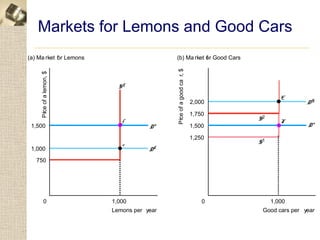
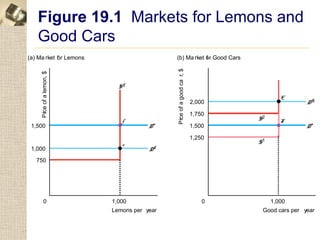
The document discusses asymmetric information in markets and how it can lead to inefficient outcomes. It provides examples of "lemons markets" where buyers cannot distinguish high-quality from low-quality goods. This can cause high-quality goods to be driven from the market if sellers cannot signal quality. The document also discusses how limited price information for consumers can give firms market power to charge above competitive prices, similar to a tourist trap model. Overall it analyzes how asymmetric information between buyers and sellers can disrupt efficient market outcomes.