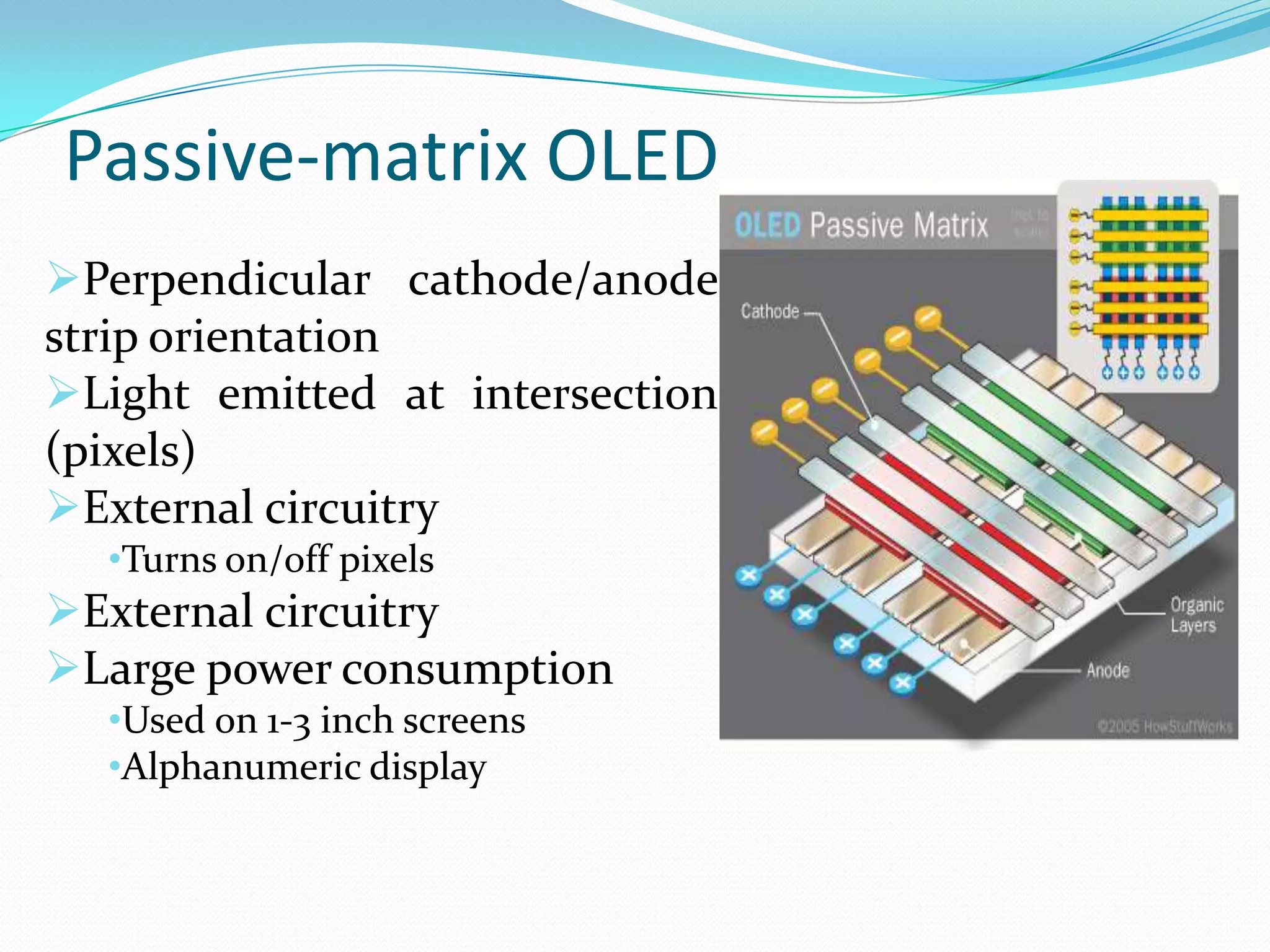
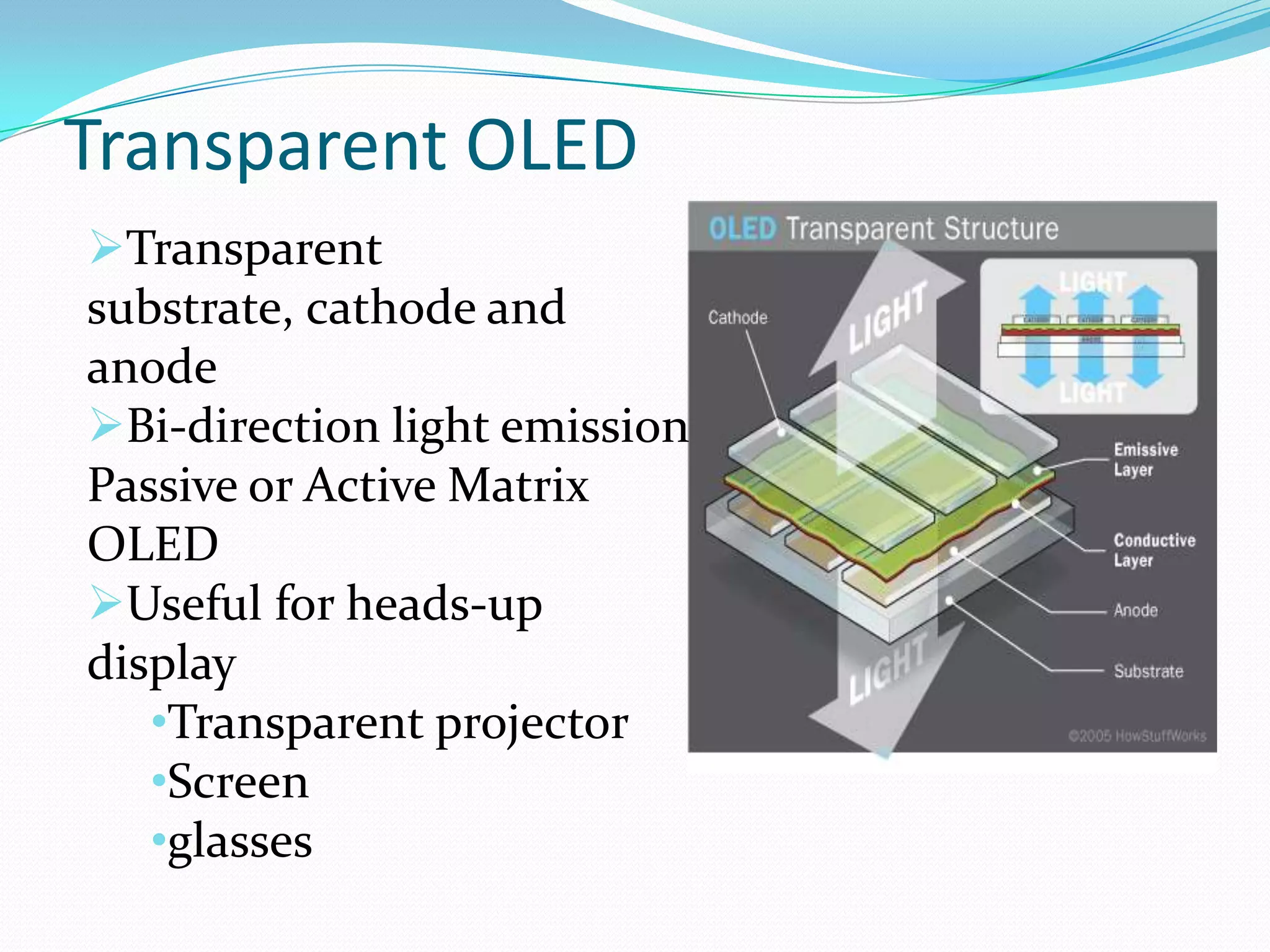
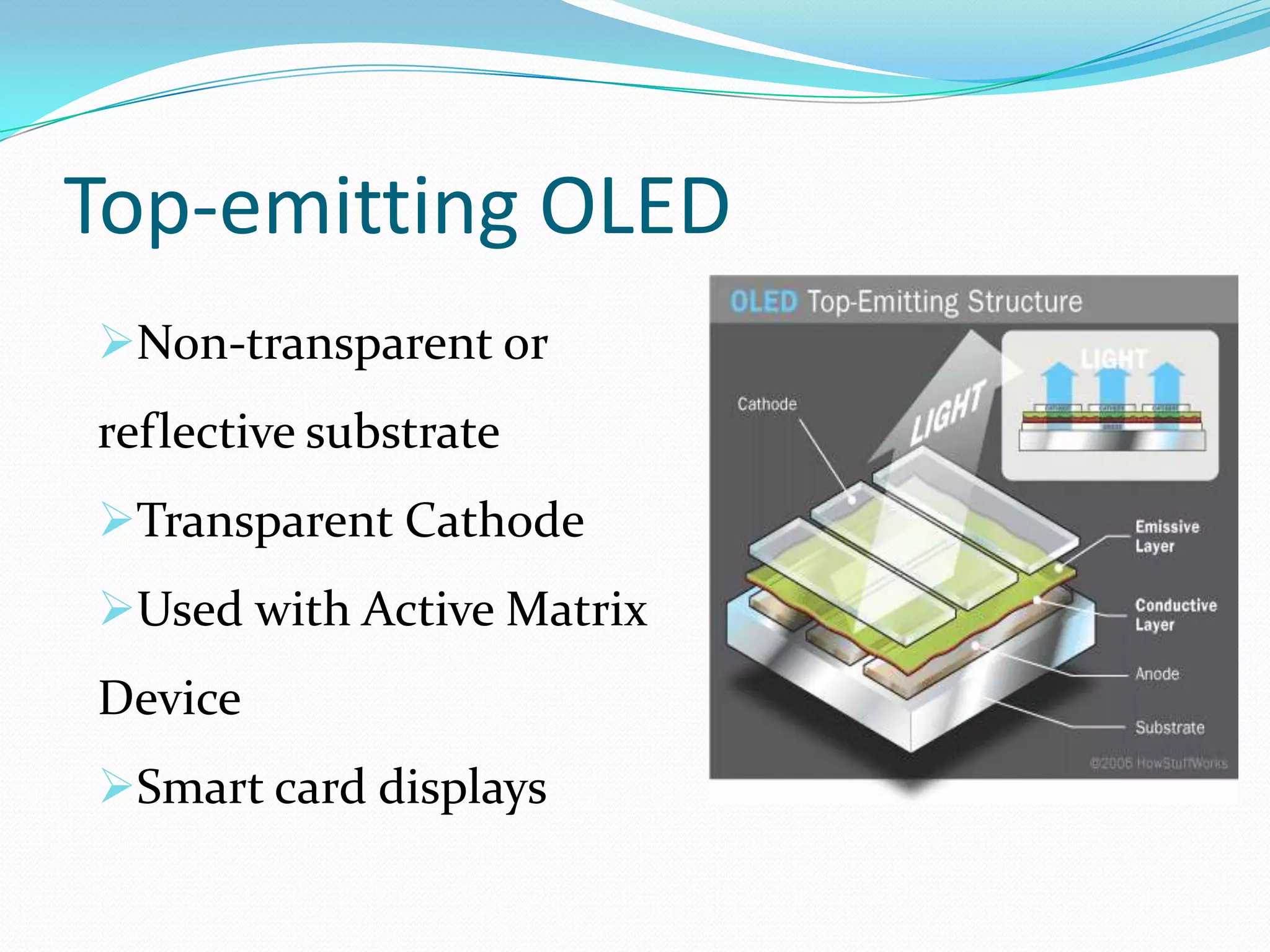
This document summarizes key aspects of OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) technology. OLEDs were first created in 1987 and have several advantages over other display technologies like LCDs, including faster response times, lower energy consumption, thinner displays, and wider viewing angles. The document describes the architecture of OLEDs including organic layers, substrates, and electrodes. It also discusses different types like passive matrix, active matrix, transparent, and foldable OLEDs. Current research is focused on improving efficiency and reducing manufacturing costs. OLED applications include TVs, phones, lighting, and future uses may include flexible and transparent displays.