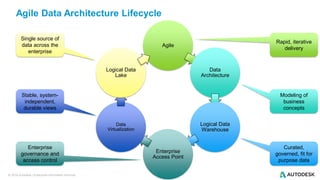
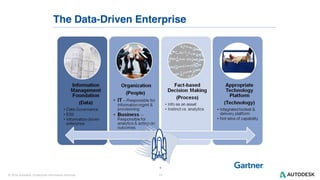
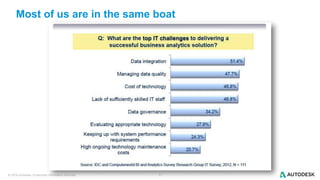
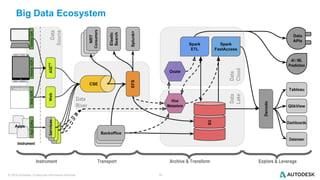
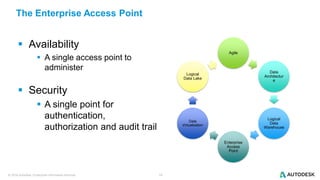
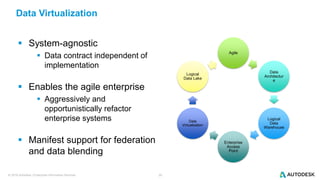
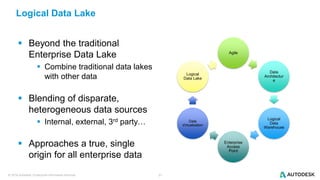
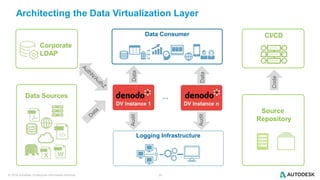
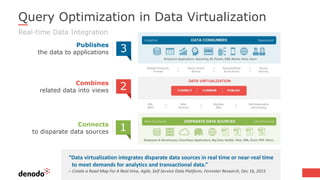
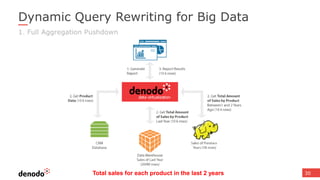
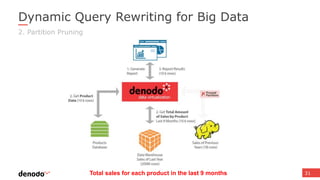
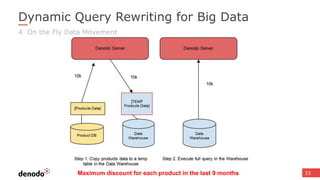
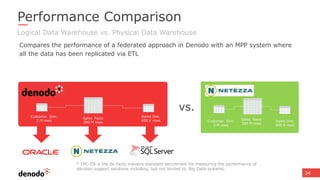
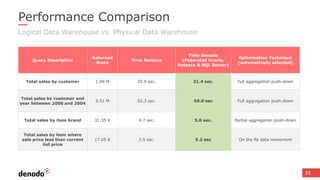
The document discusses the design and implementation of a logical data lake architecture at Autodesk, emphasizing the integration of various data sources for improved decision-making and cost reduction. It highlights the differences between a logical data warehouse and a data lake, focusing on virtualization and agile data architecture principles. Additionally, the document addresses performance considerations and optimization techniques for managing big data systems effectively.