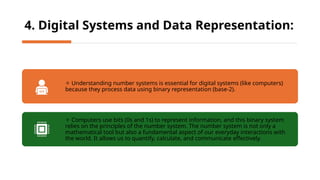
The document outlines computer number systems for grade 7, focusing on binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal systems, along with their conversions. It includes learning goals for students, detailing the significance of these systems in computing and practical applications. The text explains the characteristics and functions of each system, emphasizing the role of number systems in mathematics and digital data representation.