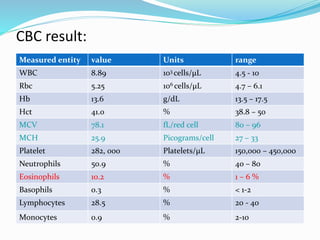
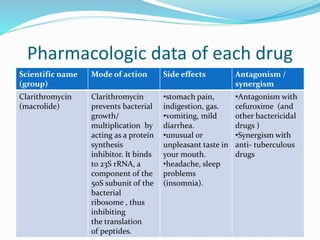
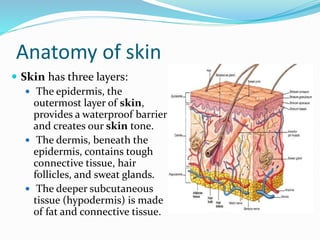
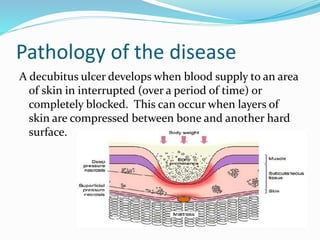
This document contains a medical case report for a 52-year-old male patient presenting with hip pain. It includes details of the patient's history, examination findings, diagnostic test results, and initial treatment plan. The patient has paraplegia and diabetes following a spinal cord injury years ago. Examination revealed a pressure ulcer on his right buttock. Blood tests showed elevated white blood cells and slightly high blood glucose. The provisional diagnosis is a decubitus ulcer, which is being treated with antibiotics, wound dressings, and positioning changes to offload pressure on the affected area.