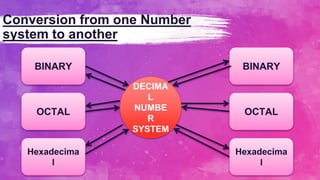
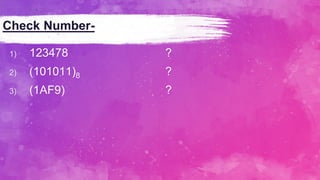This document discusses different number systems used in computers, including positional and non-positional systems. It describes the binary, decimal, octal, and hexadecimal positional number systems, explaining that each has a base and allowable digits. Converting between number systems involves determining the positional value of each digit and multiplying/summing accordingly. Examples are provided for converting between binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal.