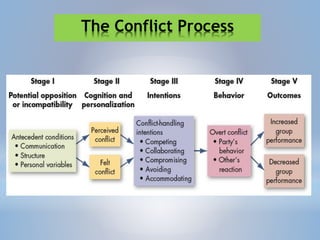
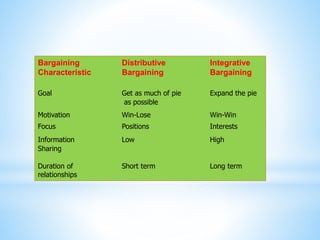
The document discusses conflict and negotiation. It defines conflict as occurring when one party perceives another has negatively affected something they care about. There are three types of conflict: task, relationship, and process. The conflict process has five stages: communication, perceived conflict, felt conflict, party behaviors, and outcomes. Negotiation is defined as parties exchanging goods or services to agree on exchange rates. There are distributive and integrative bargaining strategies, and a negotiation process involves mediators, arbitrators, or conciliators as third parties.