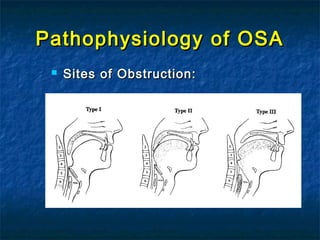
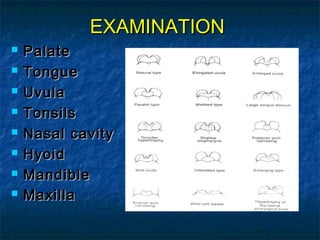
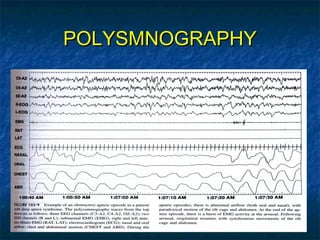
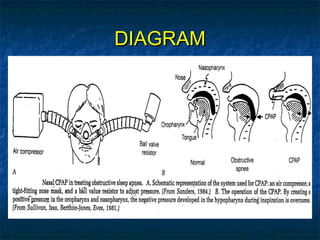
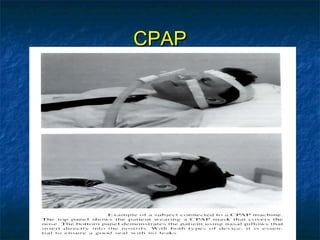
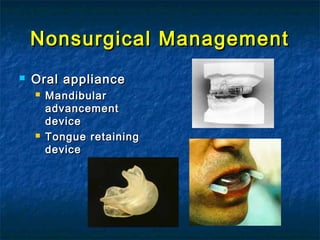
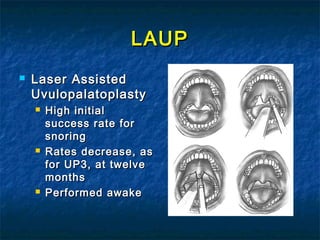
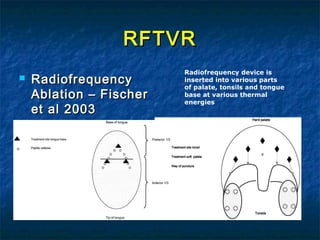
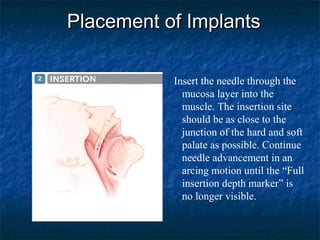
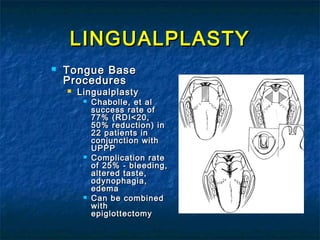
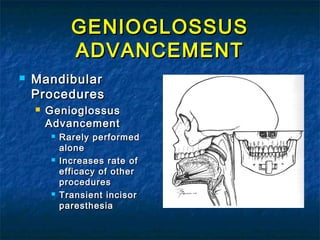
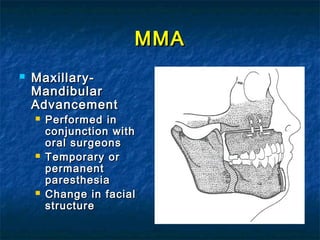
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder where the airway collapses or becomes blocked during sleep, disrupting breathing. Polysomnography is the gold standard test used to diagnose OSA by measuring breathing, oxygen levels, and brain waves during sleep. The main treatment is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, which uses mild air pressure to keep the airway open during sleep. Weight loss, avoiding alcohol, and sleeping on one's side can also help reduce OSA symptoms.