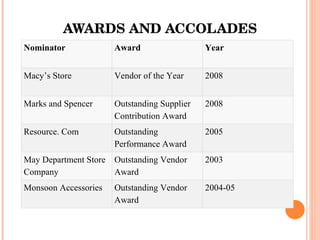
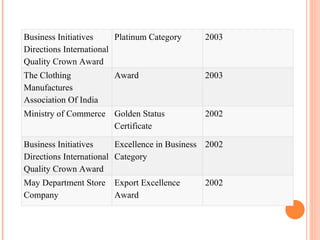
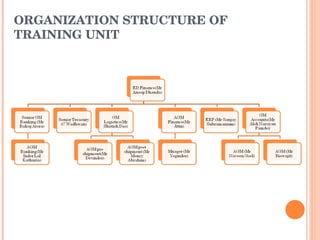
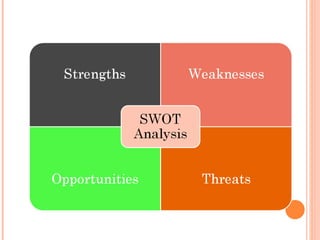
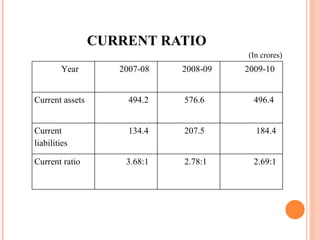
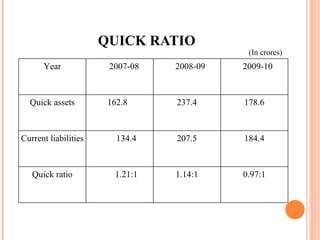
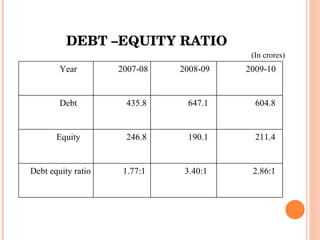
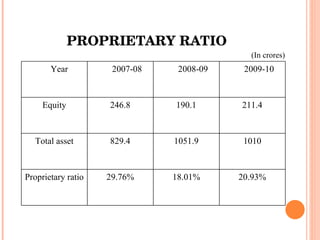
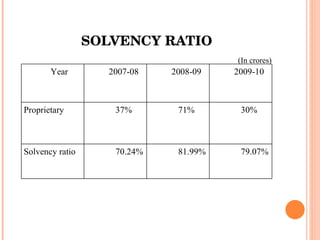
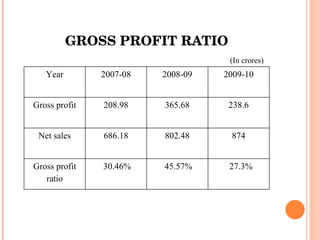
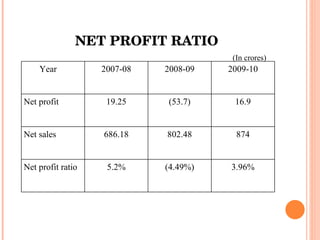
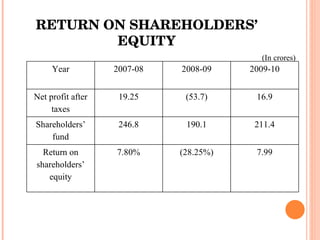
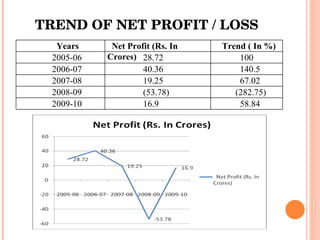
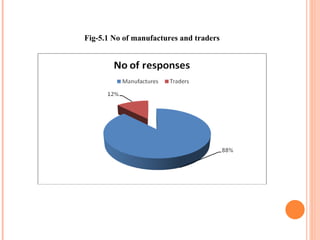
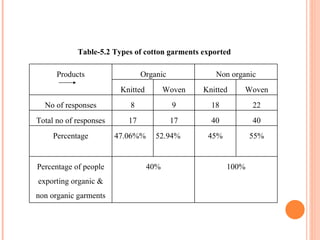
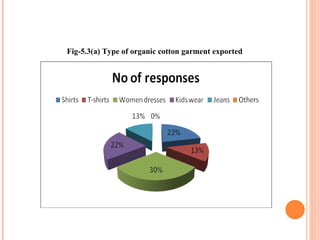
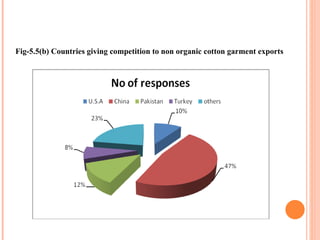
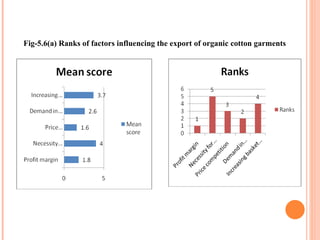
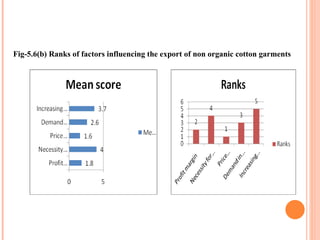
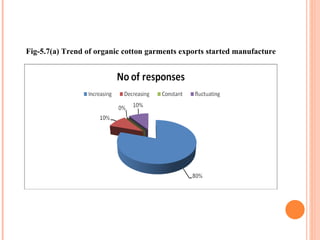
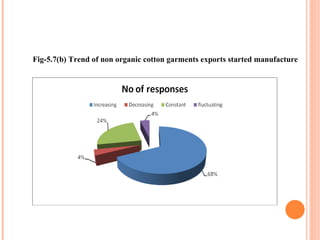
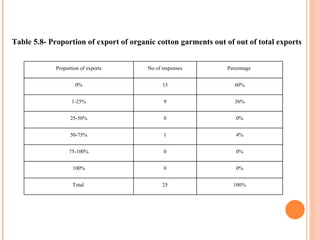
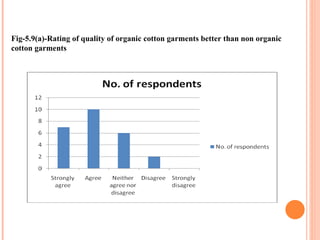
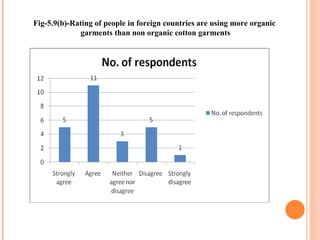
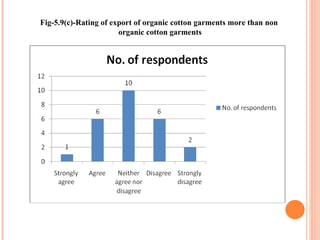
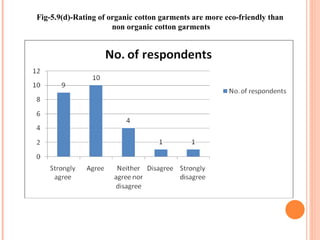
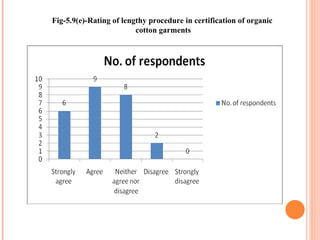
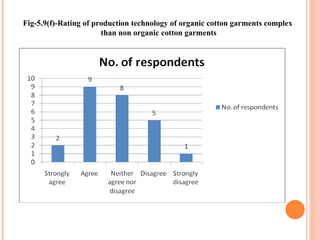
- Orient Craft Limited is a leading Indian manufacturer and exporter of garments and home textiles. It exports to major international brands and retailers across the world.
- The document provides details about Orient Craft's operations, financial performance, organic and non-organic cotton exports from India, and a comparative study of the two. It outlines the objectives, methodology, and findings of the research conducted.