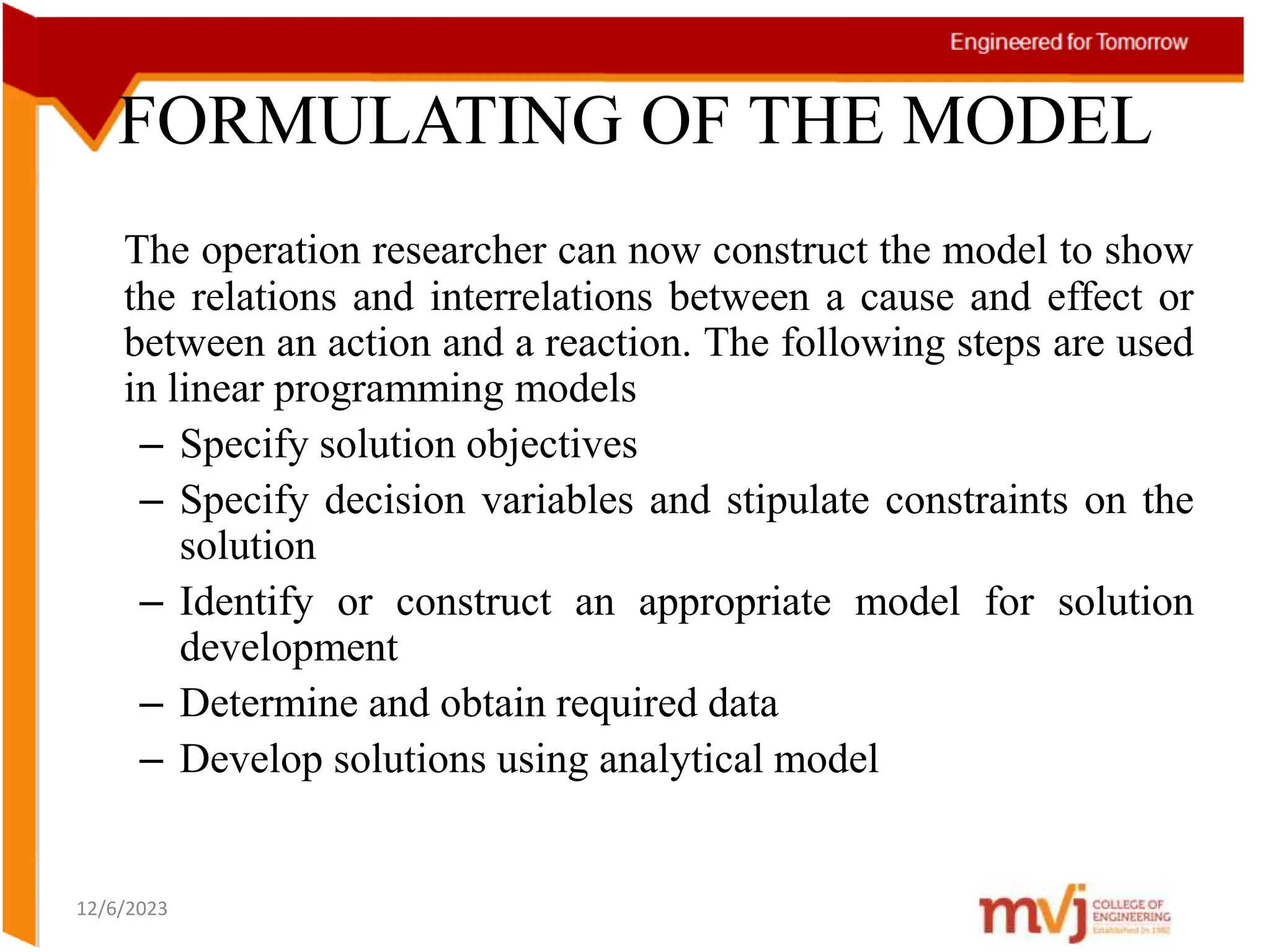
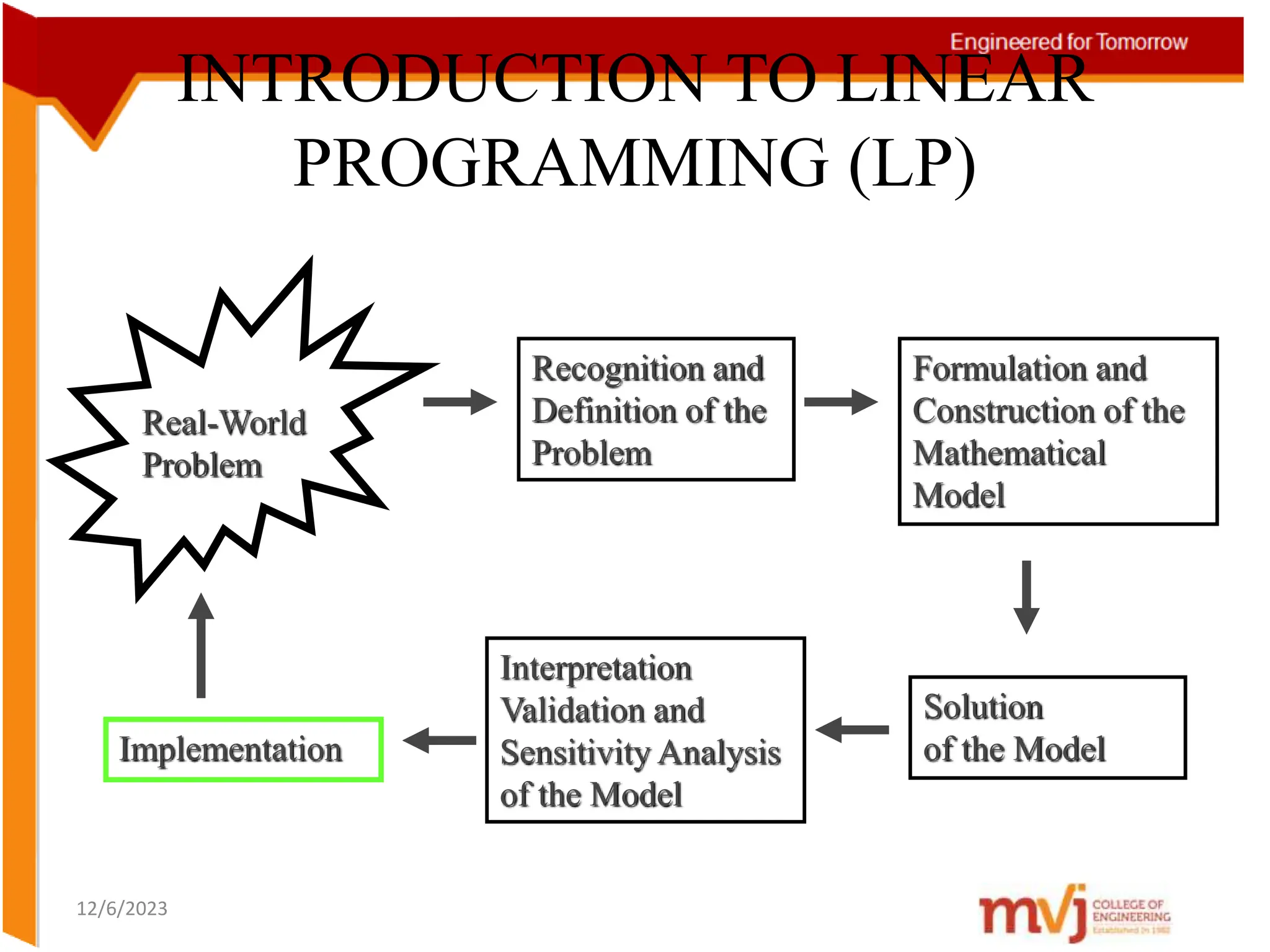
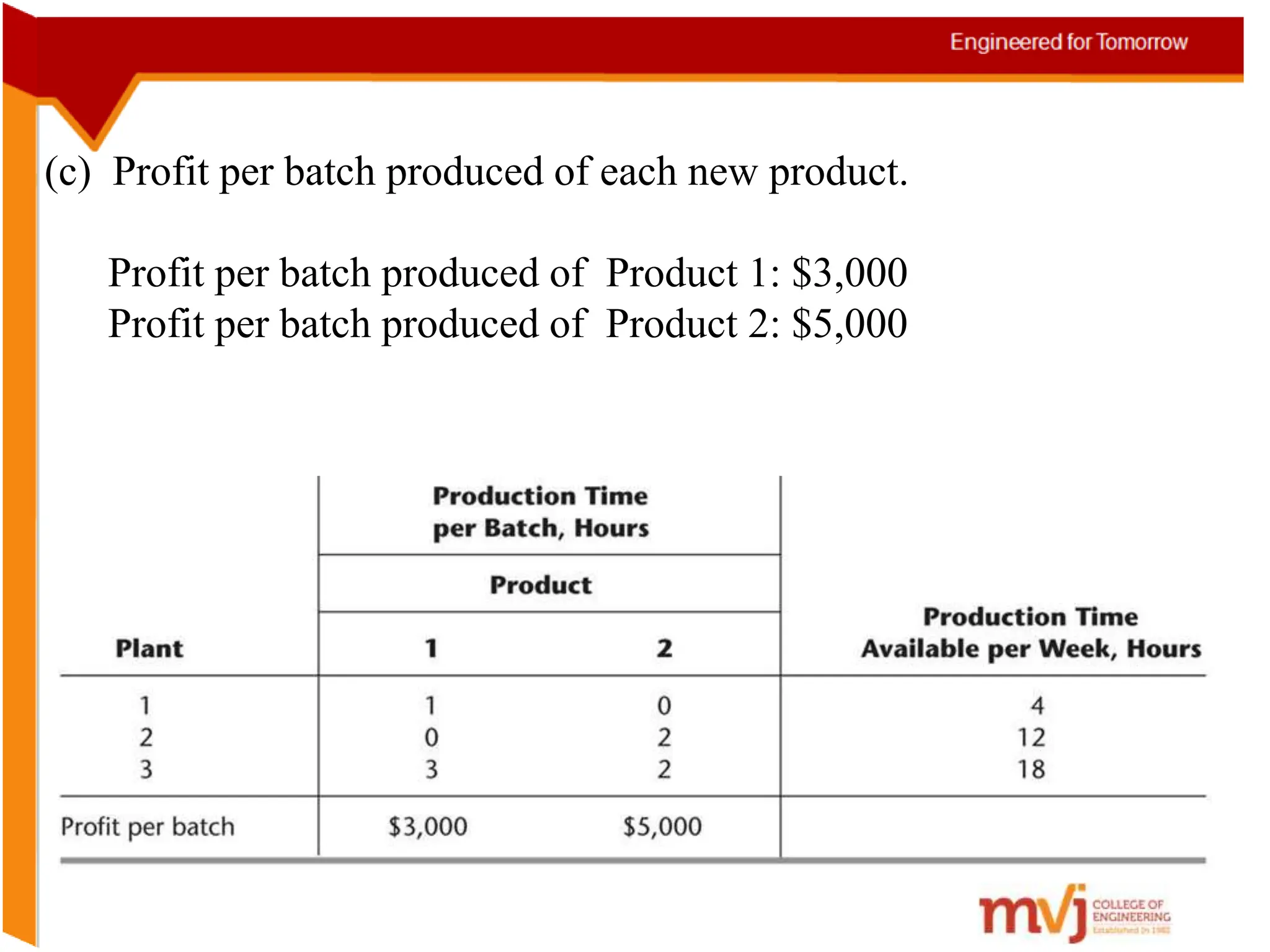
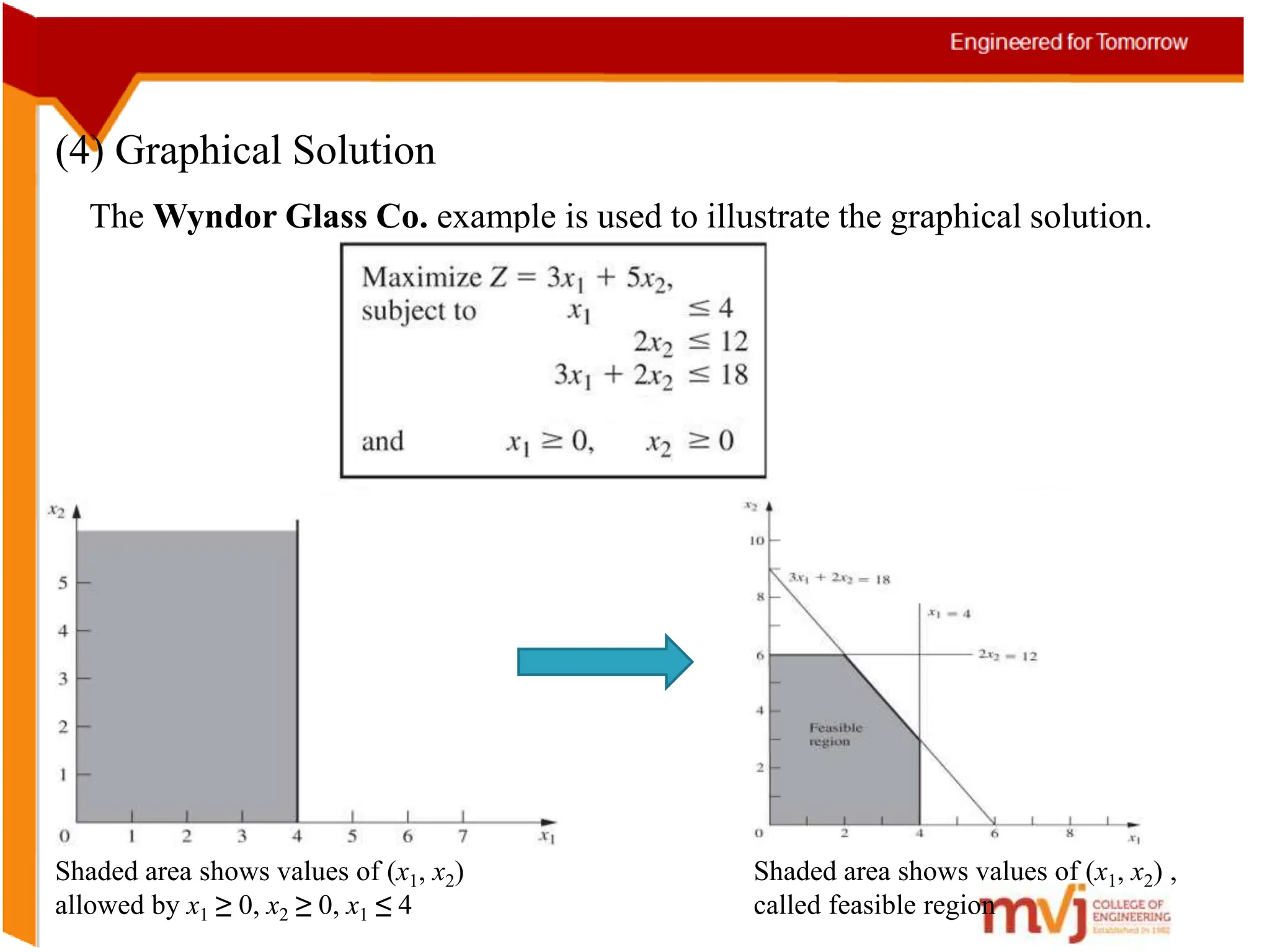
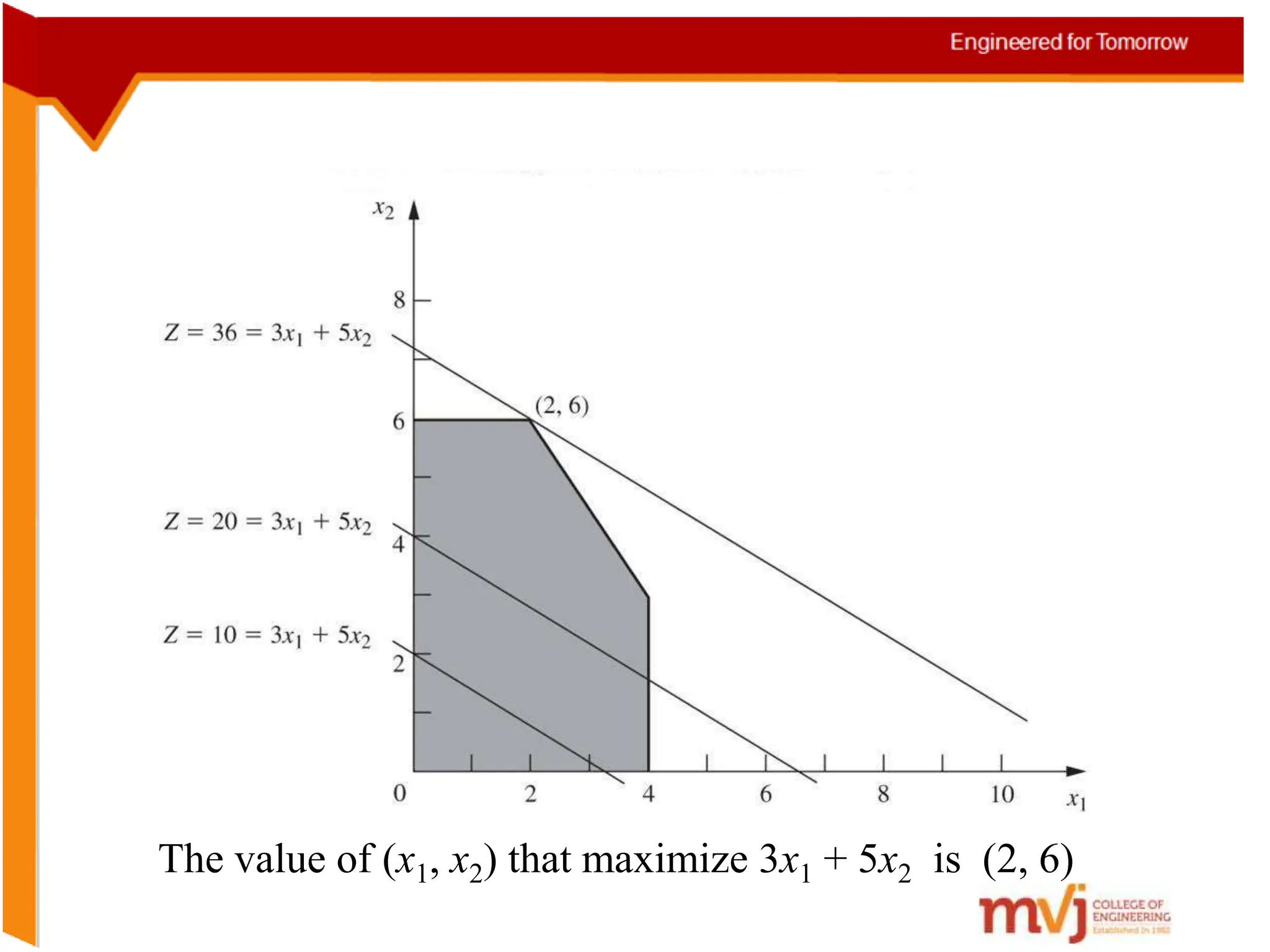
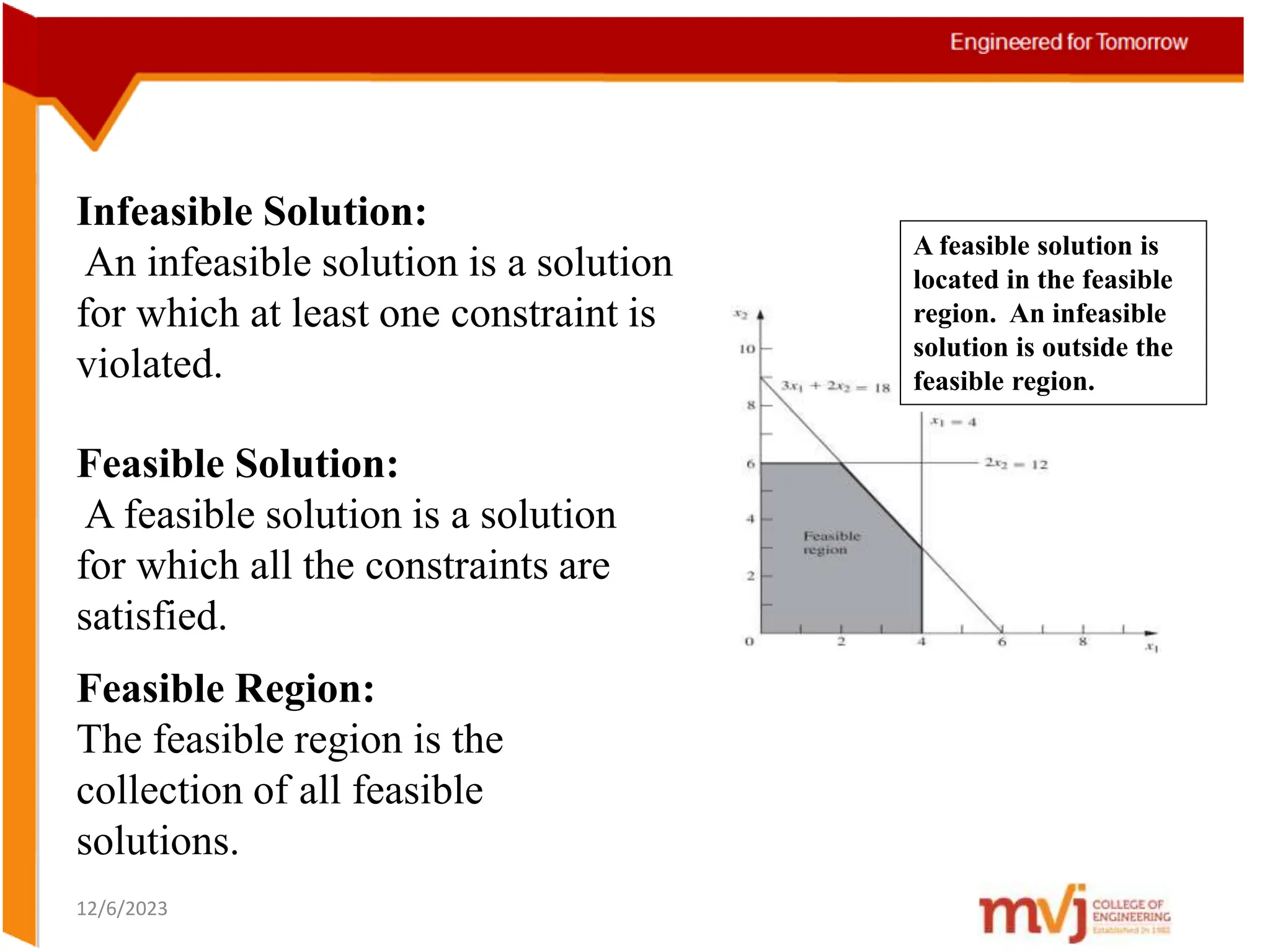
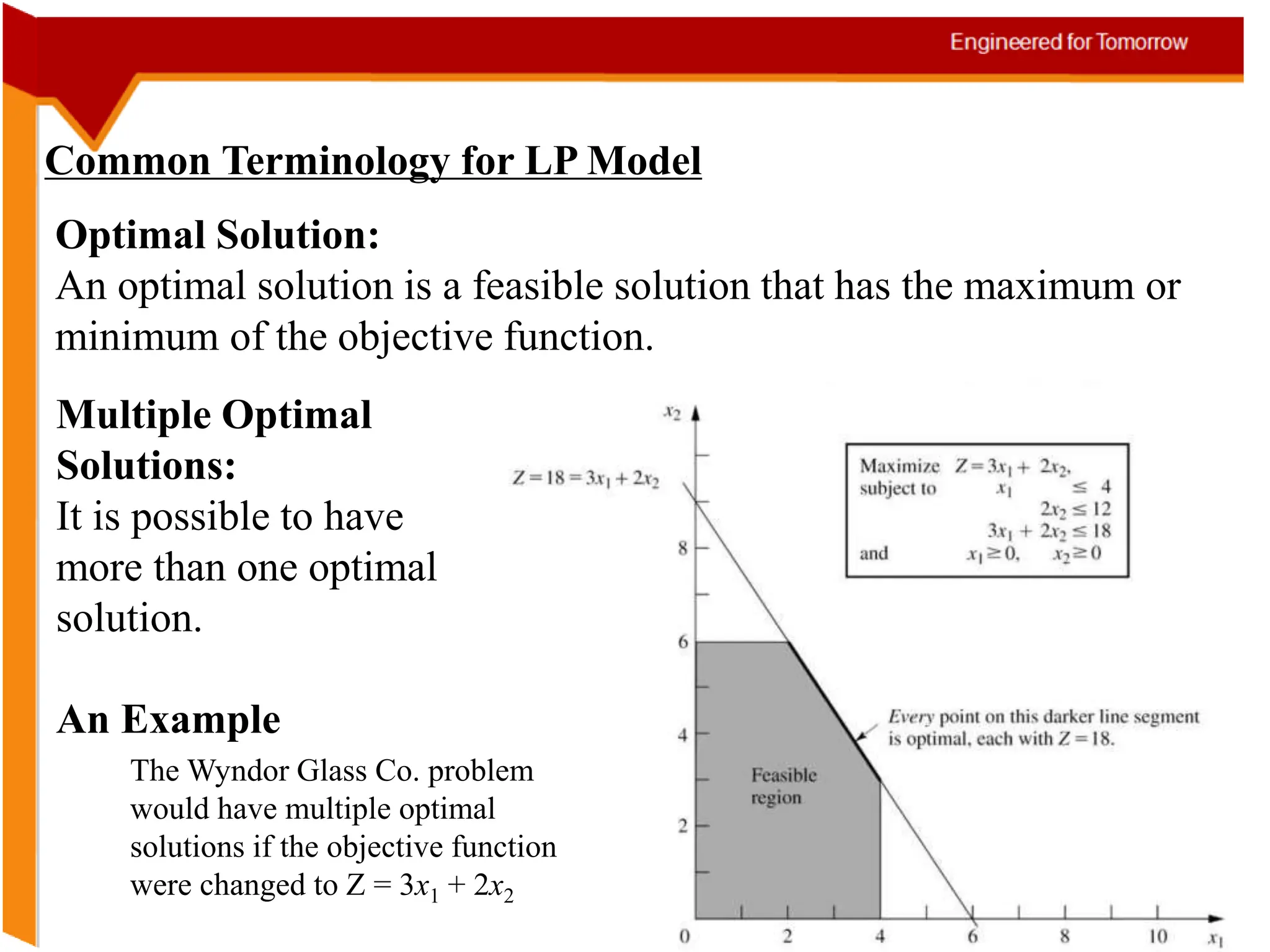
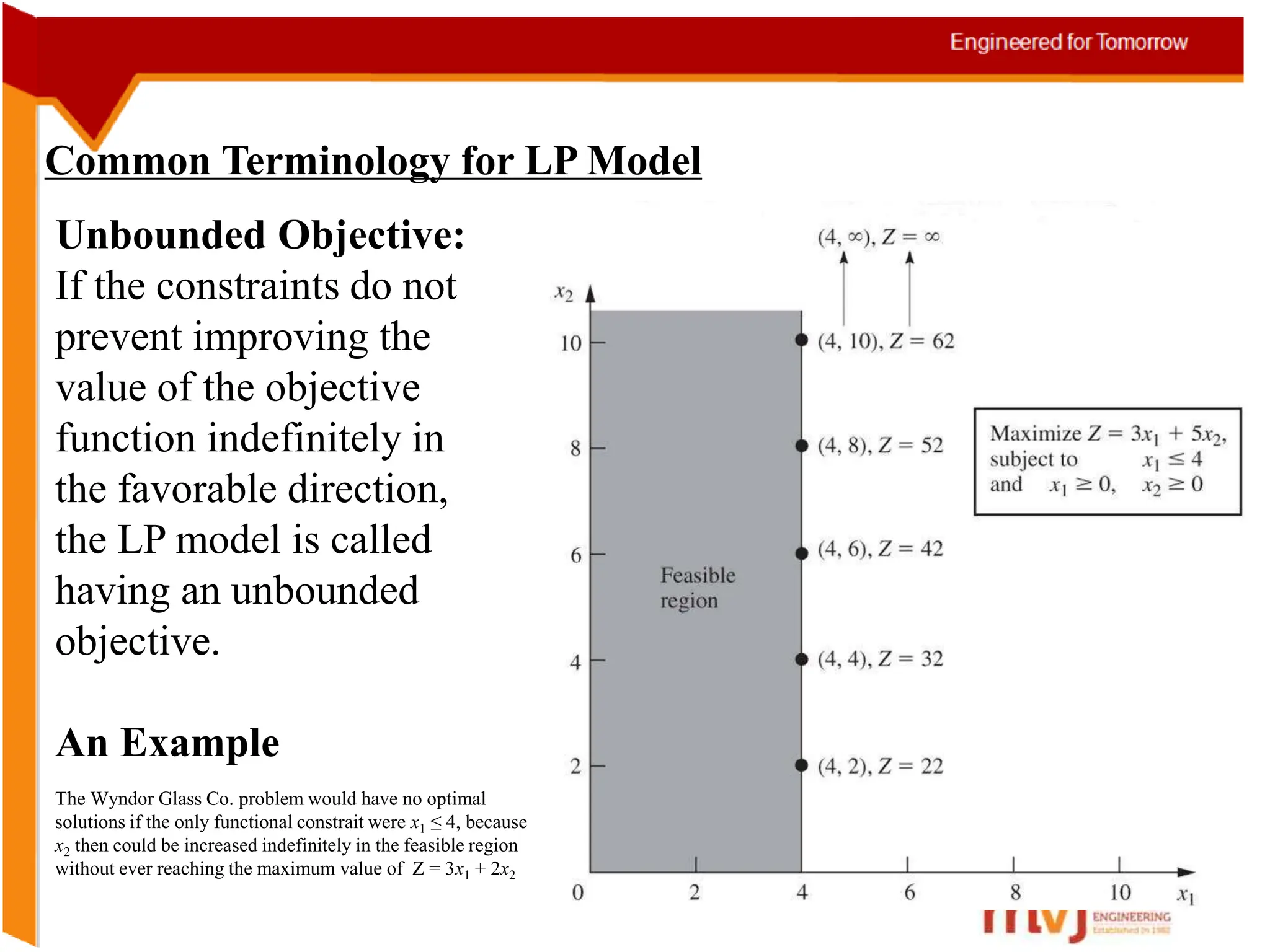
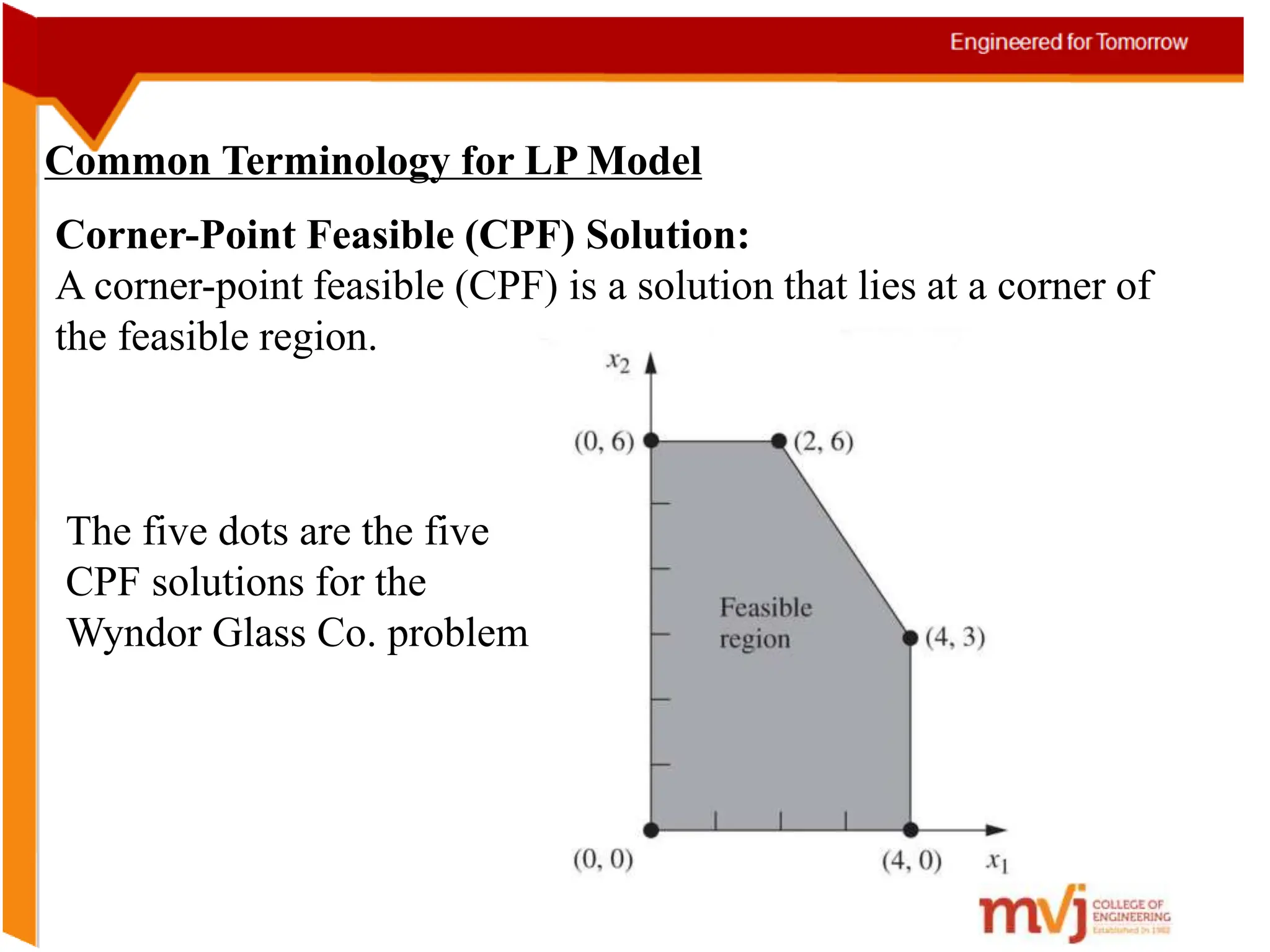
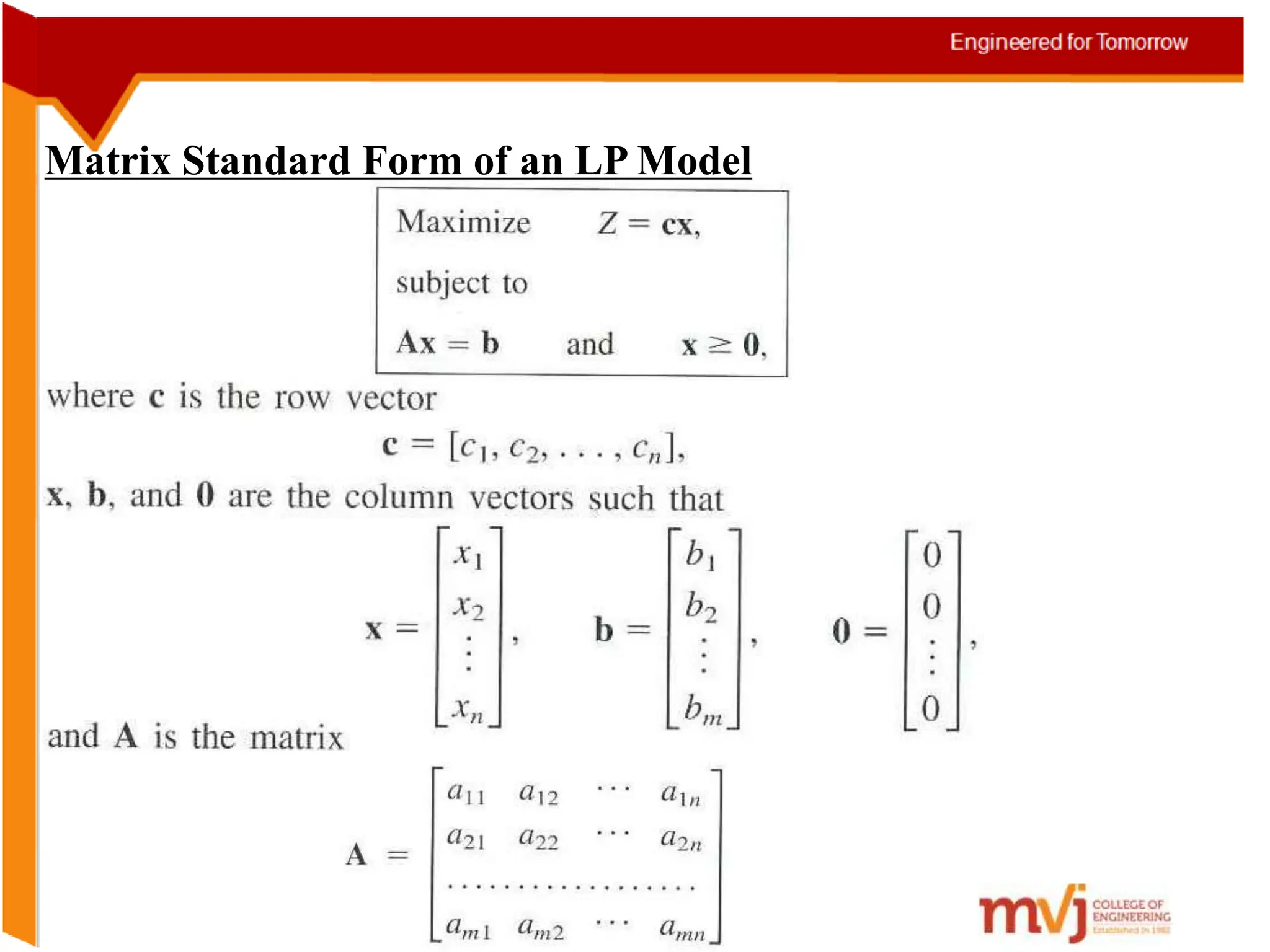
The document provides information about an Operations Research course. It includes the objective of the course, which is to develop and analyze mathematical models for decision problems and their systematic solution. It also lists the various topics that will be covered in the course, including linear programming, transportation problems, game theory, and metaheuristics. The course aims to help students identify and solve real-world business problems by applying appropriate operations research techniques.