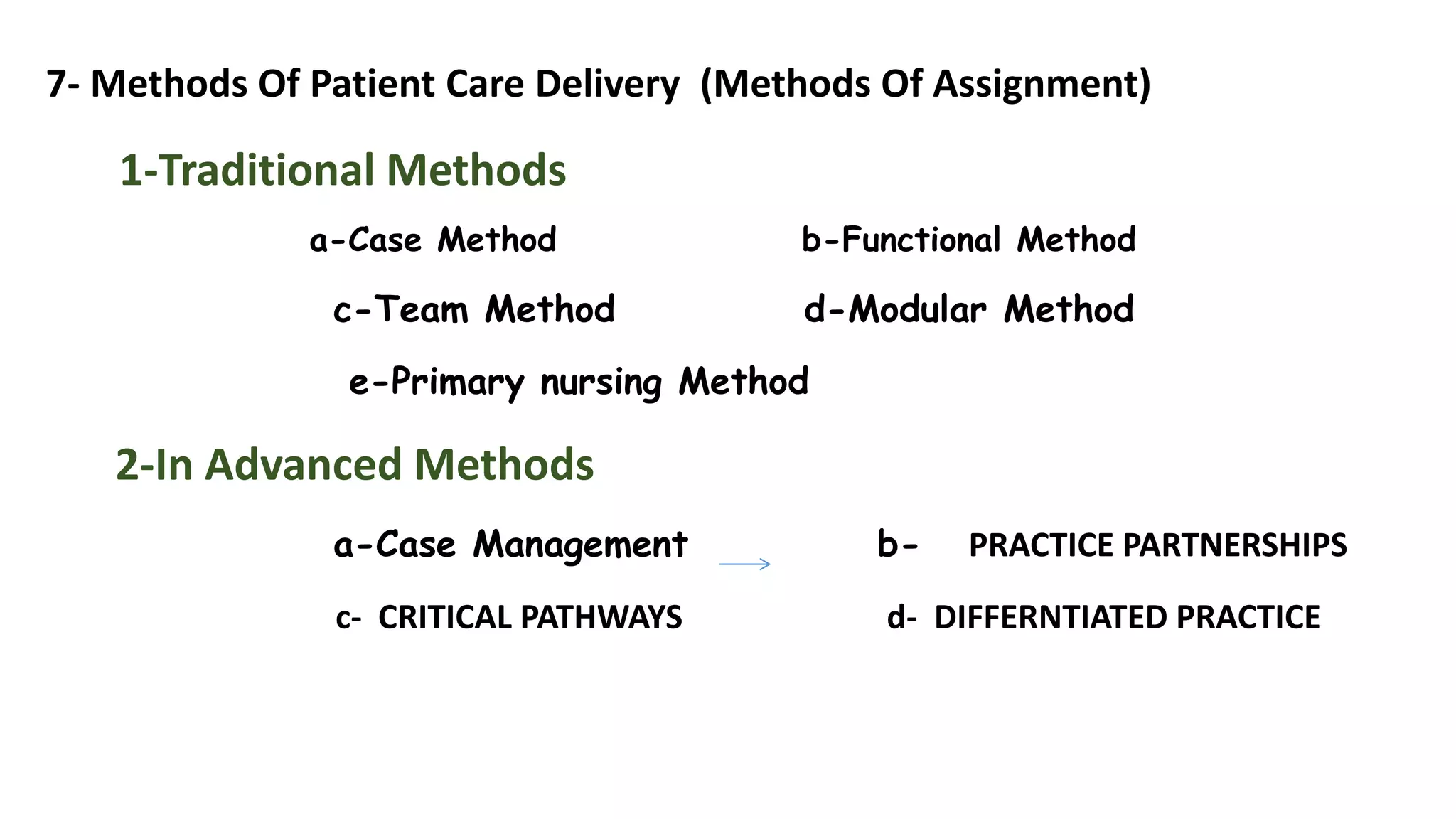
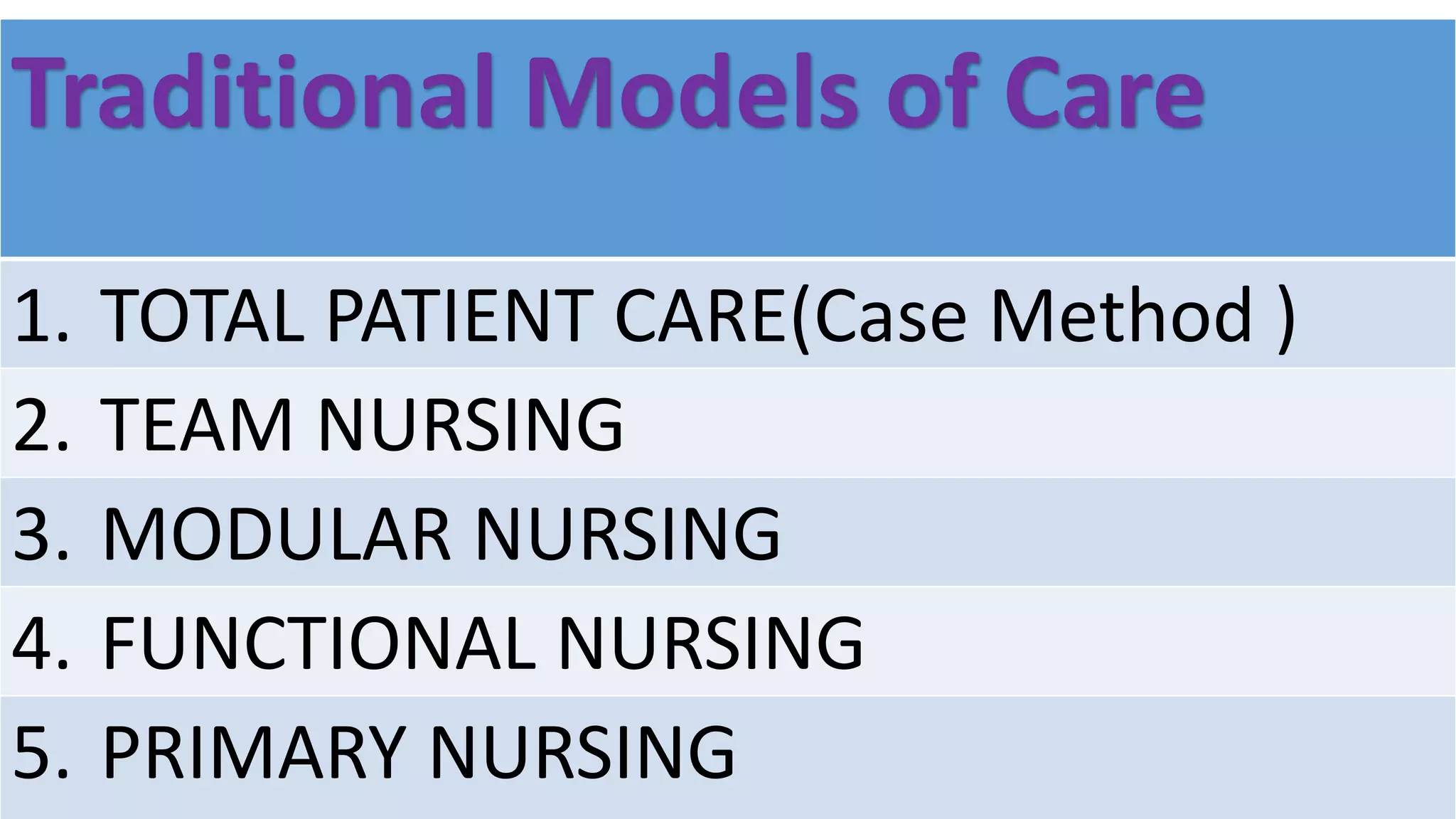
The document outlines different methods for organizing patient care delivery, including traditional methods like total patient care, functional nursing, team nursing, modular nursing, and primary nursing. It also discusses more advanced integrated models like case management, practice partnerships, critical pathways, and differentiated practice. The goal is to define these methods, compare their advantages and disadvantages, and provide guidance on selecting the most appropriate model based on organizational goals and patient population.