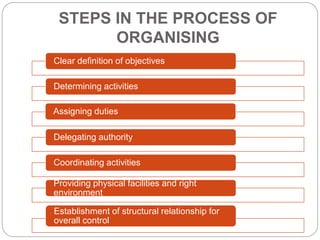
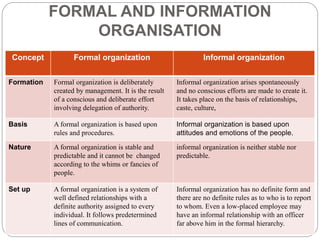
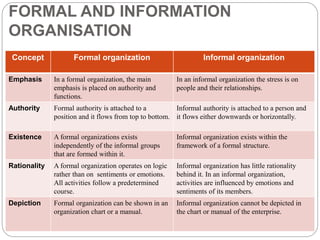
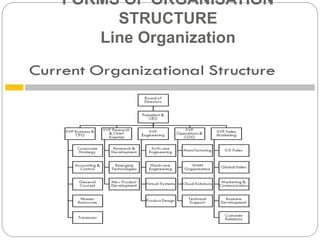
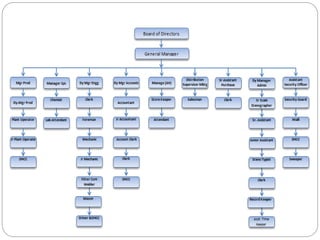
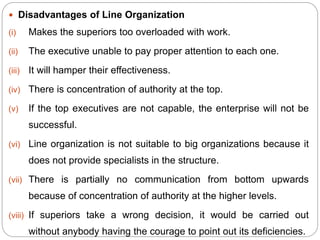
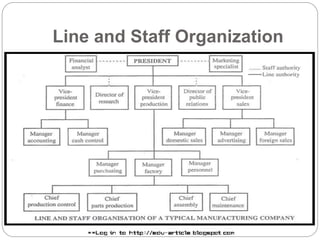
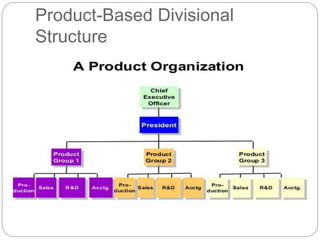
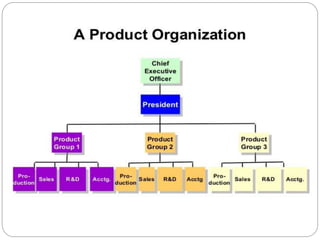
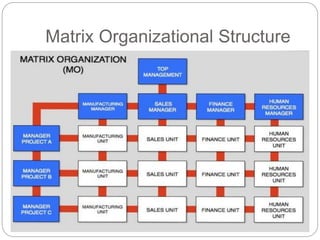
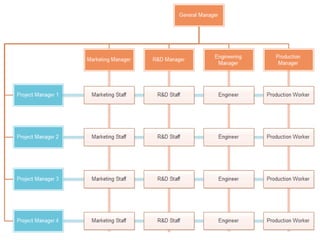
Organizing is the backbone of management and involves grouping activities and assigning managers to supervise them in the best way to achieve organizational goals. There are formal and informal aspects to organizational structure. Formally, tasks are divided and responsibilities are delegated through clear lines of authority. Informally, personal relationships also influence how work gets coordinated. Common organizational structures include line, line and staff, and divisional structures. Line structures keep authority centralized but may overload leaders. Line and staff structures add specialists to support line managers but can cause conflicts. Divisional structures group activities by product or customer for focus but coordination across divisions is needed. The choice of structure involves tradeoffs to support the organization's objectives.