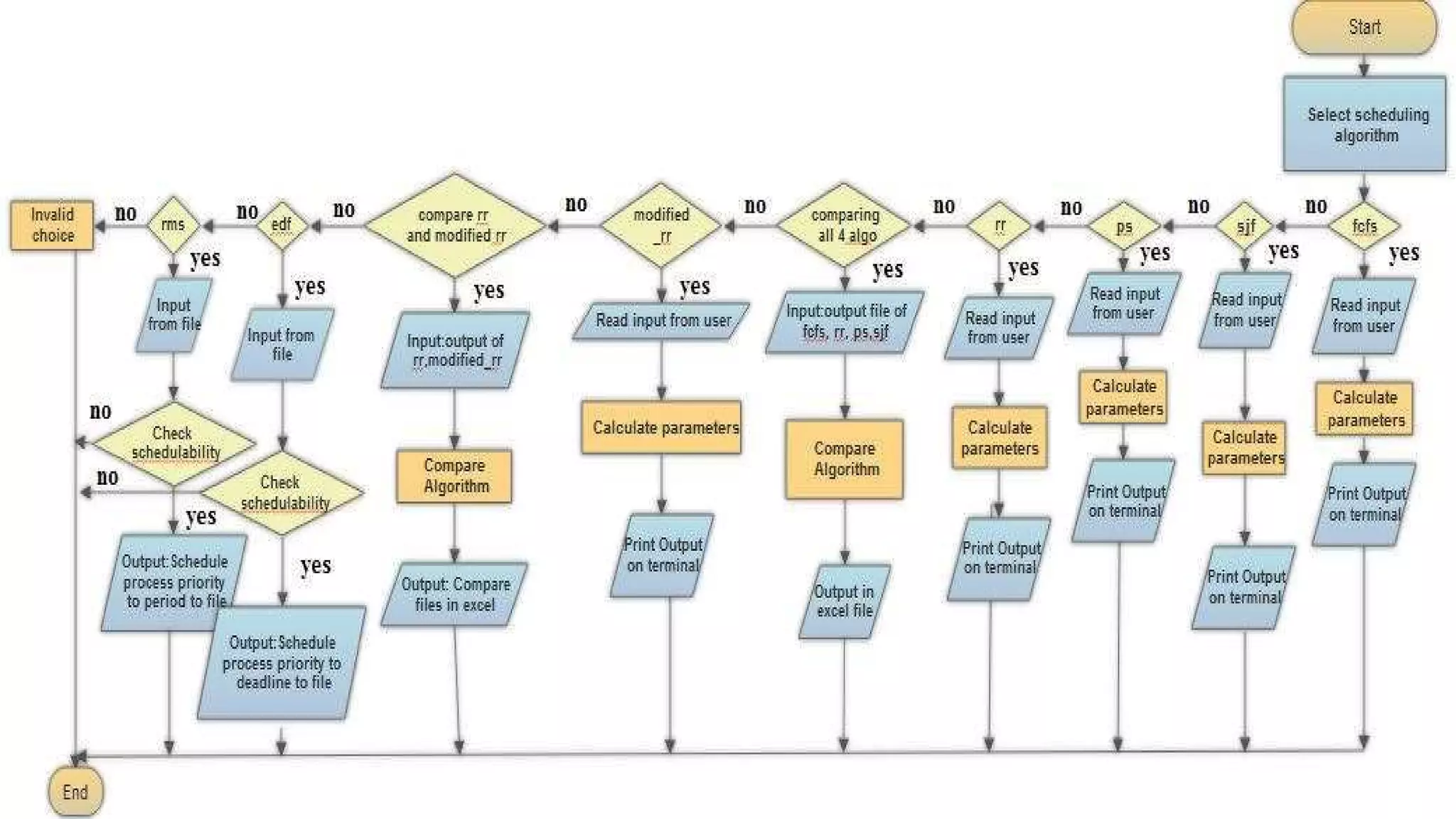
The document presents a CPU scheduling algorithm project that was created by a group. It implemented and analyzed several CPU scheduling algorithms including FCFS, Round Robin, Shortest Job First, Priority Scheduling, Earliest Deadline First, and Rate Monotonic Scheduling. It also proposed a Modified Round Robin algorithm and showed through analysis that it provided around 40% better performance than the traditional Round Robin algorithm in terms of reduced wait time, turnaround time, and context switches while improving throughput. The project was developed using C programming and compared the different scheduling algorithms through generated bar graphs.