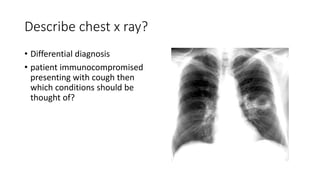
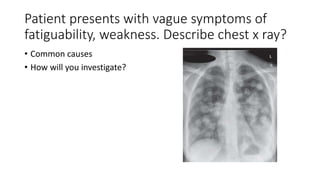
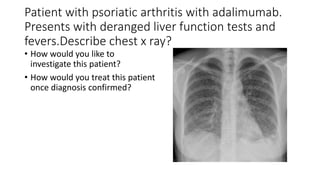
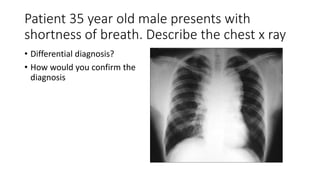
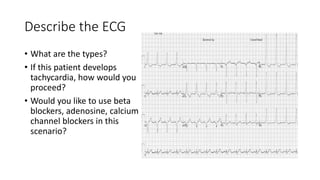
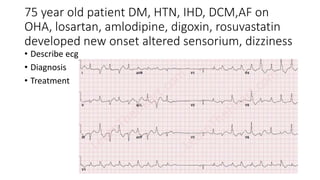
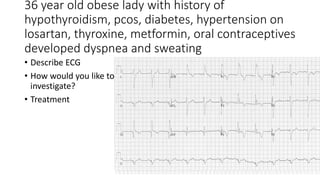
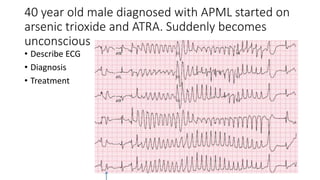
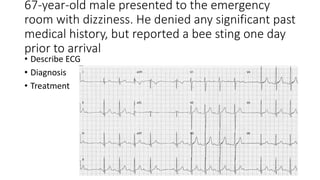
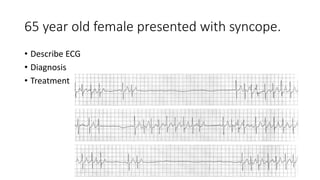
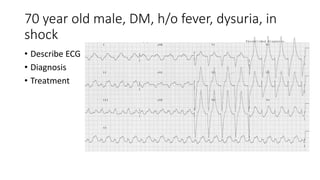
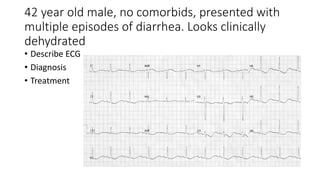
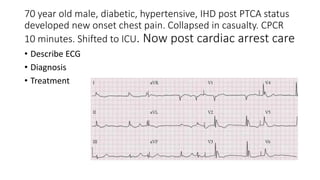
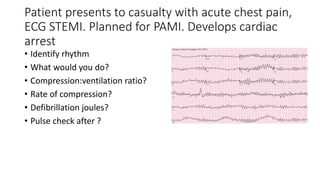
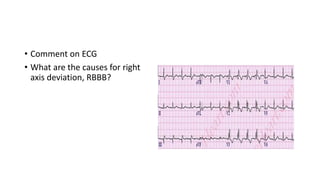
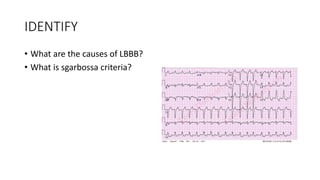
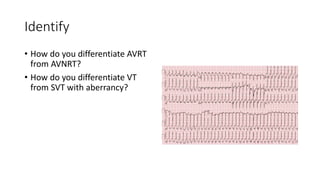
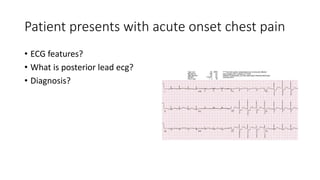
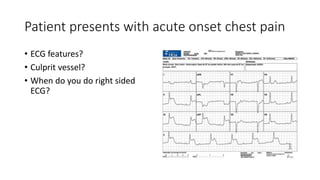
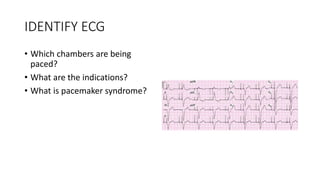
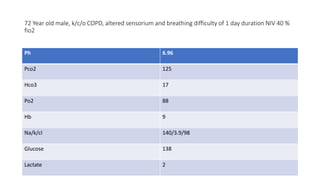
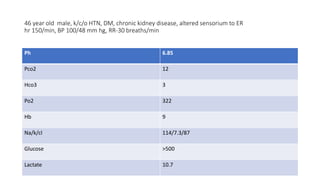
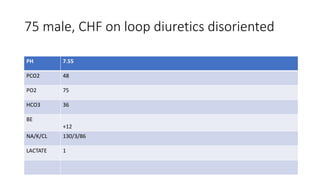
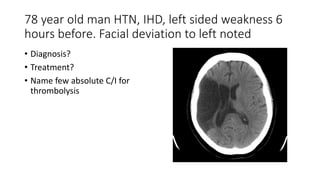
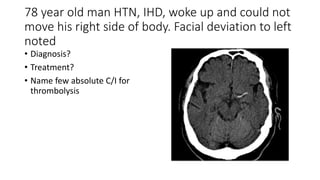
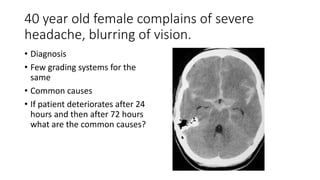
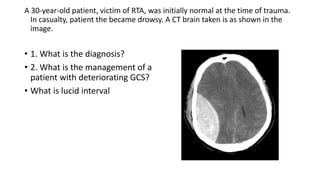
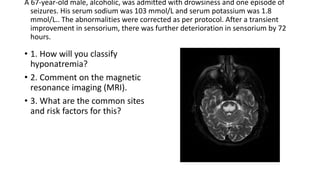
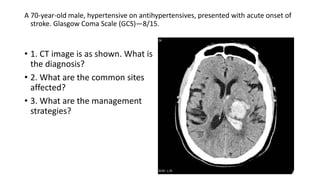
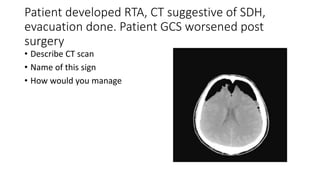
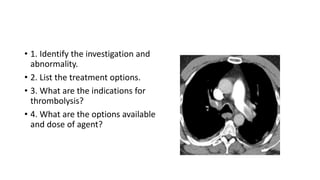
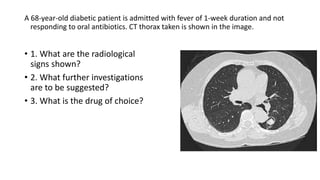
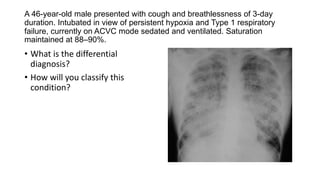
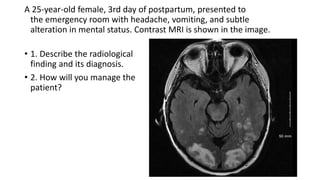
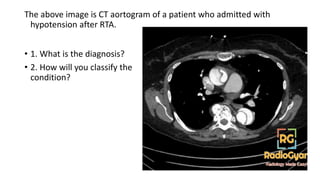
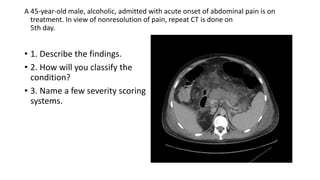
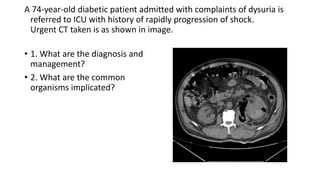
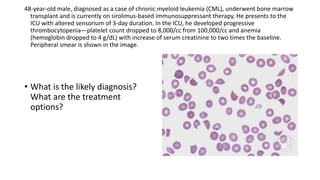
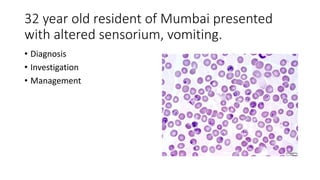
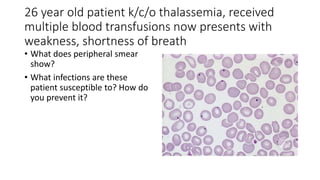
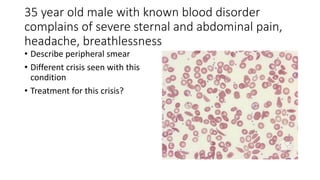
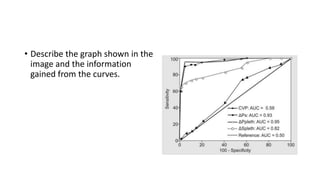
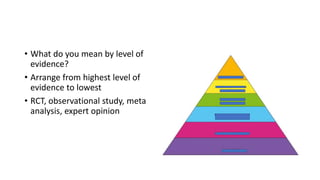
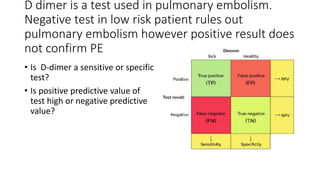
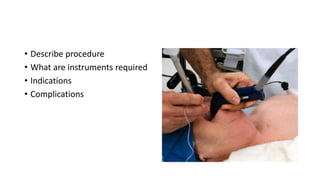
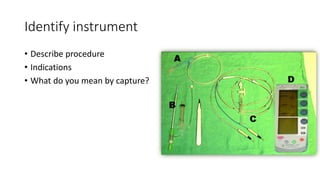
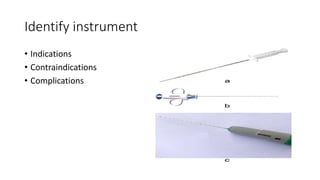
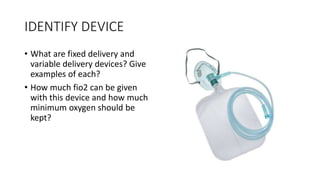
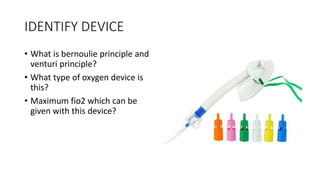
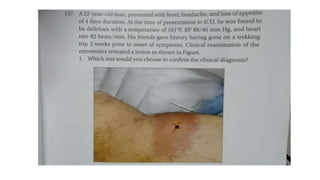
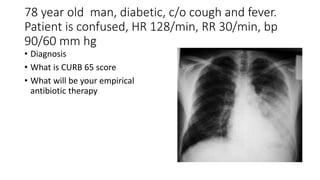
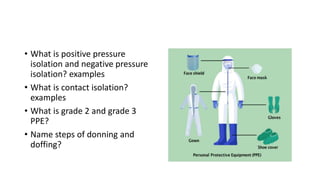
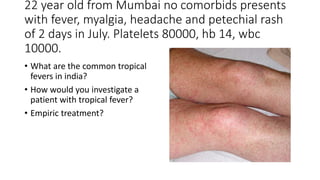
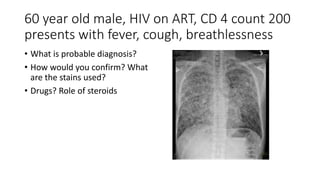
This document contains multiple questions asking to identify medical devices, procedures, and patient scenarios. For each, the responder is asked to identify the device/procedure/scenario, indicate relevant indications or contraindications, and describe management steps or potential complications. The questions cover a wide range of topics including imaging tests, laboratory investigations, medical procedures, ventilation devices, and patient presentation.