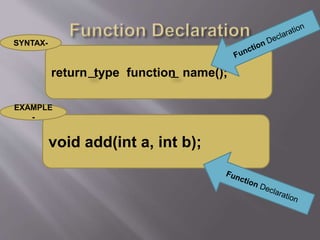
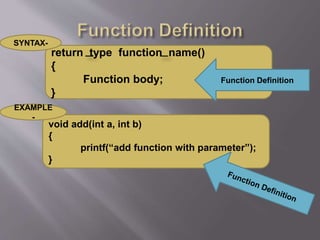
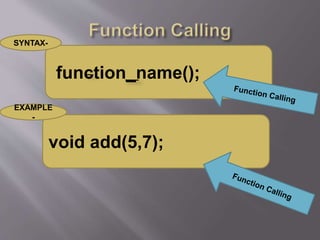
The document outlines the structure and components of a 'C' program, highlighting the role of functions, comments, and preprocessor directives. It discusses the importance of standard and console input/output header files, and provides examples of basic functions like printf() and scanf(). Additionally, it explains the use of local variables, library functions, and user-defined functions, as well as the character set used in 'C' programming.















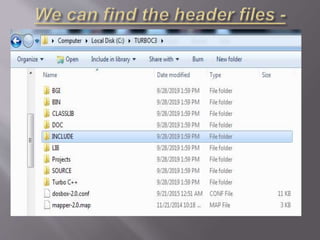
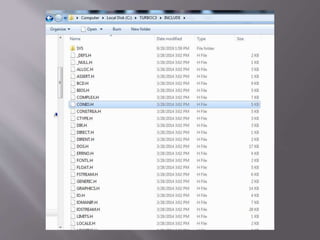
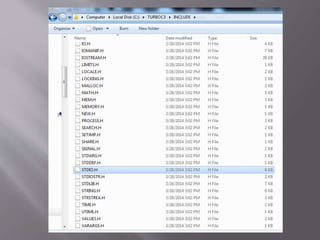








![Symbols Name Symbols Name Symbols Name
+ Plus ) Right
parenthesis
? Question
Mark
* Astrisk { Left curly
braces
& Ampersand
Backward slash } Right curly
braces
@ At the rate
/ Forward slash [ Left bracket $ Dollar sign
< Less than ] Right Bracket ` Tilde sign
> Greater than , Comma - Minus,
Hyphen
( Left parenthesis : Colon % Percentage
= Equal sign ; Semi-colon | Vertical bar
. Period ‘ ‘ Single
Quotes
^ Caveat sign
“ “ Double quotes ! Exclamation # Hash](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cstructure-200331105925/85/C-structure-30-320.jpg)
