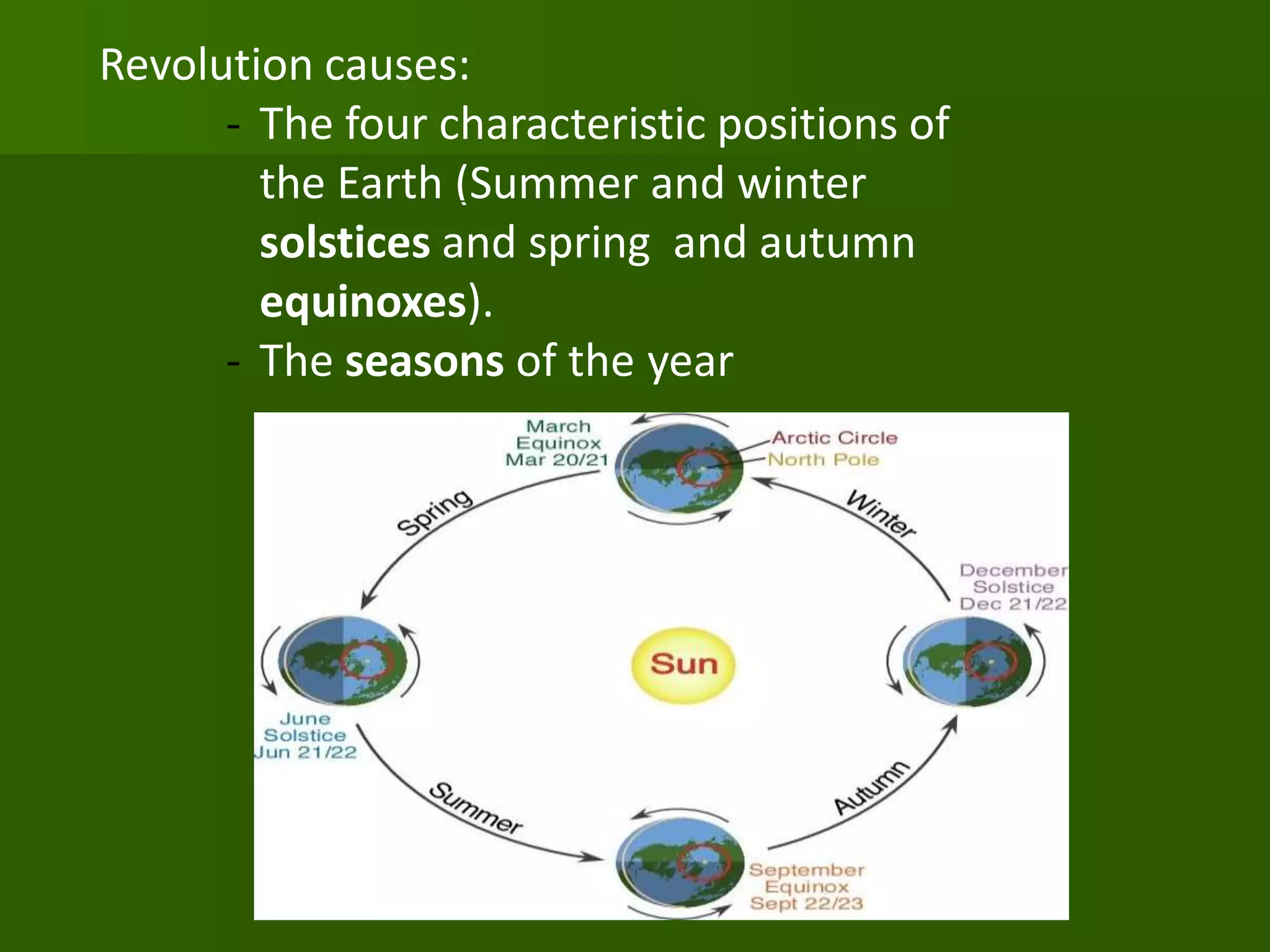
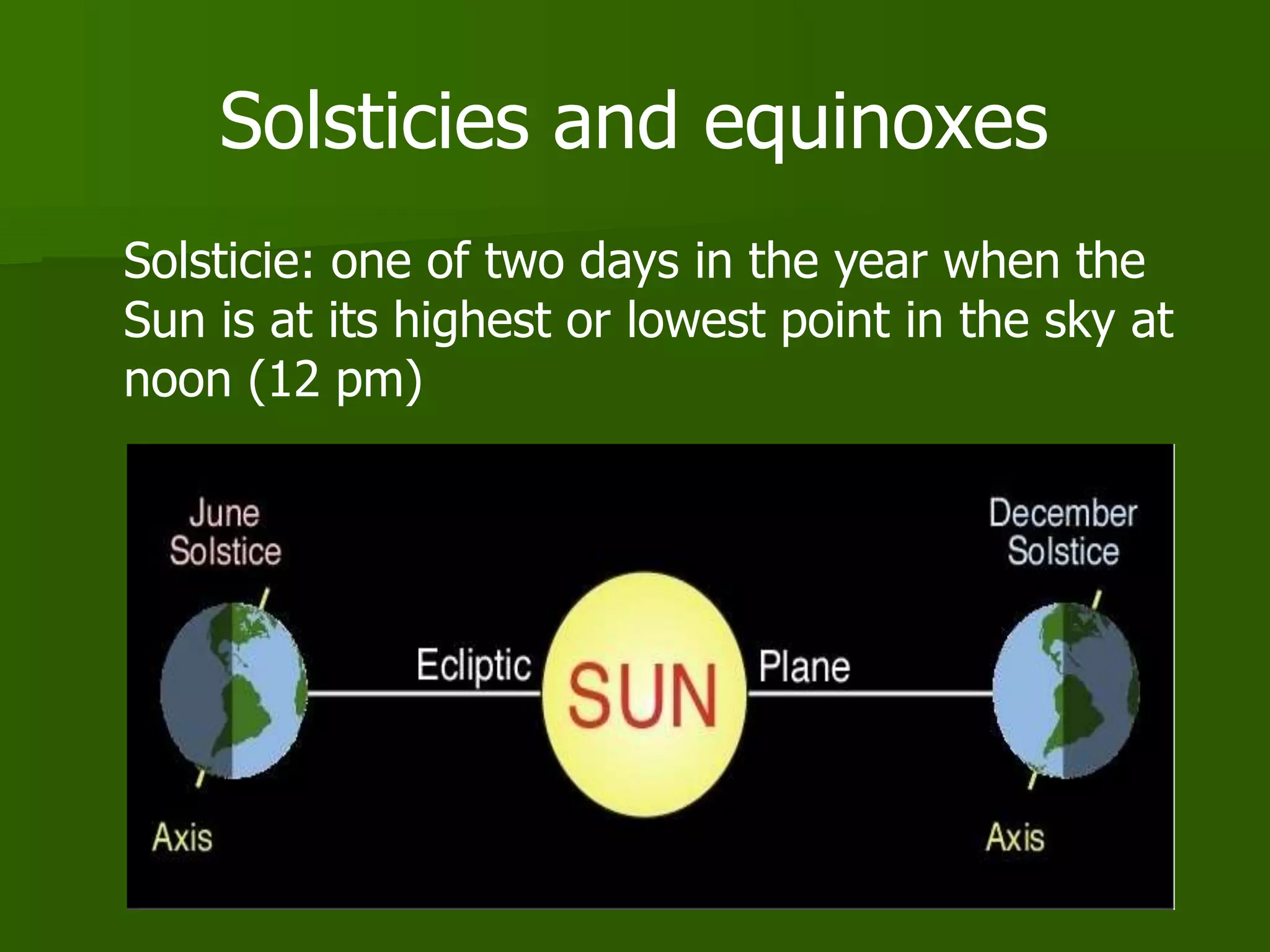
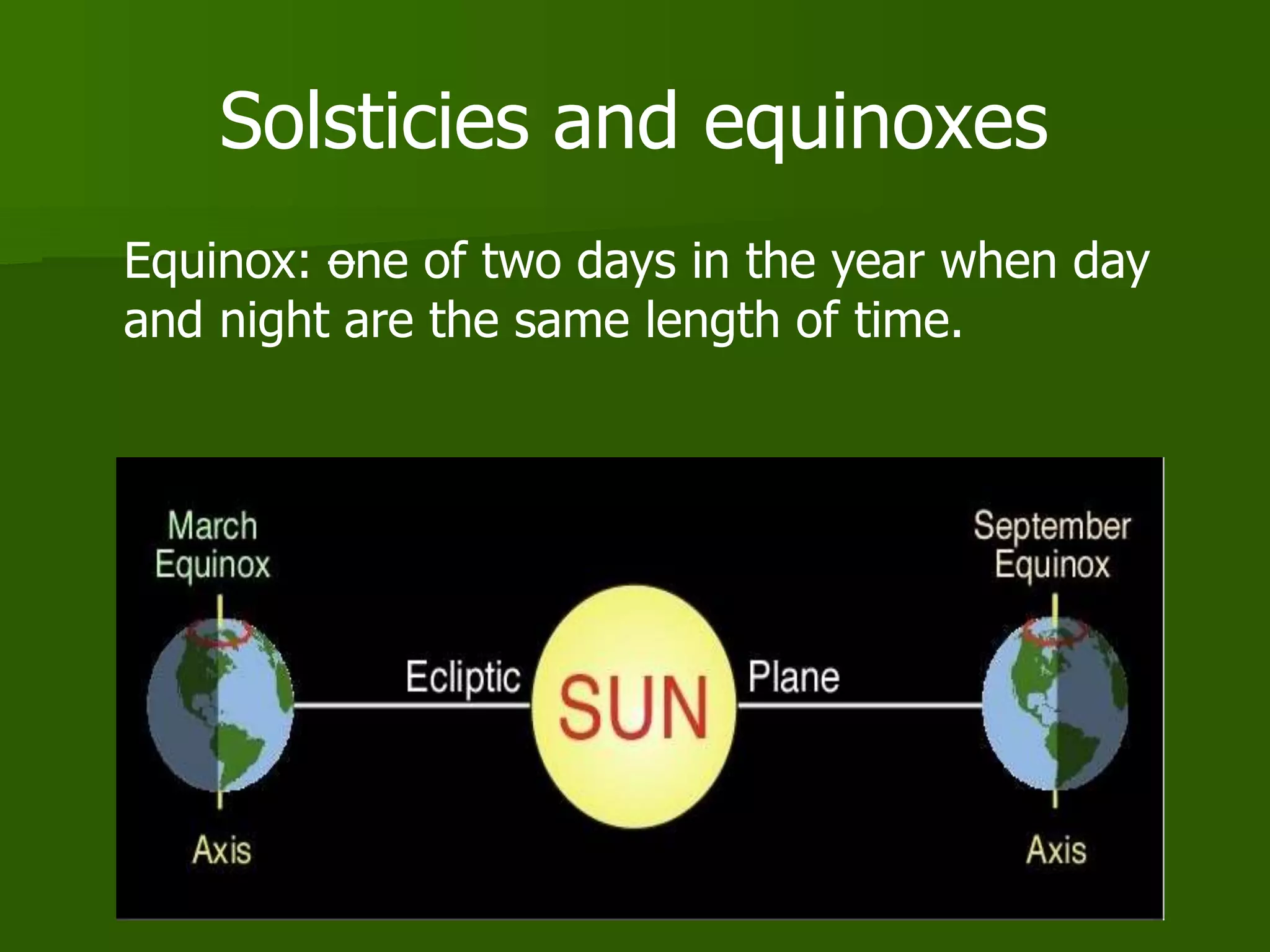
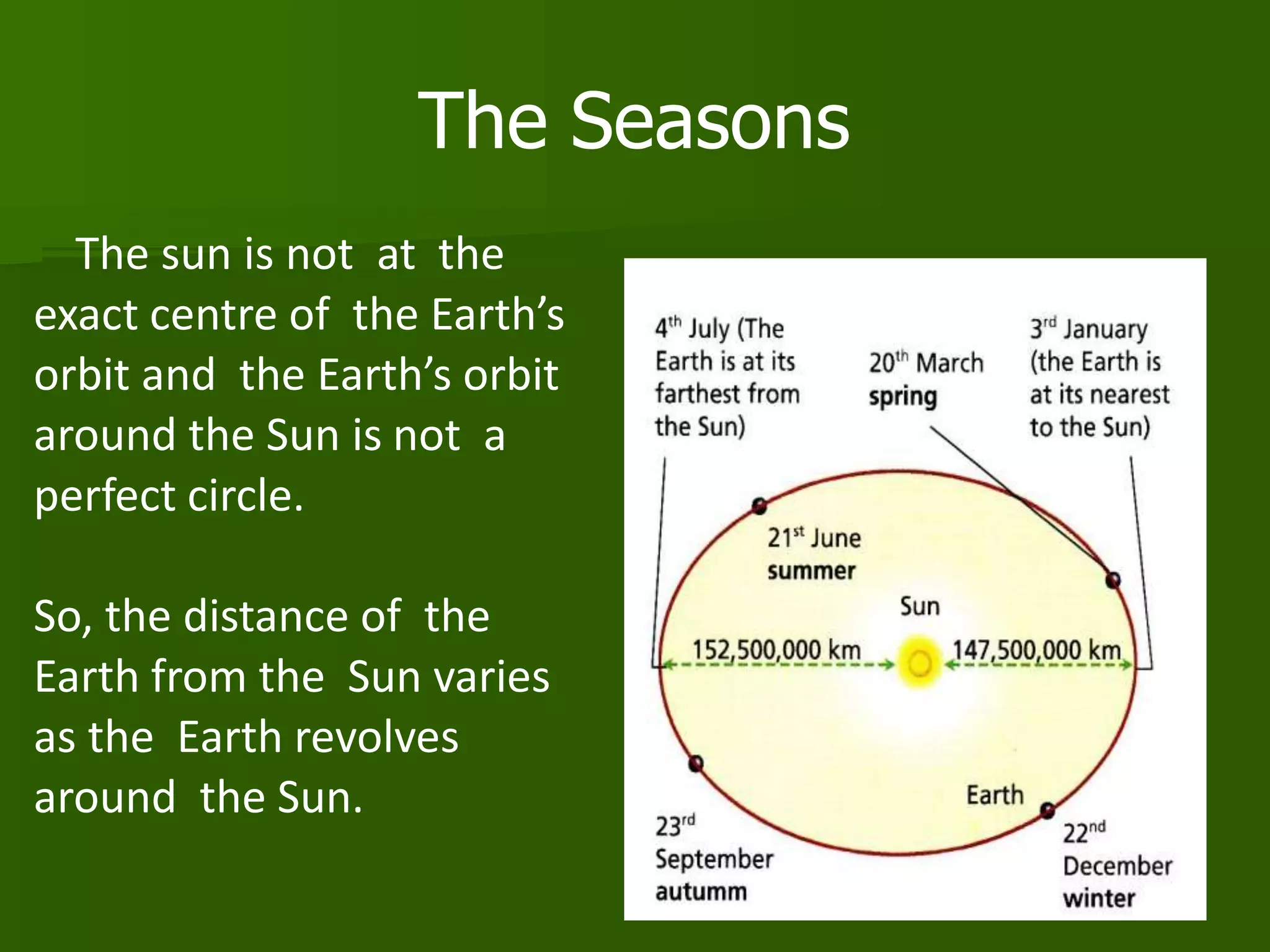
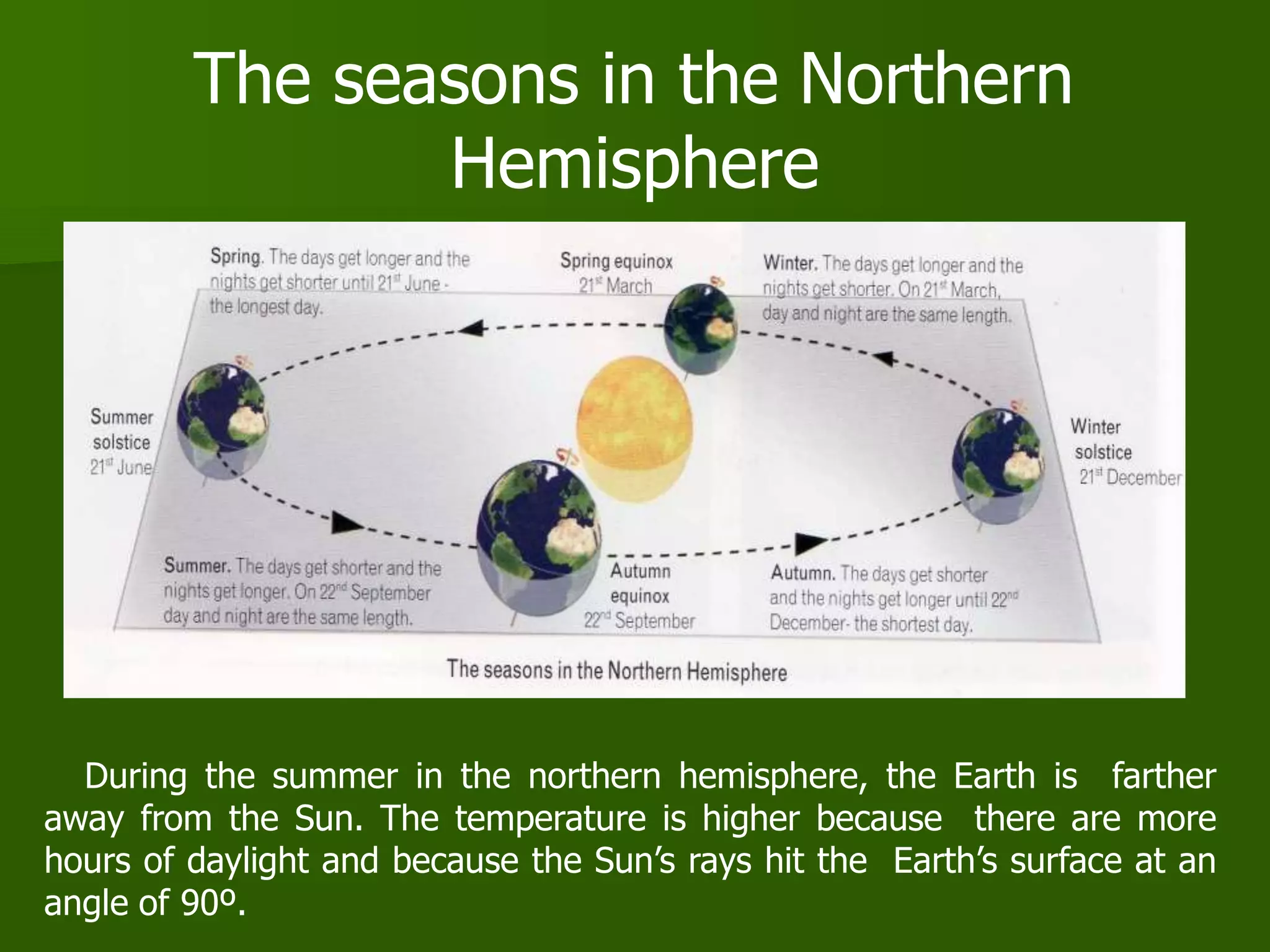
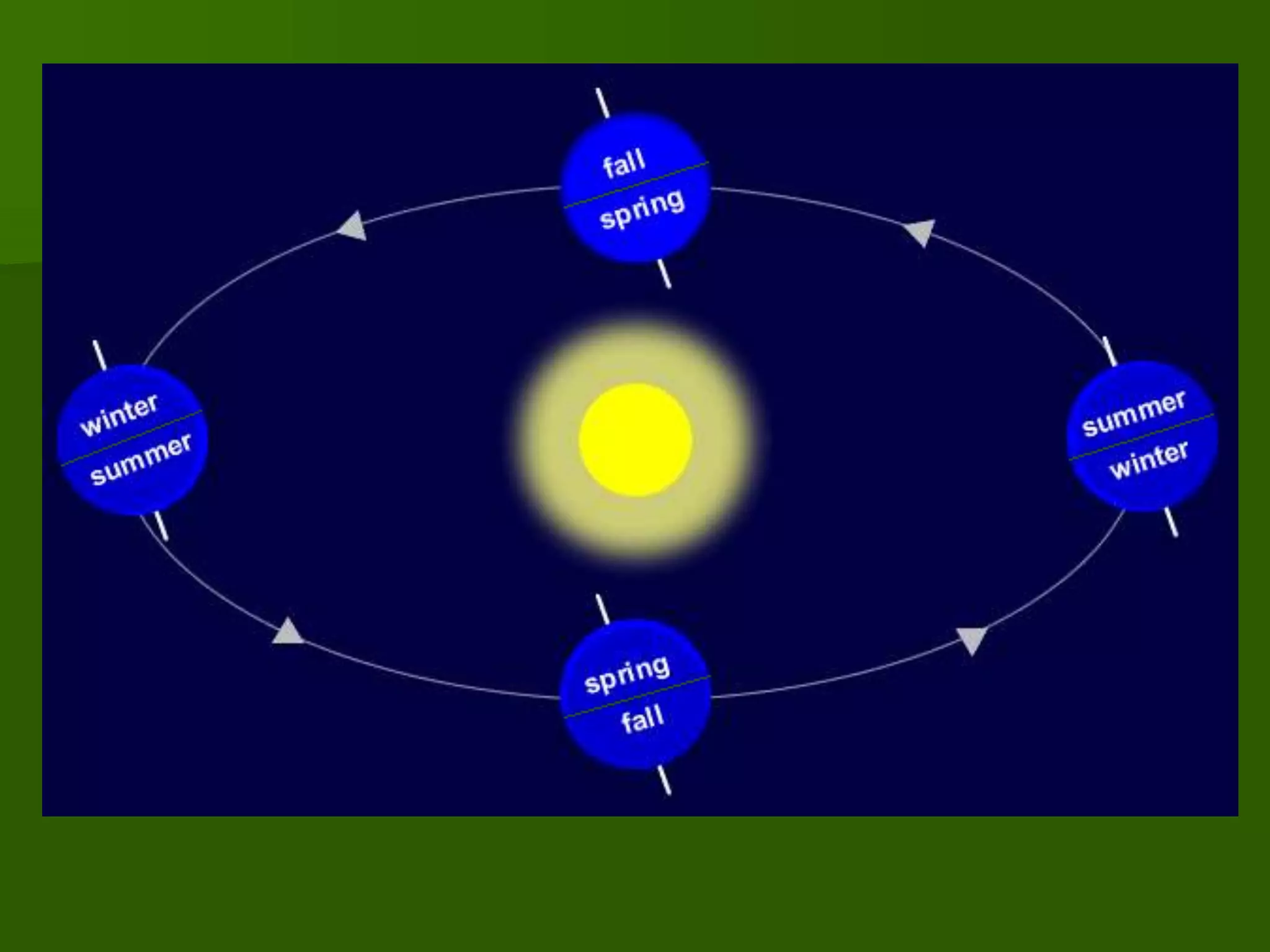
The document discusses the movements of the Earth and how they cause natural phenomena. It explains that the Earth rotates on its axis over 24 hours, causing day and night, and revolves around the sun over 365 days, causing the seasons. Specifically, the tilt of the Earth's axis of rotation relative to its orbit around the sun results in varying intensities of sunlight over different parts of the planet throughout the year, producing warmer summers and colder winters in the Northern Hemisphere. The solstices and equinoxes mark the Earth's characteristic positions during its revolution and further influence seasonal changes.