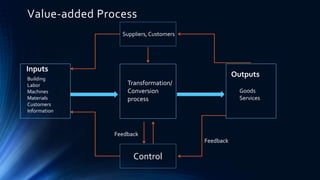
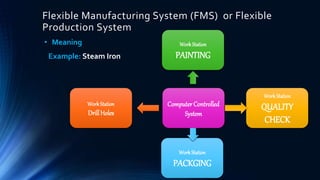
This document discusses operations management. It defines operations management as keeping the lights on in an organization, with strategy providing direction and management driving progress. It then outlines several key functions of operations management like forecasting, capacity planning, scheduling, inventory management and quality control. It provides examples of operations management at companies like Nestle, discussing topics like inventory management, production capacity, and the supply chain for transporting milk. Finally, it discusses the roles and responsibilities of production managers in selecting products and processes, planning and controlling production and quality.