The document summarizes key concepts regarding nuclear forces and nuclear structure:
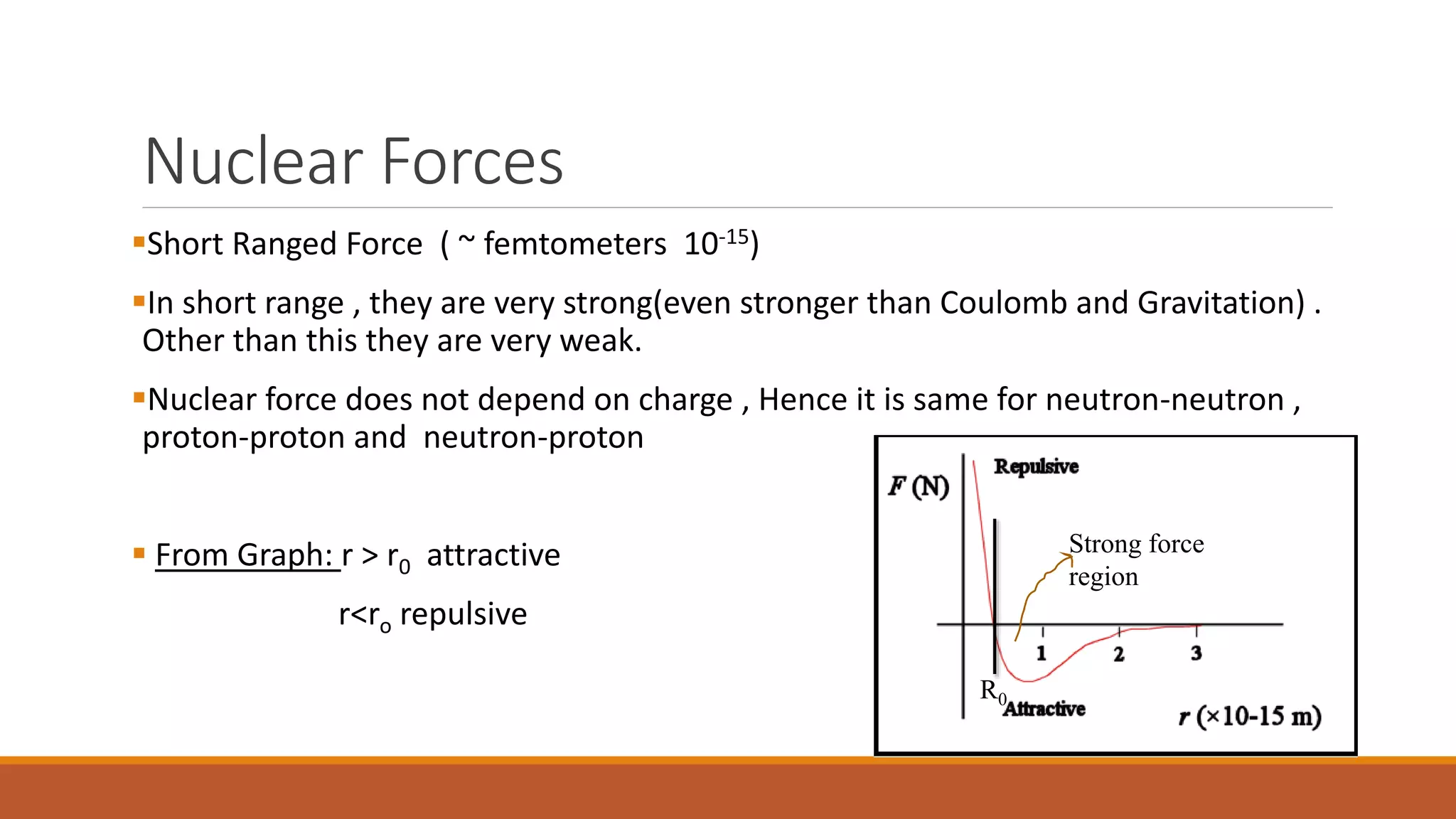
1) Nuclear forces are very strong over short ranges (~femtometers) and act independently of charge between nucleons. The force is attractive at longer ranges but repulsive at very short ranges.
2) Basic properties of nuclei include that atomic mass (A) equals protons + neutrons, atomic number (Z) equals protons, and nuclear density is constant regardless of mass number.
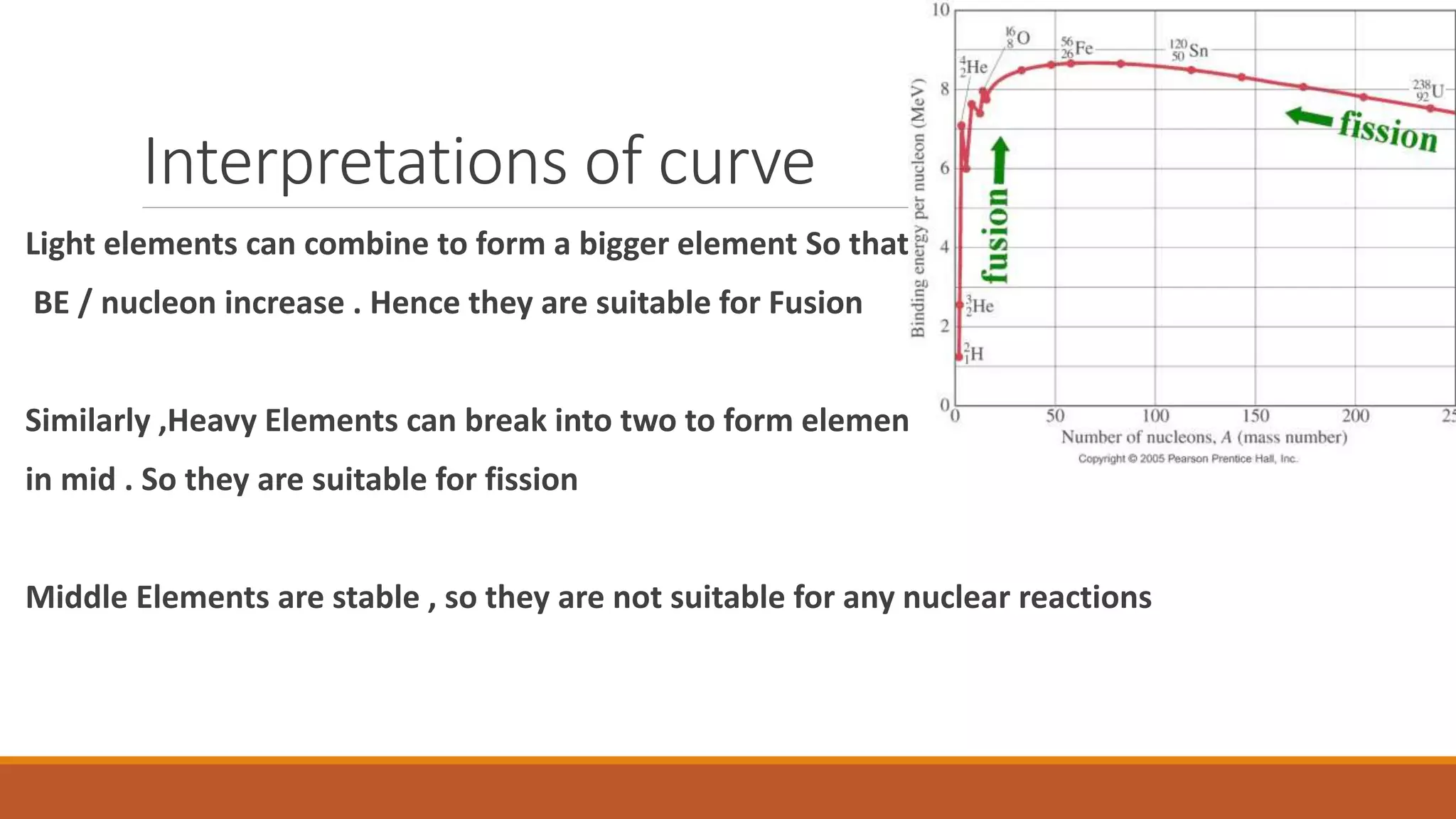
3) Binding energy explains nuclear stability - breaking nuclei requires energy equal to the binding energy per nucleon, which is highest for mid-sized nuclei like iron.
4) Radioactive decay processes like alpha, beta, and gamma decay occur to reach