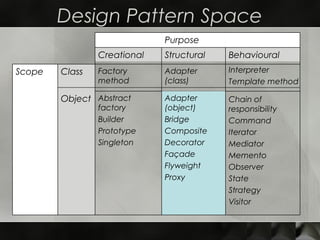
This document discusses design patterns, beginning with how they were introduced in architecture in the 1950s and became popularized by the "Gang of Four" researchers. It defines what patterns are and provides examples of different types of patterns (creational, structural, behavioral) along with common patterns in each category. The benefits of patterns are that they enable reuse, improve communication, and ease the transition to object-oriented development. Potential drawbacks are that patterns do not directly lead to code reuse and can be overused. Effective use requires applying patterns strategically rather than recasting all code as patterns.