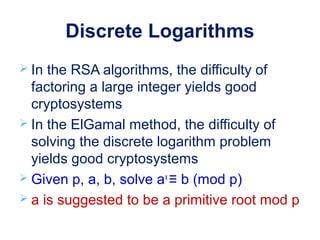
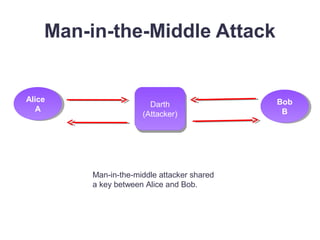
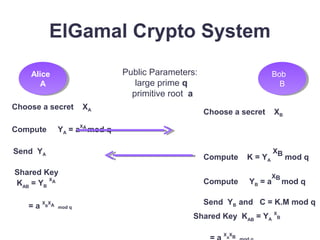
This document discusses several public key cryptosystems based on discrete logarithms, including Diffie-Hellman key exchange, ElGamal encryption, and ElGamal digital signatures. It provides examples of how each system works using mathematical operations like exponentiation modulo a prime number. Diffie-Hellman allows two parties to securely generate a shared secret key over an insecure channel. ElGamal encryption and signatures extend this idea to allow public key encryption and digital signatures based on the difficulty of solving discrete logarithms.


















![2222
ElGamal Digital Signature
Zp* = <g>, m ∈ Zp message
A signs message m.
Alice: A = ga
, public key = (p, g,A), secret key = x.
Alice: k random with gcd(k,p-1)=1
r = gk
(mod p)
s = (m – xr)(1/k) mod p-1 [m = sk + xr (mod p-1)]
Signature = (r,s)
Verify gm
=rs
hr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/otherpublickeysystems-140619083311-phpapp01/85/Other-public-key-systems-22-320.jpg)
