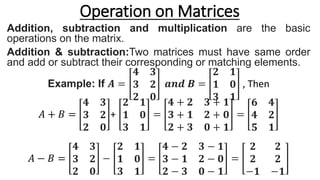
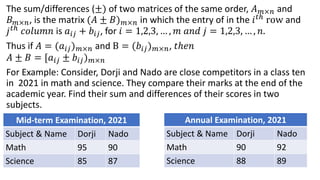
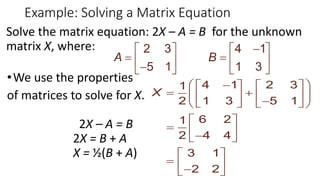1. Addition and subtraction are basic matrix operations where corresponding elements are added or subtracted if the matrices have the same order.
2. Matrix multiplication is also a basic operation on matrices.
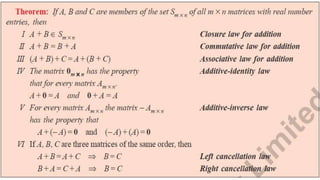
3. For matrix addition and subtraction to be defined, the matrices must have the same number of rows and columns. For matrix multiplication to be defined, the number of columns of the first matrix must be equal to the number of rows of the second matrix.