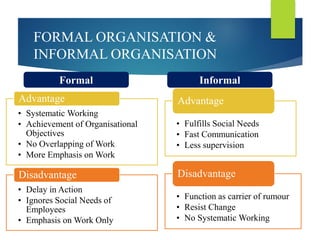
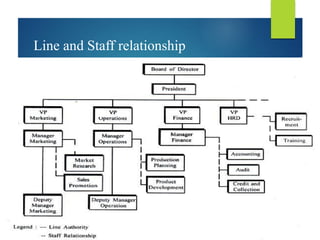
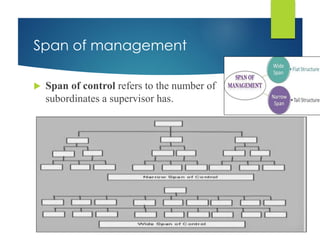
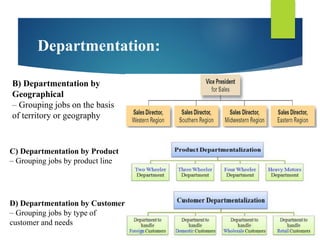
The document discusses the concept of organization, defining it as a group of people cooperating towards common goals under leadership, with a focus on both formal and informal organizational structures that impact effectiveness and communication. It contrasts formal organization, characterized by clear roles and fixed authority, with informal organization, which arises from personal relationships and fulfills social needs. Additionally, it covers various organizational issues, including employee problems, work specialization, span of management, delegation, unity of command, and departmentation methods.