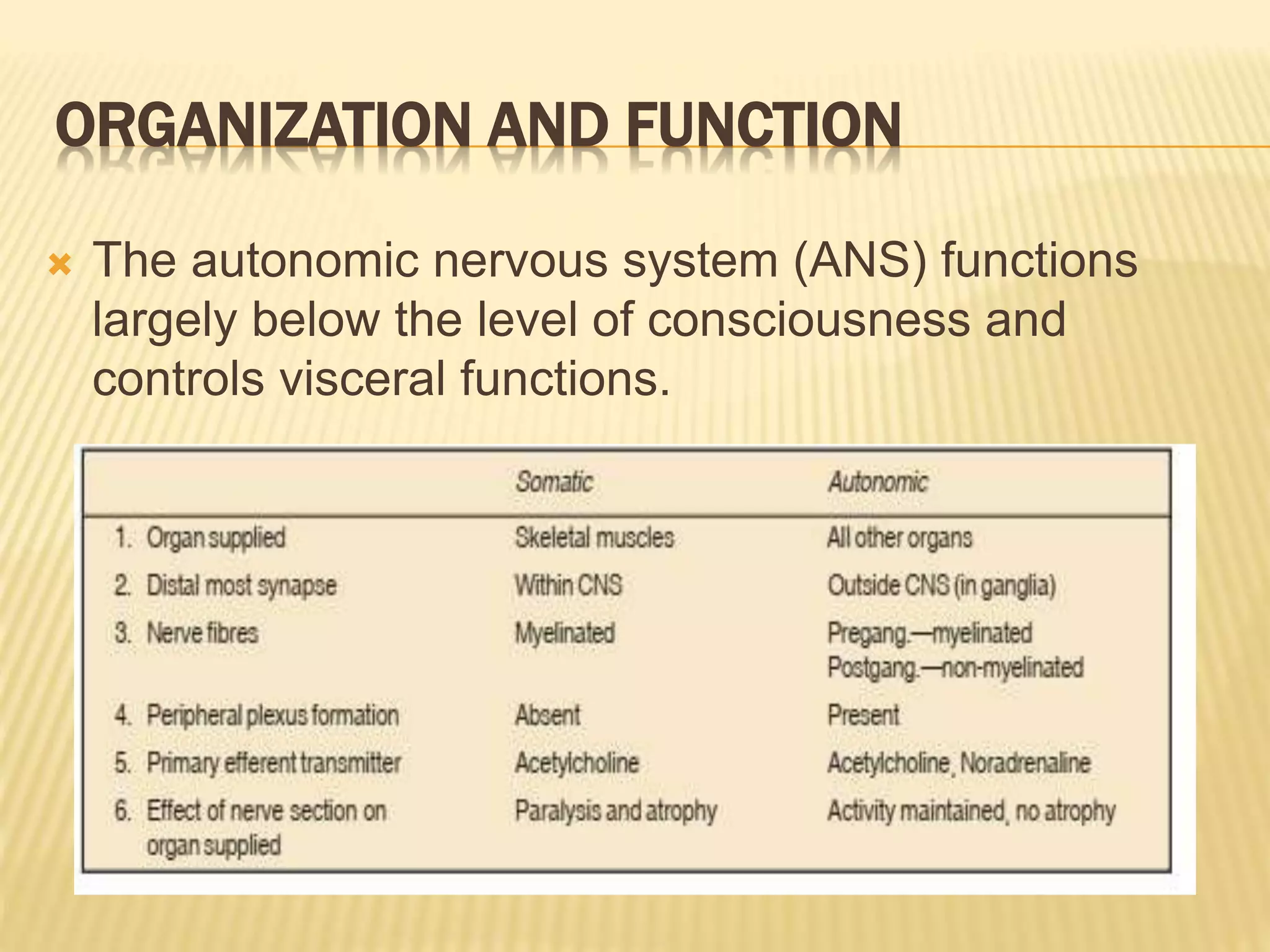
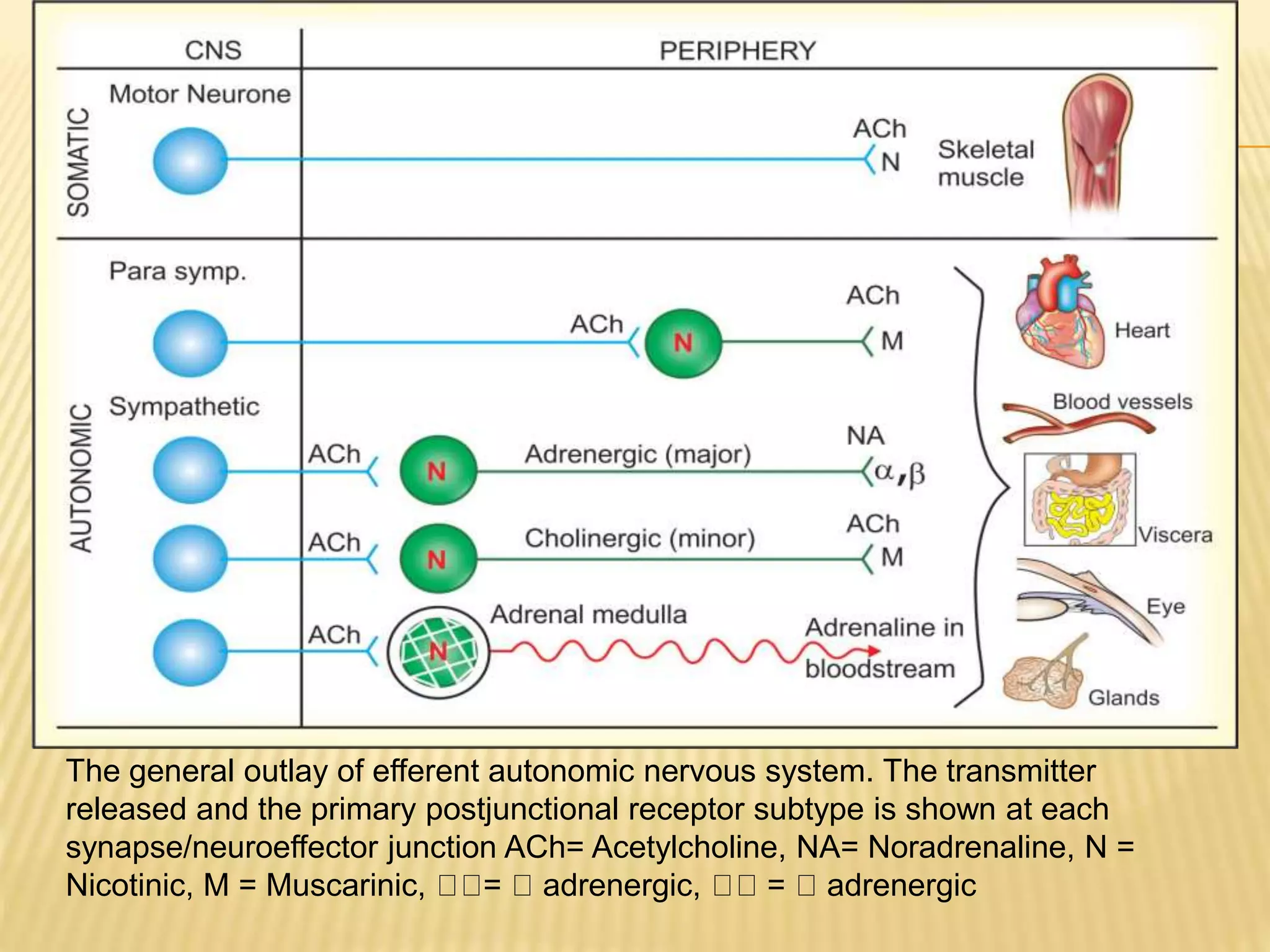
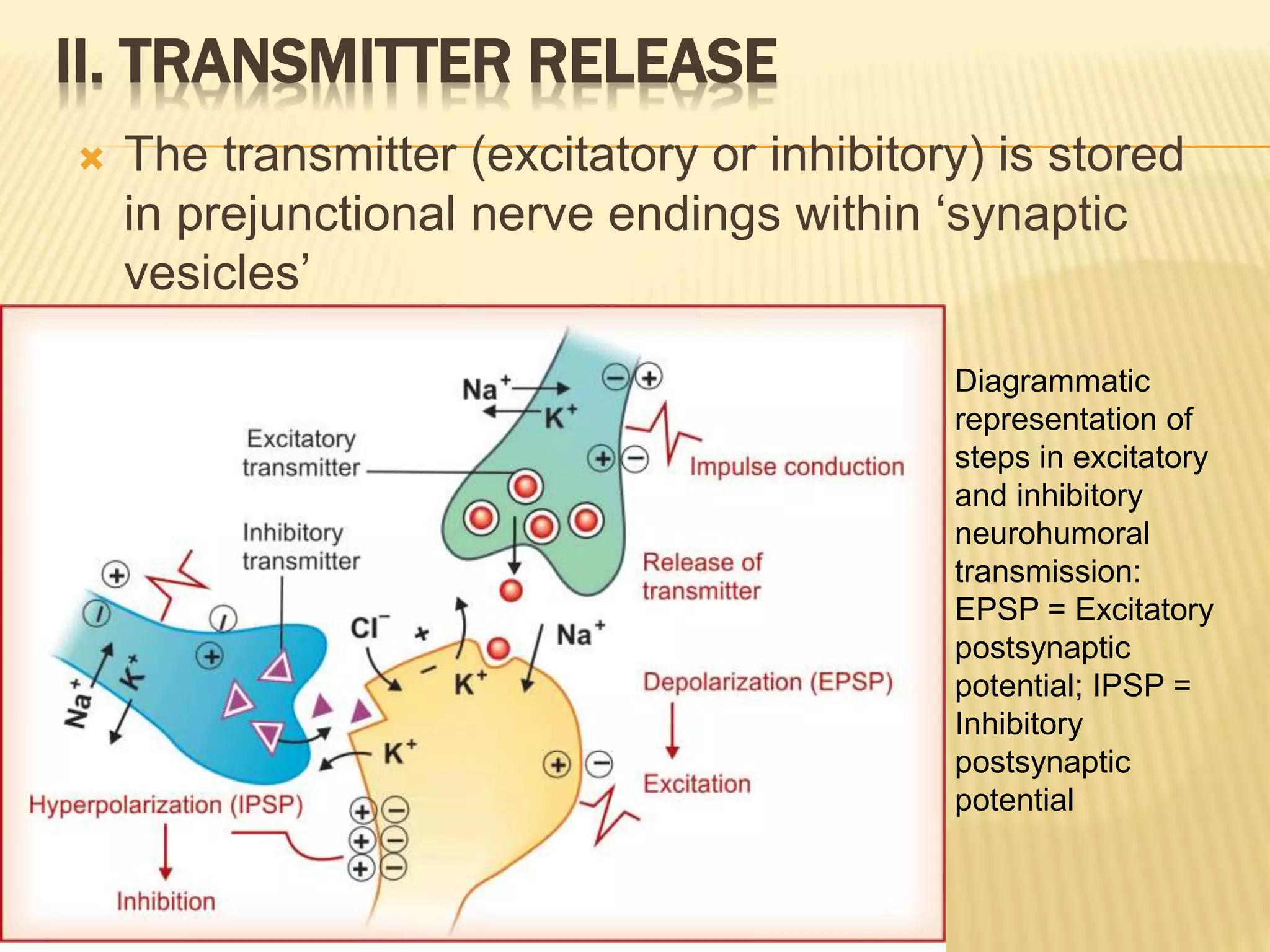
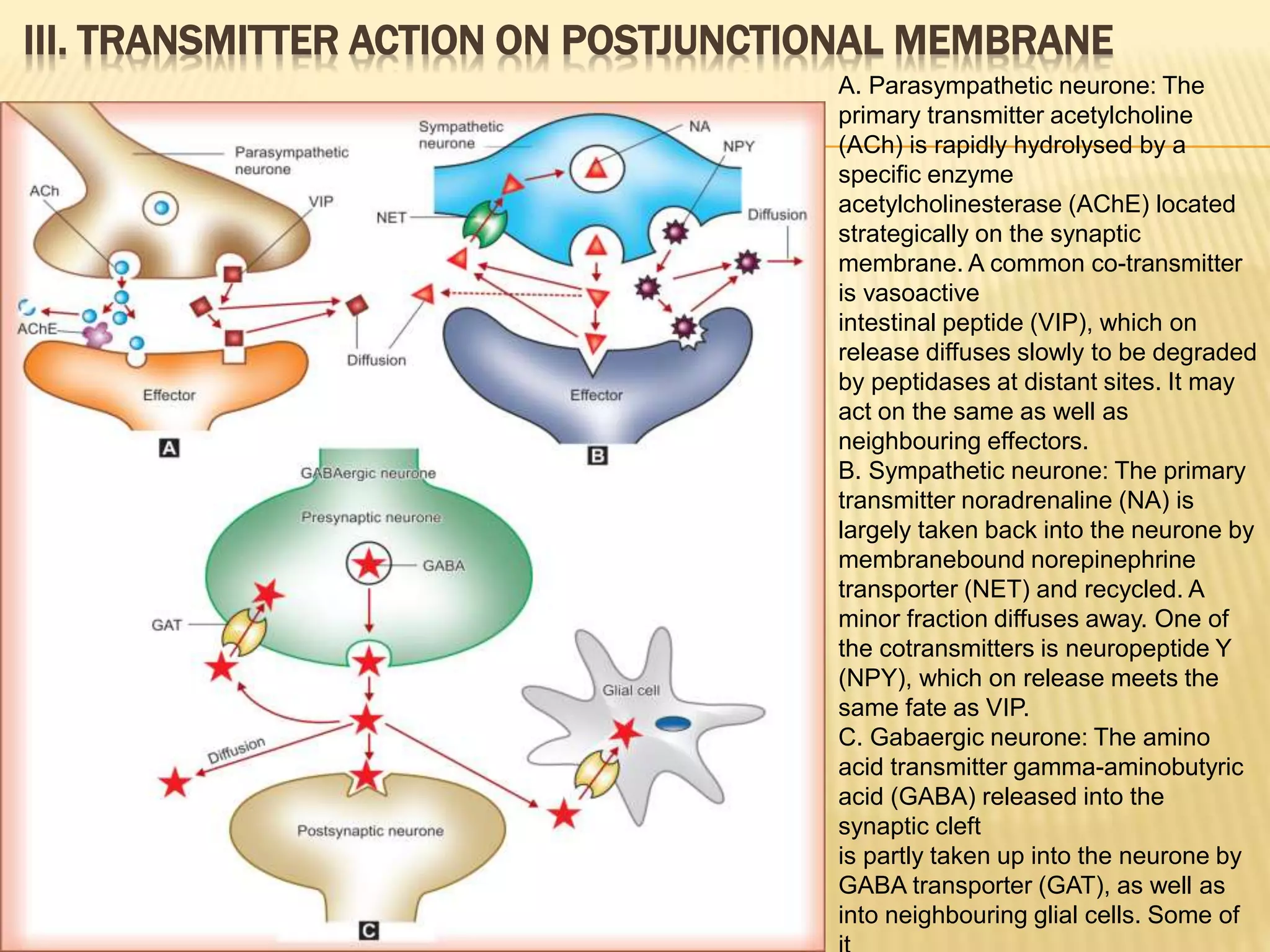
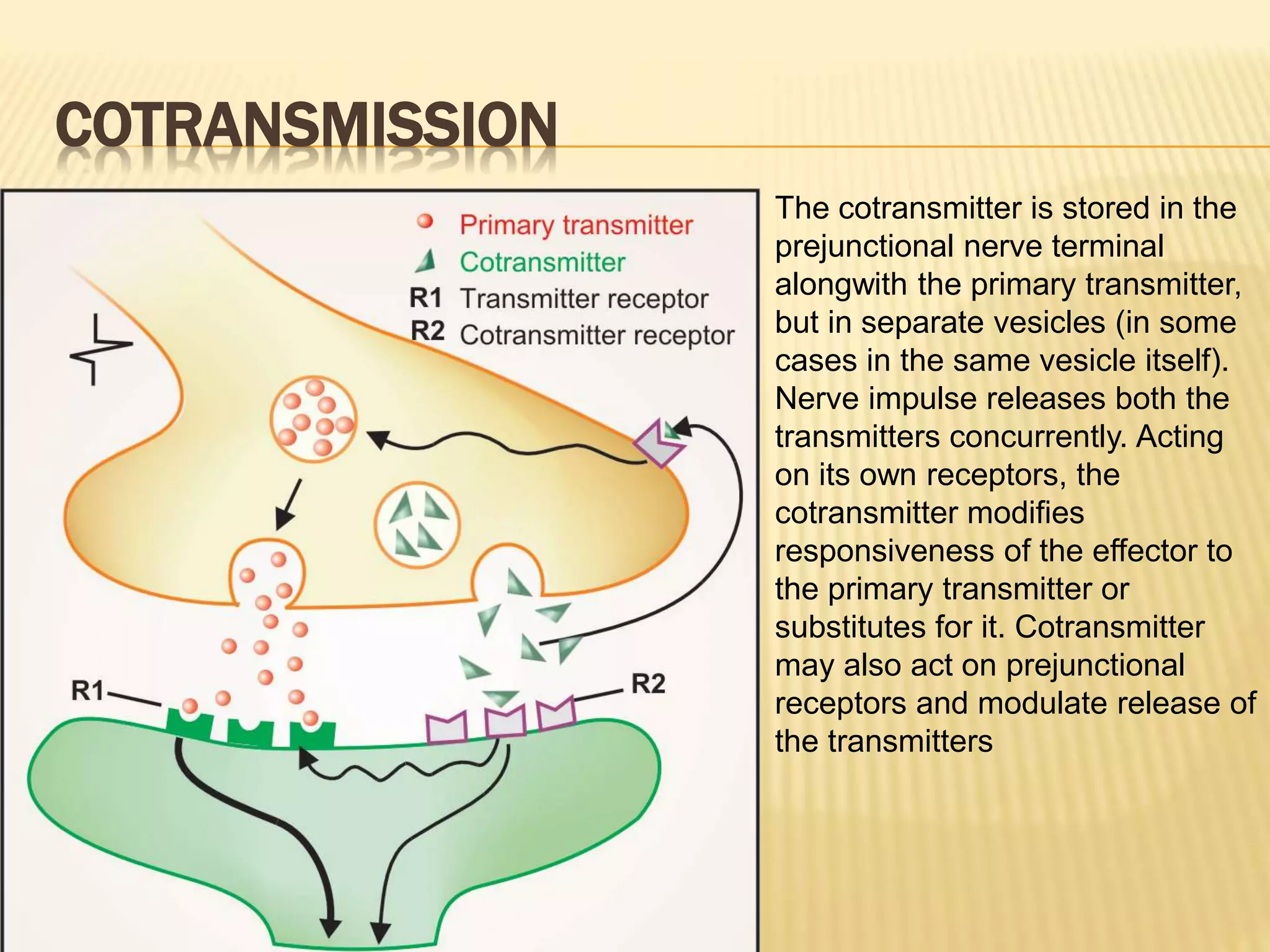
The autonomic nervous system functions below consciousness to control visceral functions. It has two divisions - the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic nervous system uses norepinephrine as its primary neurotransmitter, while the parasympathetic nervous system uses acetylcholine. Neurotransmission in the autonomic nervous system involves impulse conduction, transmitter release from synaptic vesicles, transmitter action on postjunctional membranes, generation of a postjunctional potential, and termination of transmitter action through reuptake or degradation. Many neurons also release cotransmitters that can modify or substitute the action of the primary transmitter.