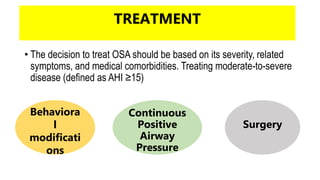
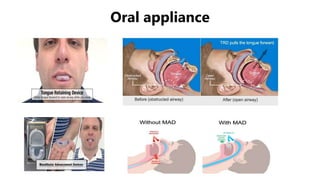
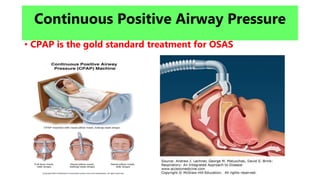
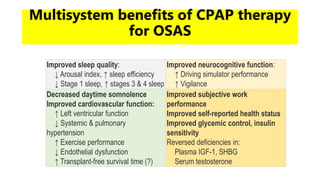
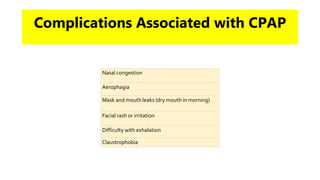
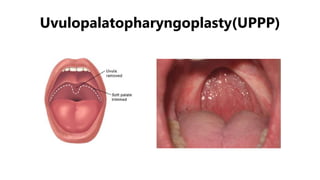
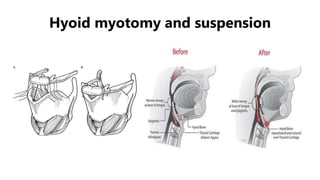
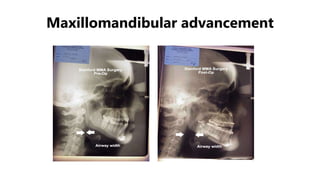
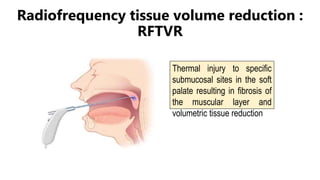
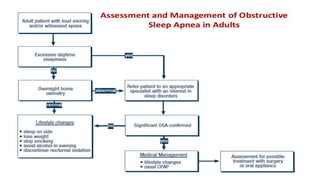
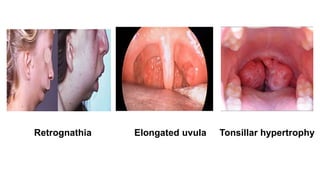
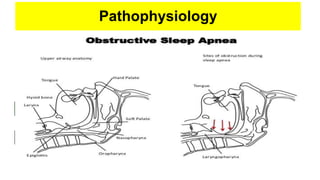
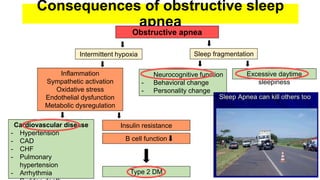
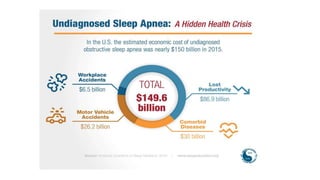
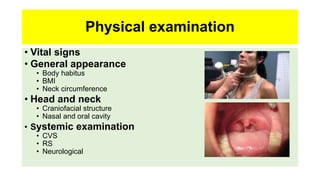
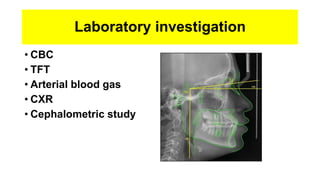
This document discusses obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It begins with a case study of a 67-year-old man presenting with snoring and daytime sleepiness. It then defines OSA and discusses its pathophysiology and risk factors. The approach to diagnosis involves taking a history, physical exam, and polysomnography. Treatment options include behavioral modifications, oral appliances, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), and various surgical procedures. CPAP is the gold standard treatment and can provide numerous health benefits by improving sleep quality and cardiovascular and metabolic outcomes.












![Polysomnography
LEVELS Parameters Measured
I [Standard attend in-lab PSG] EEG, EOG, EMG, ECG, airflow,
respiratory effort, O2 saturation, usually
video (all conducted in a sleep
laboratory with a sleep professional
present)
II [Comprehensive portable Minimum of seven channels including
EEG, EOG, chin EMG, ECG/HR,
respiratory effort, and O2 saturation
III [Modified portable sleep
apnea testing]
Minimum of four channels including
ECG/HR, O2 saturation and at least
The American Academy of Sleep medicine [AASM] has defined four levels of sleep studies.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osasyndrome-180908143051/85/Obstructive-sleep-apnea-20-320.jpg)
![Standard attended PSG
o Total sleep time
o Sleep efficiency
o Sleep stage
percentage
o Sleep latency
o Arousals
o Apnea
o Hypopnea
o Respiratory effort
related
arousal[RERA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osasyndrome-180908143051/85/Obstructive-sleep-apnea-21-320.jpg)