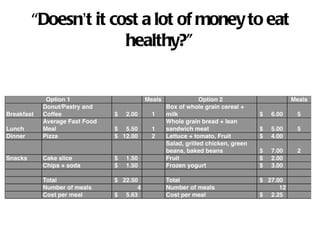
The document discusses obesity, its definitions, prevalence, and health consequences, emphasizing the importance of nutrition, exercise, and sleep hygiene for weight management. It outlines practical tips for a healthier lifestyle, including calorie intake, dietary changes, and exercise routines. The document also stresses the need for commitment and consistency in pursuing health goals, while encouraging a spiritually motivated approach to wellness.