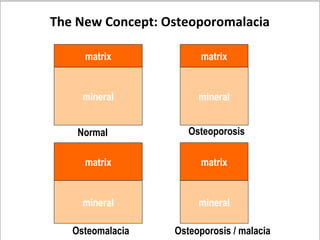
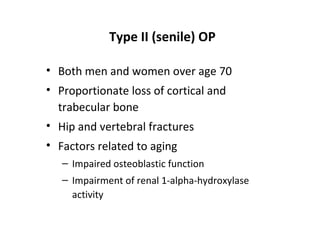
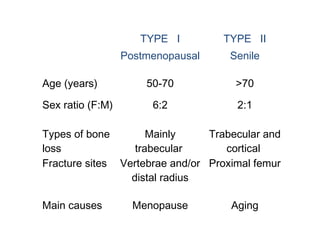
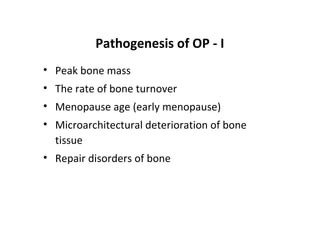
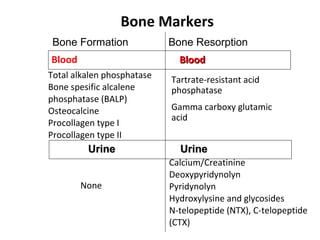
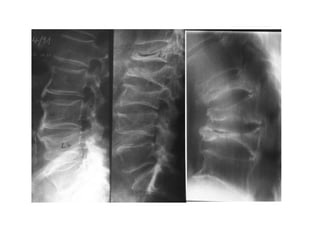
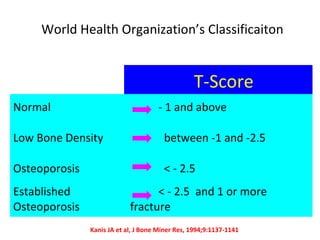
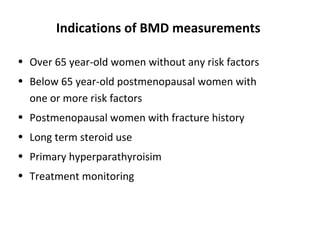
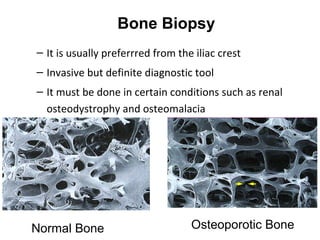
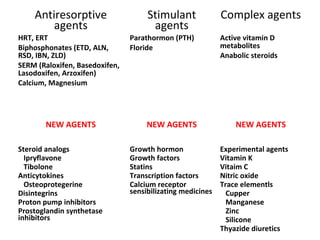
Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease characterized by low bone mass and structural deterioration of bone tissue, leading to bone fragility and increased risk of fractures. It is diagnosed through laboratory tests, imaging like x-rays and DXA scans, and medical history. Management involves lifestyle changes like exercise and diet, medication to reduce bone loss or stimulate bone formation, and physical therapy to prevent falls and fractures. Regular exercise is important for building bone density and strength.