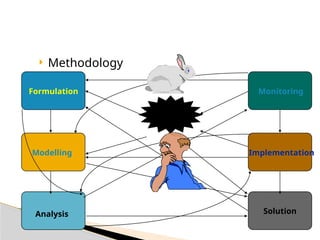
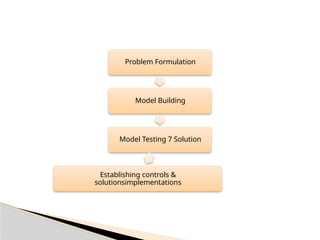
Operations Research (OR) is a discipline that applies scientific methods and advanced analytical techniques to optimize decision-making in various fields, initially developed during World War II to solve military resource allocation problems. OR is now widespread in sectors like healthcare, finance, and industrial management, focusing on minimizing costs and maximizing profits through systematic problem analysis and model development. The process involves observing problem environments, model building, data collection, solution testing, and implementation, while facing challenges such as employee resistance and computational complexities.