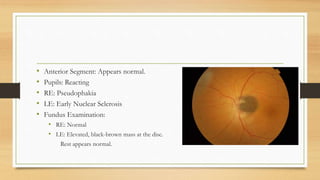
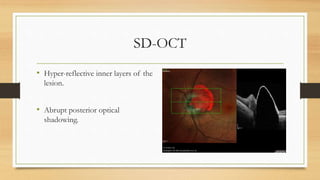
1) A 42-year-old woman was found to have an elevated black-brown mass on her left optic disc during a routine eye exam.
2) B-scan ultrasound found an iso-echoic, elevated lesion over the optic nerve head with no internal reflectivity.
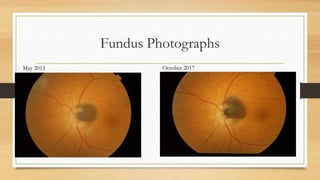
3) Over two years of follow-up the lesion increased slightly in size but the patient's vision remained stable at 6/6.
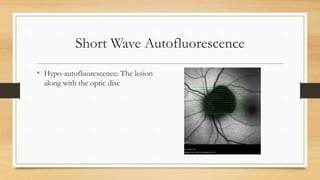
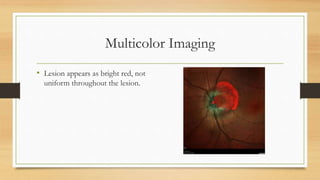
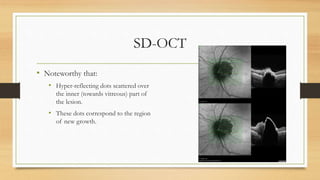
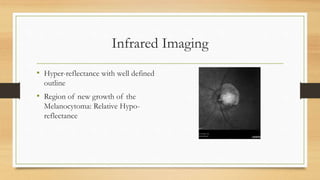
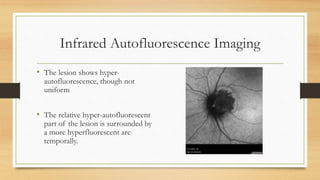
4) Infrared and infrared autofluorescence imaging helped determine the growth and activity of the optic disc melanocytoma by showing features of the lesion and a region of new growth.