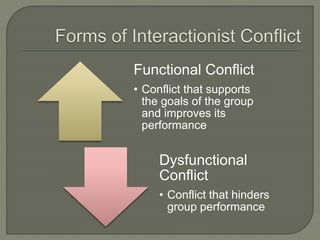
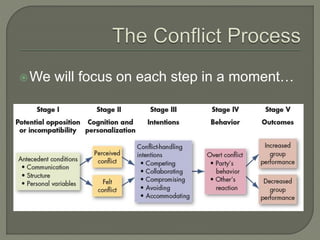
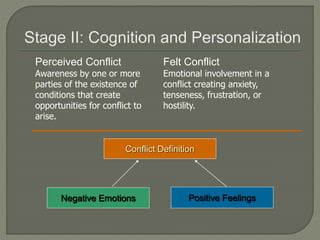
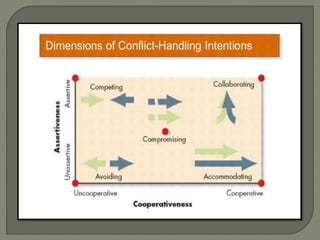
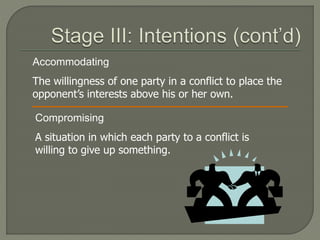
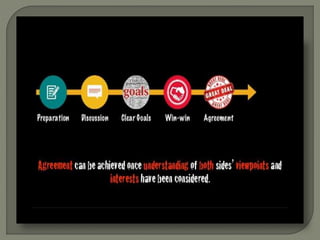
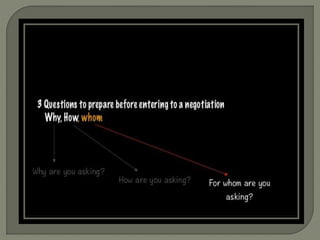
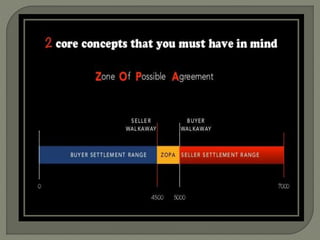
The document discusses conflict in groups and its management. It defines different types of conflict including functional and dysfunctional conflict. Functional conflict supports group goals and performance, while dysfunctional hinders it. The document also outlines various causes of conflict including communication issues, group structure problems, and personal variables. It then discusses five approaches to conflict - competing, collaborating, avoiding, accommodating, and compromising. Finally, it notes potential functional and dysfunctional outcomes of conflict and how to create functional conflict to improve group performance and decision making.