The document discusses three main topics: attitudes, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment.
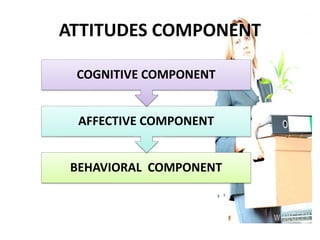
For attitudes, it defines attitudes as positive or negative feelings towards people, objects or situations. Attitudes have three components - cognitive, affective, and behavioral.
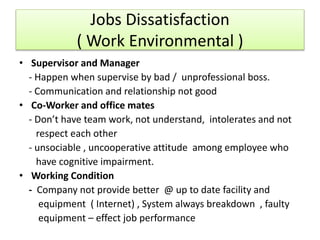
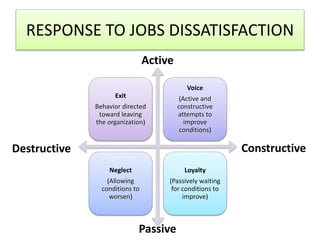
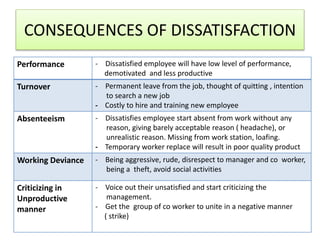
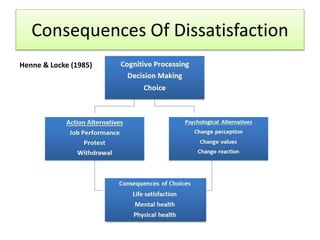
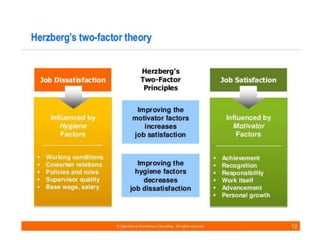
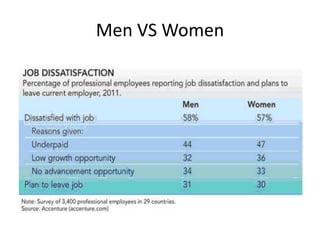
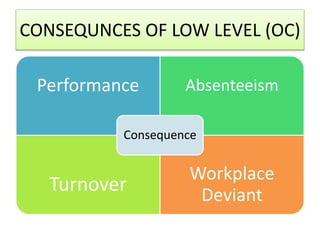
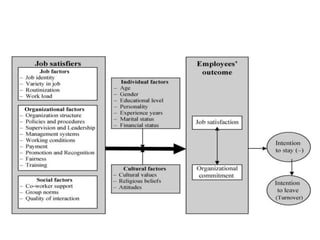
For job satisfaction, it defines it as positive feelings about one's job. Major causes of dissatisfaction are low pay, lack of promotion opportunities, unfair rewards, poor supervision, and bad work conditions. Consequences include low performance, increased turnover and absenteeism.
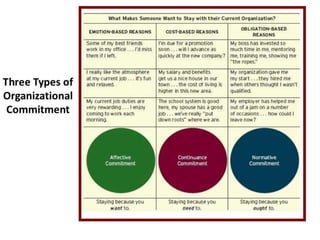
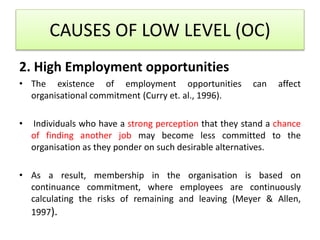
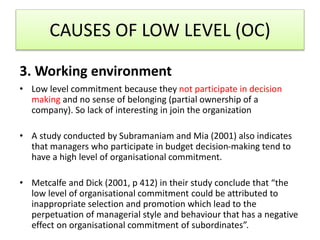
For organizational commitment, it defines it as acceptance of an organization's goals and desire to remain a member. There are three types of commitment - affective, continuance, and normative. Low