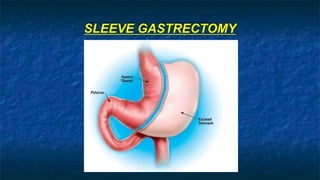
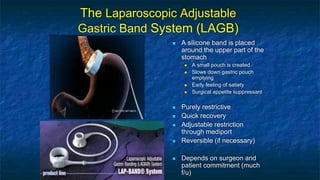
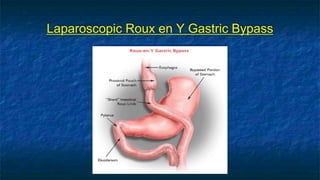
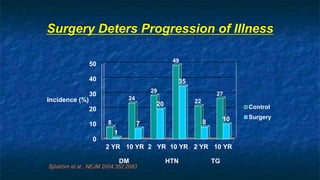
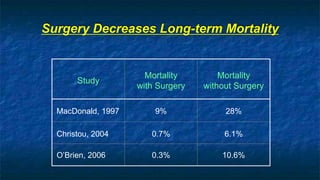
The document discusses obesity and its relationship to renal failure. It defines obesity based on Body Mass Index (BMI) and describes its various degrees. Obesity is linked to numerous medical implications including hypertension, diabetes, respiratory issues, and renal failure. Obese individuals often experience structural, hemodynamic and metabolic changes to the kidneys over time. These changes can eventually lead to renal failure if not addressed. The document also discusses bariatric surgery options for weight loss such as gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy, and gastric bypass, and how they work to restrict food intake and digestion to help control obesity-related conditions and reduce mortality risks over time.




![ Obesity is a U.S. public health epidemic:
64% Americans overweight
30% Americans obese
10% morbidly obese
400,000 deaths /year from obesity related causes
[90,000 deaths/yr from colon + breast ca]
#2 cause of preventable deaths
#1 is smoking
PAKISTAN ---- # 9 in World Obesity Index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obesityrf-180403162822/85/Obesity-Renal-Failure-6-320.jpg)