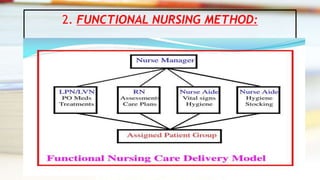
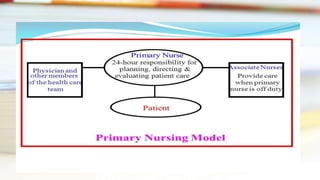
This document discusses different methods of assigning nursing staff to provide patient care, including case method nursing, functional nursing, team nursing, primary nursing, and progressive patient care. Each method is described in terms of how nursing duties are organized and divided among staff. The advantages and disadvantages of each approach are also outlined.