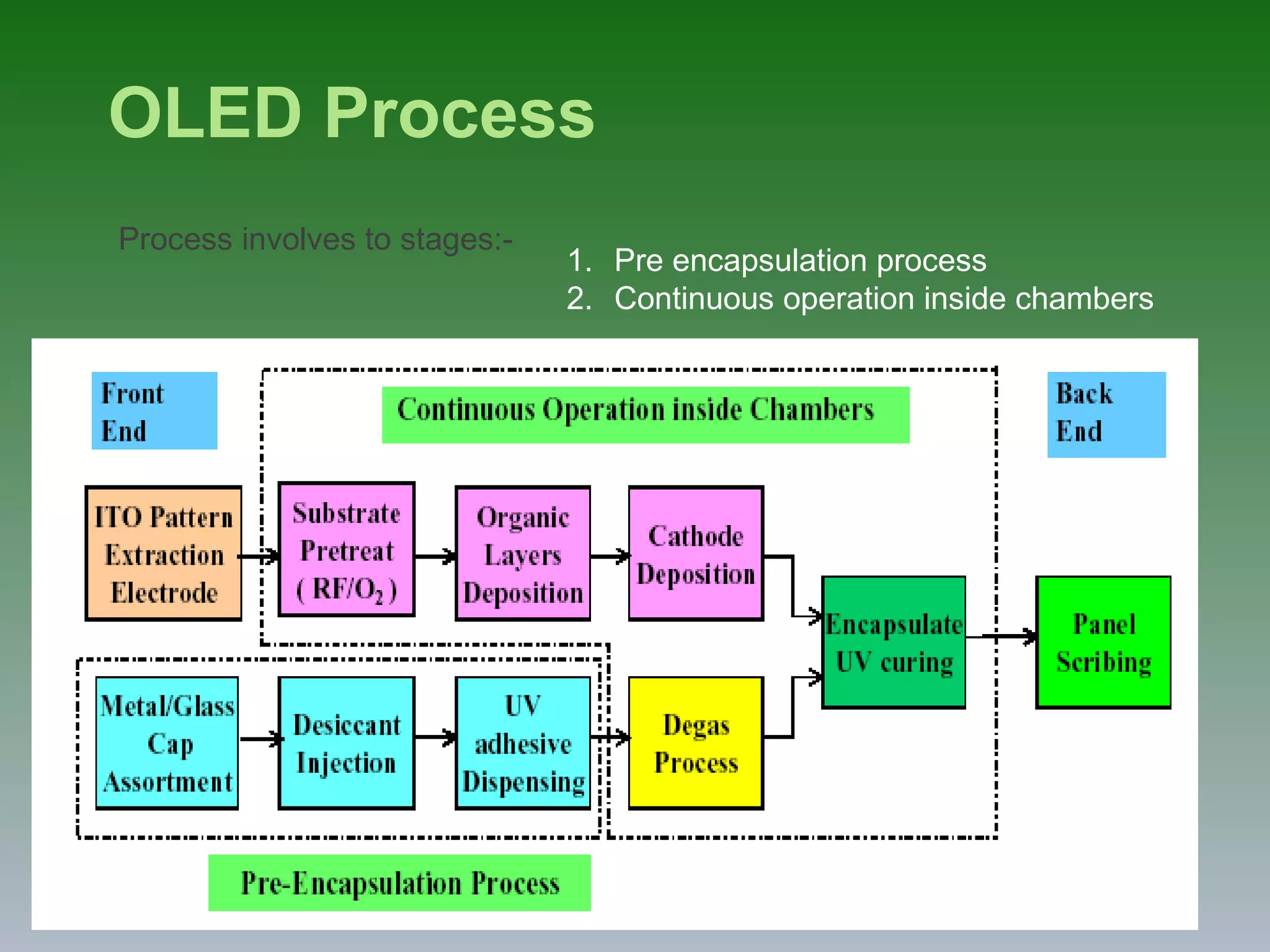
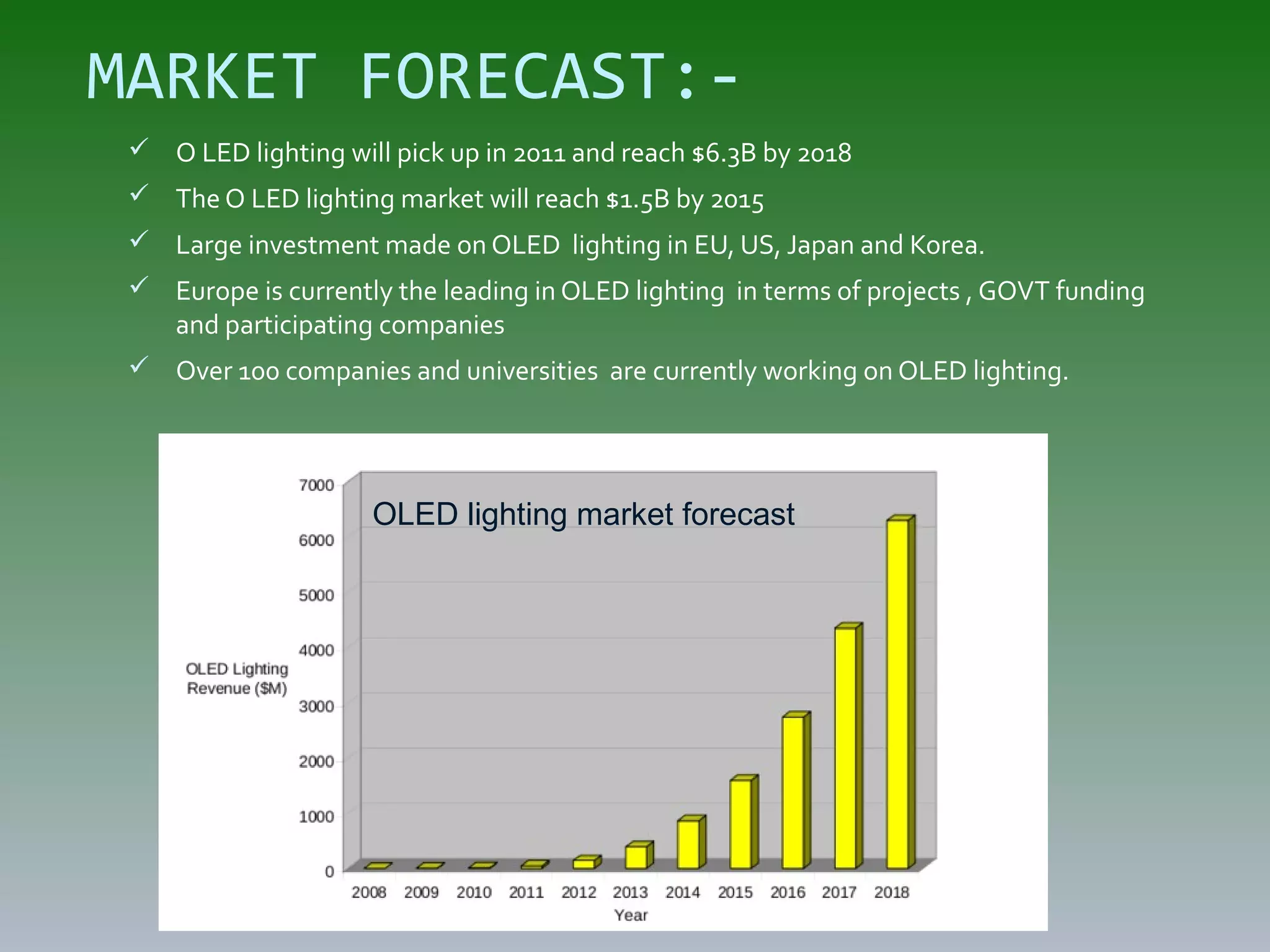
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) is a light emitting technology that uses organic compounds between electrodes to emit light in response to an electric current. OLEDs are used in digital displays and do not require backlighting. There are different types of OLEDs including passive matrix OLEDs, active matrix OLEDs, and transparent OLEDs. OLEDs have advantages over LCDs like being thinner, more flexible, and having higher contrast ratios and wider viewing angles. However, OLEDs also have disadvantages like shorter lifetimes, higher costs, and material stability issues that are being addressed through ongoing research and development.