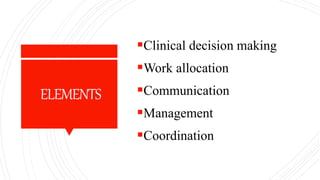
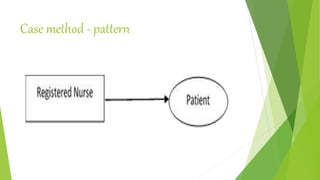
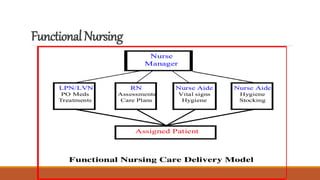
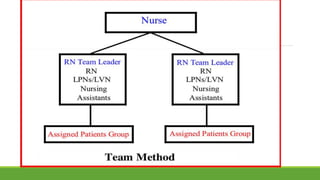
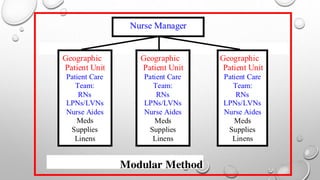
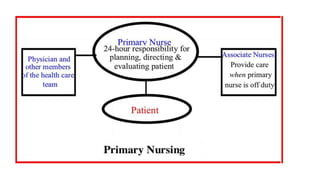
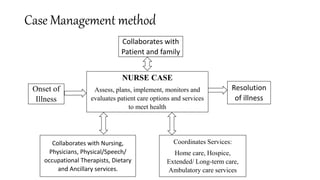
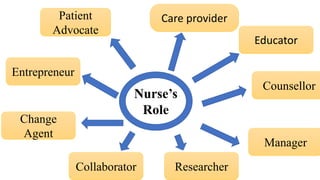
The document discusses various patterns of nursing care delivery systems used in India. It defines nursing care delivery as combining nursing services to meet patient needs across care settings. The key elements include clinical decision making, work allocation, communication, and management. Traditional methods like case method, functional method, and team method are explained along with their advantages and disadvantages. Advanced methods like case management, critical pathways, and primary nursing are also summarized. Factors influencing nursing care delivery systems are organizational policies, staffing, education, budgets, and patient needs.