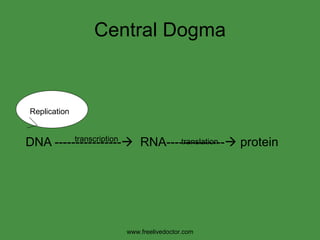
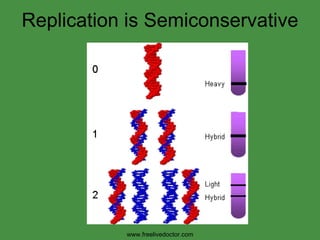
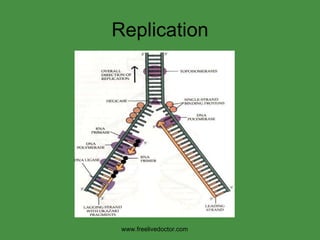
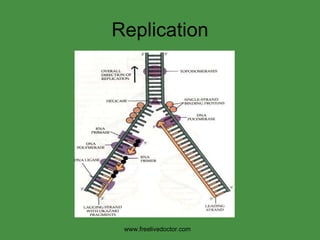
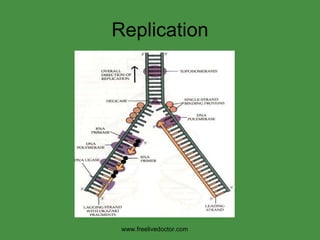
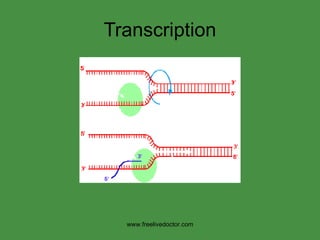
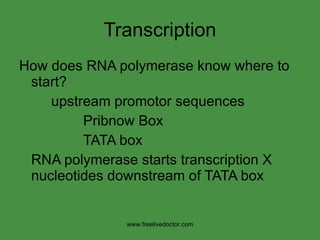
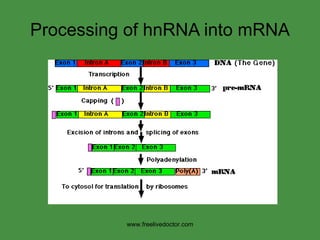
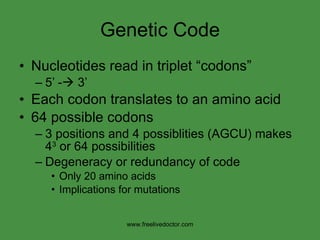
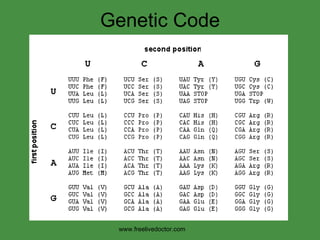
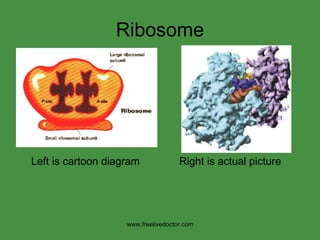
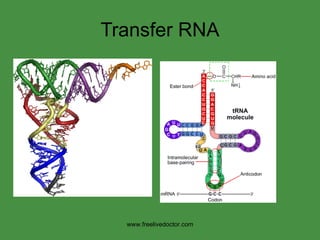
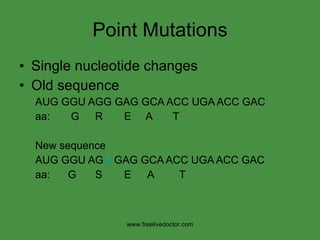
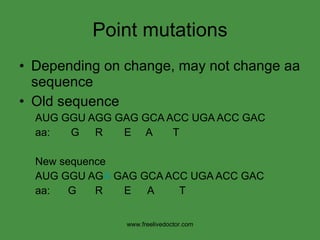
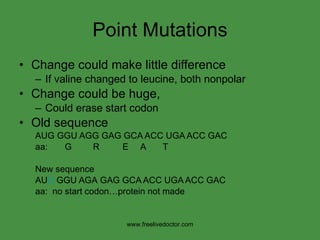
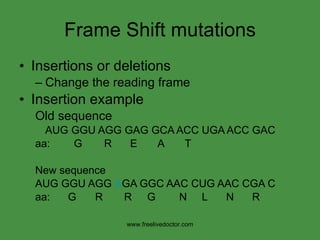
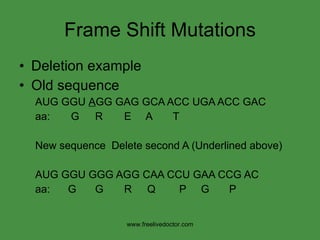
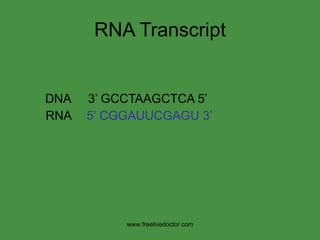
The document summarizes key concepts in nucleic acid chemistry and the central dogma of biology. It describes DNA replication as semiconservative, with each parental strand serving as a template for a new daughter strand. Transcription involves DNA being copied into RNA, and translation involves RNA being used to build proteins according to the genetic code. Mutations can occur through point mutations or frameshift mutations, sometimes resulting in changes to the amino acid sequence of proteins.