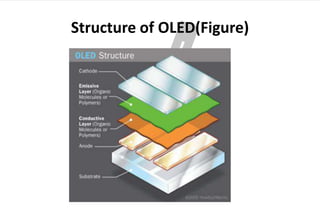
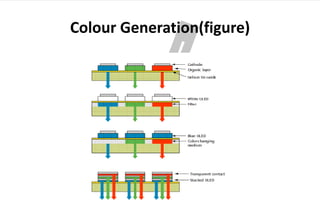
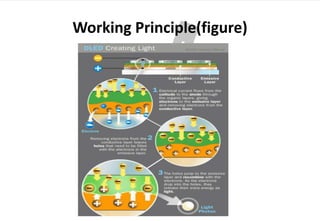
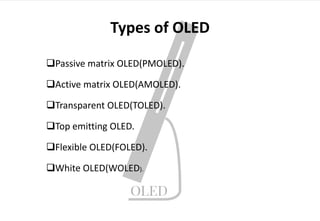
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) is an emerging display technology that uses thin films of organic molecules to emit light when electricity is applied. Key advantages of OLEDs include thinner/lighter/more flexible displays without needing a backlight, as well as higher contrast ratios, brighter colors, and wider viewing angles. The first OLED device was developed in 1987, and now many companies are developing various OLED displays for applications like phones, TVs, and more. The basic structure of an OLED involves organic layers sandwiched between an anode and cathode, and different layer deposition and pixel approaches can generate red, green, and blue colors or white light.