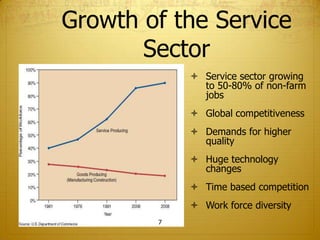
This document discusses operational success in organizations and provides information about improving products, services, and both simultaneously. It also covers the historical development of operations management, how operations management works in practice and across organizations, and key aspects of today's operations management environment.