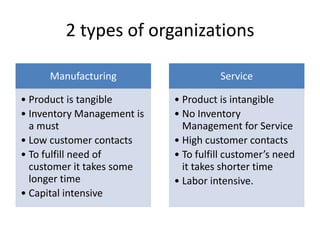
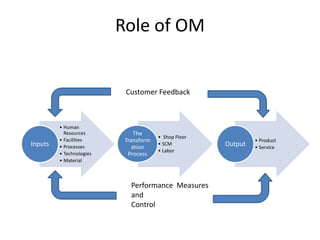
The document discusses key topics in operations management, including the roles and functions of operations managers, historical developments in the field, characteristics of manufacturing and service operations, and current issues facing operations management such as globalization, technology, the environment, and supply chain management. It provides definitions and descriptions of operations management, production systems, and the various departments involved in managing business operations from a strategic to tactical level.


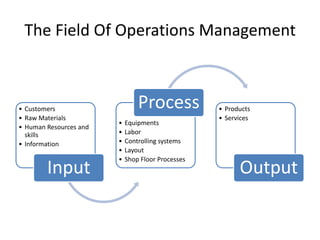

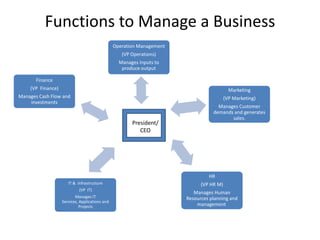
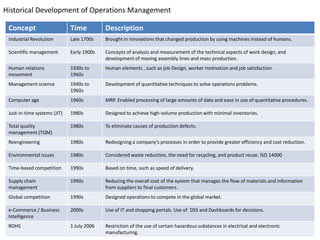
![Various departments in Operations Management
[Assignment 1- Try to answer and fill the column to help your favorite co.]
General Decisions to be made Decisions specific to product or service Department
What are the unique features of the Operations strategy
Decision
Strategic
business that will make it competitive?
What are the unique features of the Product design
product?
What are the unique features of the Process selection
process that give the product its
unique characteristics?
What sources of supply should we use Supply chain
to ensure regular and timely receipt of managements
the exact materials we need? How do
we manage these sources of supply?
How will managers ensure the quality Quality management
of the product, measure quality, and
identify quality problems?
What is the expected demand for the Forecasting
product?
Where will the facility be located? Location analysis
How large should the facility be? Capacity planning
How should the facility be laid out? Facility layout
What are the different jobs and how and Job design and work
who can do those tasks and measure the measurement
performance
Decision
Tactical
When will orders be Inventory
placed and how much will be kept in management
stock?
Who will work on what schedule? Scheduling](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/om001-120609112230-phpapp01/85/Om001-8-320.jpg)