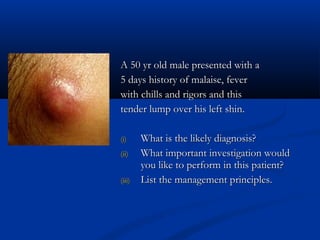
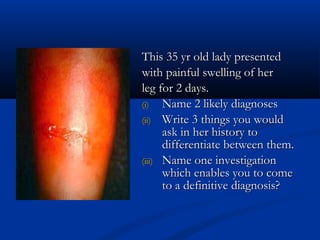
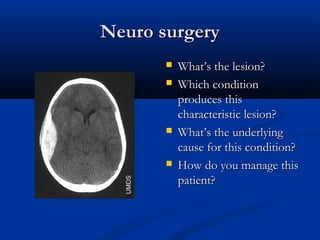
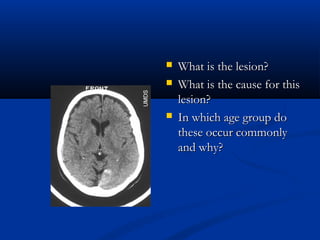
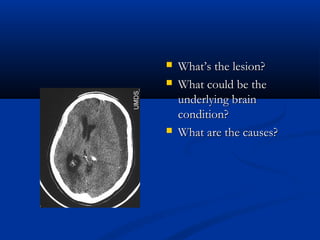
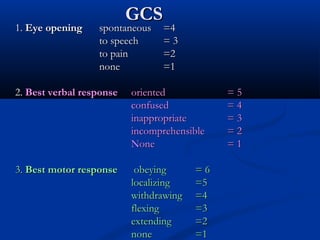
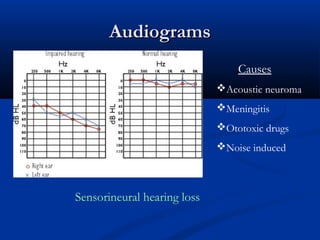
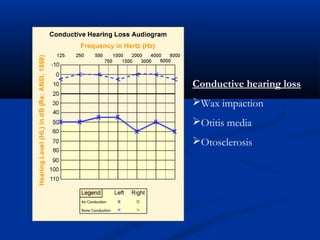
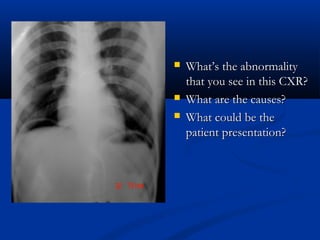
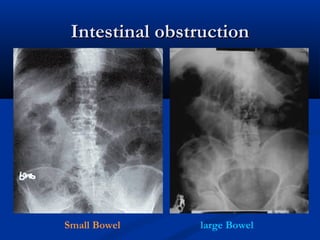
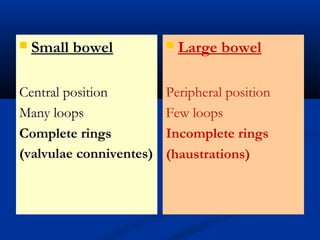
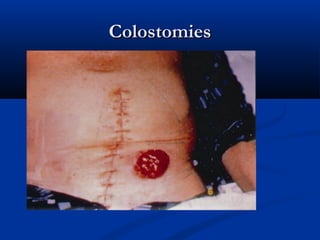
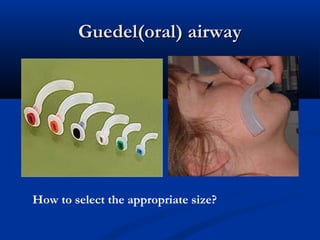
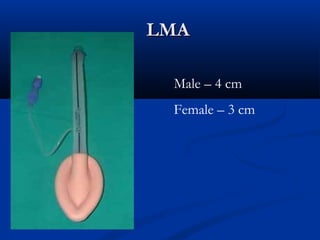
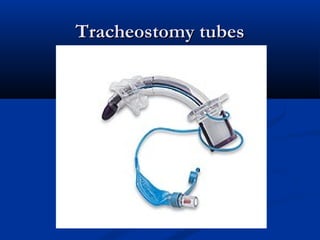
The document discusses various surgical cases and medical conditions, focusing on diagnosis, investigations, and management principles for different scenarios. It includes case studies involving abscesses, cellulitis, intercostal tube usage, and specific medical procedures like NG tubes and urinary catheters. Additionally, it highlights clinical assessments and treatment options for injuries and conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome.