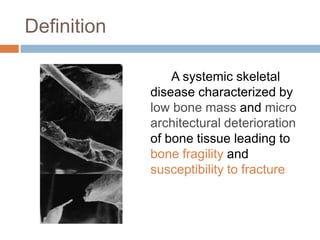
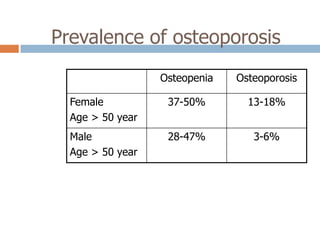
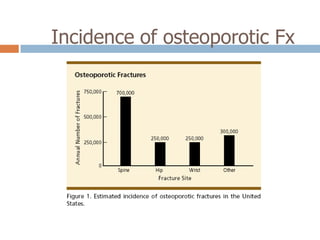
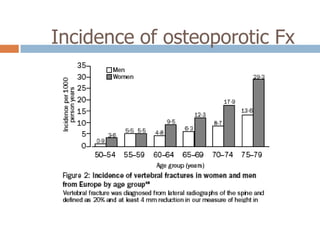
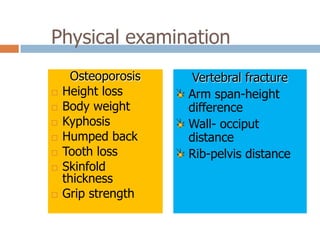
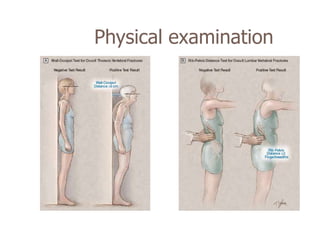
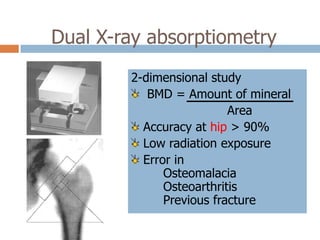
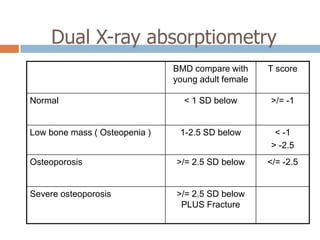
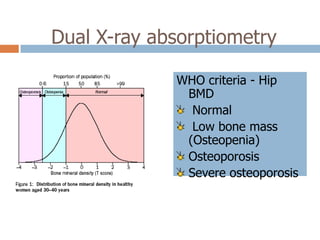
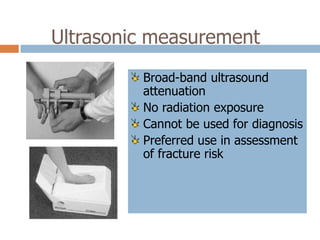
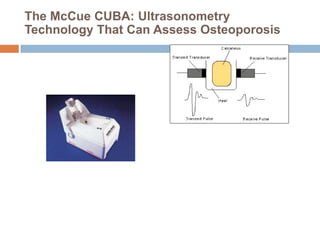
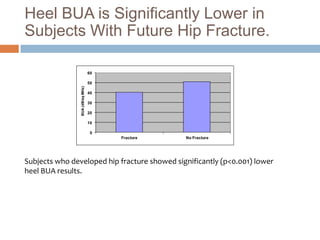
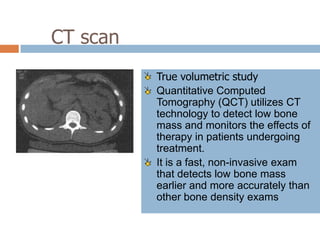
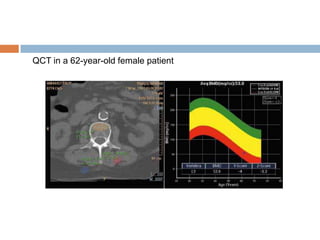
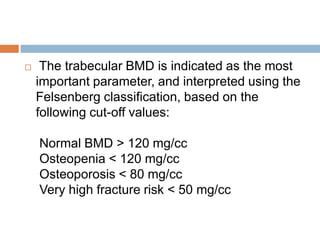
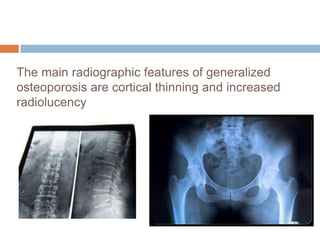
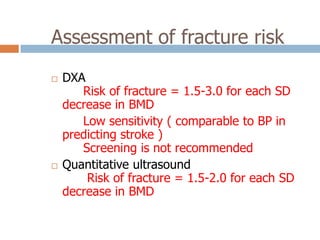
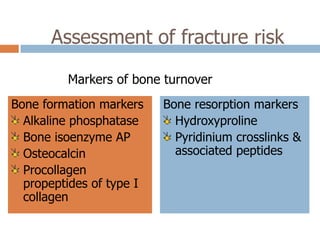
This document discusses the diagnosis and assessment of osteoporosis. It defines osteoporosis as a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and susceptibility to fractures. It describes who is at risk and the different types of osteoporosis. Physical exams and various imaging techniques can be used to diagnose osteoporosis such as dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans, quantitative ultrasound, CT scans, and plain radiography. Factors like BMD T-scores, clinical risk factors, and markers of bone turnover help assess fracture risk in patients.