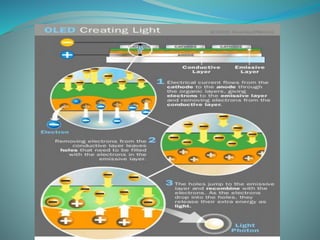
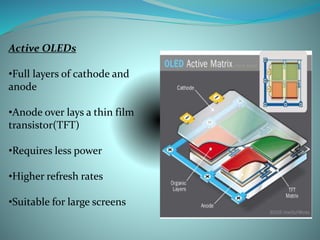
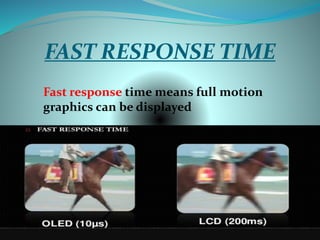
OLEDs emit light when electricity is applied to a film of organic material. They have faster response times than LEDs and can be made transparent or flexible. An OLED is made of an emissive organic layer sandwiched between a cathode and anode. When voltage is applied, electrons from the cathode combine with holes from the anode in the emissive layer, emitting light. OLEDs are being used in TVs, phones, and other devices but have shorter lifetimes than LEDs, especially for blue colors.