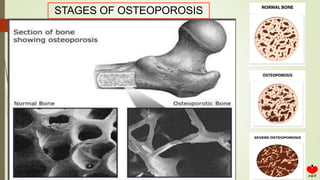
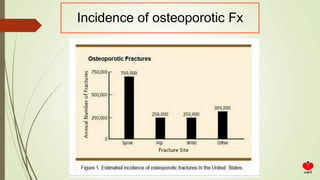
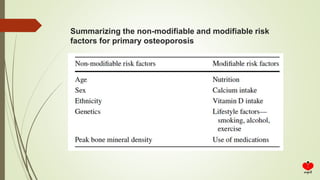
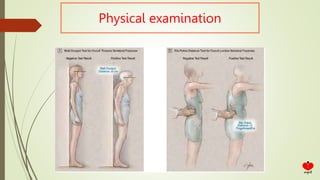
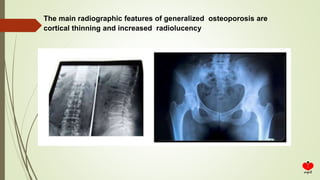
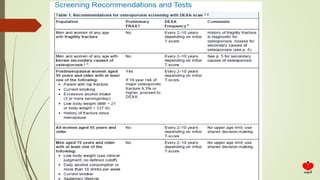
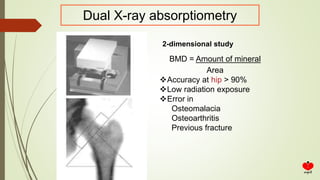
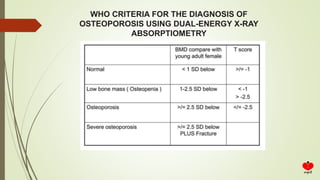
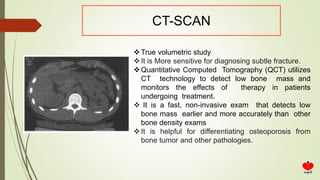
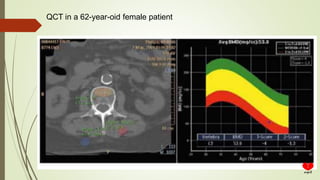
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone microarchitecture, leading to increased bone fragility and risk of fracture. It is diagnosed based on a combination of clinical history, risk factors, physical examination, imaging findings, and bone mineral density (BMD) measurement via dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. BMD T-scores are used to classify individuals as having normal bone density, osteopenia, or osteoporosis according to World Health Organization criteria. Other imaging techniques like quantitative computed tomography and peripheral BMD measurement can provide additional information.