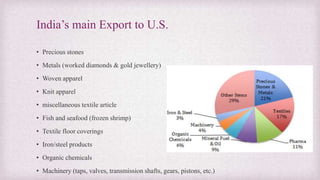
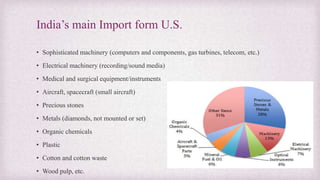
The document discusses the trade relations between the United States and India. It provides background on why countries trade, details on India's international economic relations and its strong economic relations with several countries including the US. It then focuses on the history, growth and details of trade between India and the US, including key exports and imports. It also discusses investment between the two countries and some challenges and barriers to trade.

































![Will Indo- U.S. Relation Suffer
• Trump criticized Asian economies like China, Japan, and Korea for cheating the U.S. through currency
manipulation or bad trade practices.
• India was one of the few countries that escaped his wrath. However, India will not escape the negative
impacts of the trade policies Trump proposed during the campaign.
• India’s positive goods trade balance will diminish if the U.S. erects trade walls.
• India is set to benefit from greater integration with the global economy, Trump’s actions could depress
already sluggish global trade and growth.
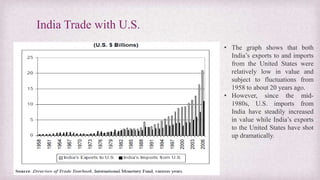
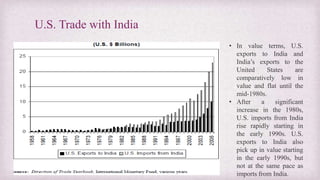
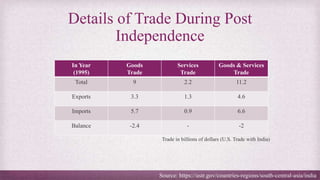
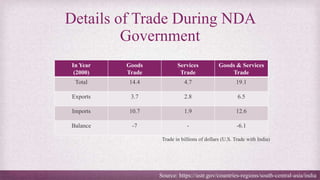
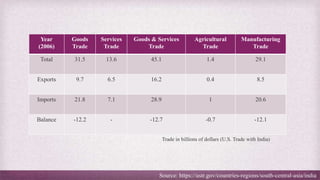
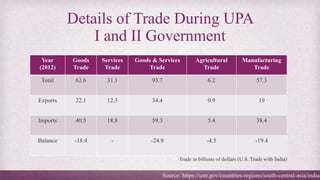
• After growing at a steady pace from 2000 to 2013, bilateral trade has been stagnant in recent years. That
might continue under President Trump.
• If Trump seeks to reduce temporary work visas. Trump criticized the U.S. H-1B non-immigrant
specialty worker visa program during the campaign, saying it “decimate[s]” American jobs.
• The Indian government has long sought more H-1B visas for its citizens, who are already the greatest
recipients of them.
• If President Trump keeps his promise to reduce H1-Bs, India would likely see fewer of its citizens
coming to work in the United States, putting its IT companies under greater pressure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/traderelationsu-170709172203/85/Trade-relations-US-India-the-changing-faces-49-320.jpg)


