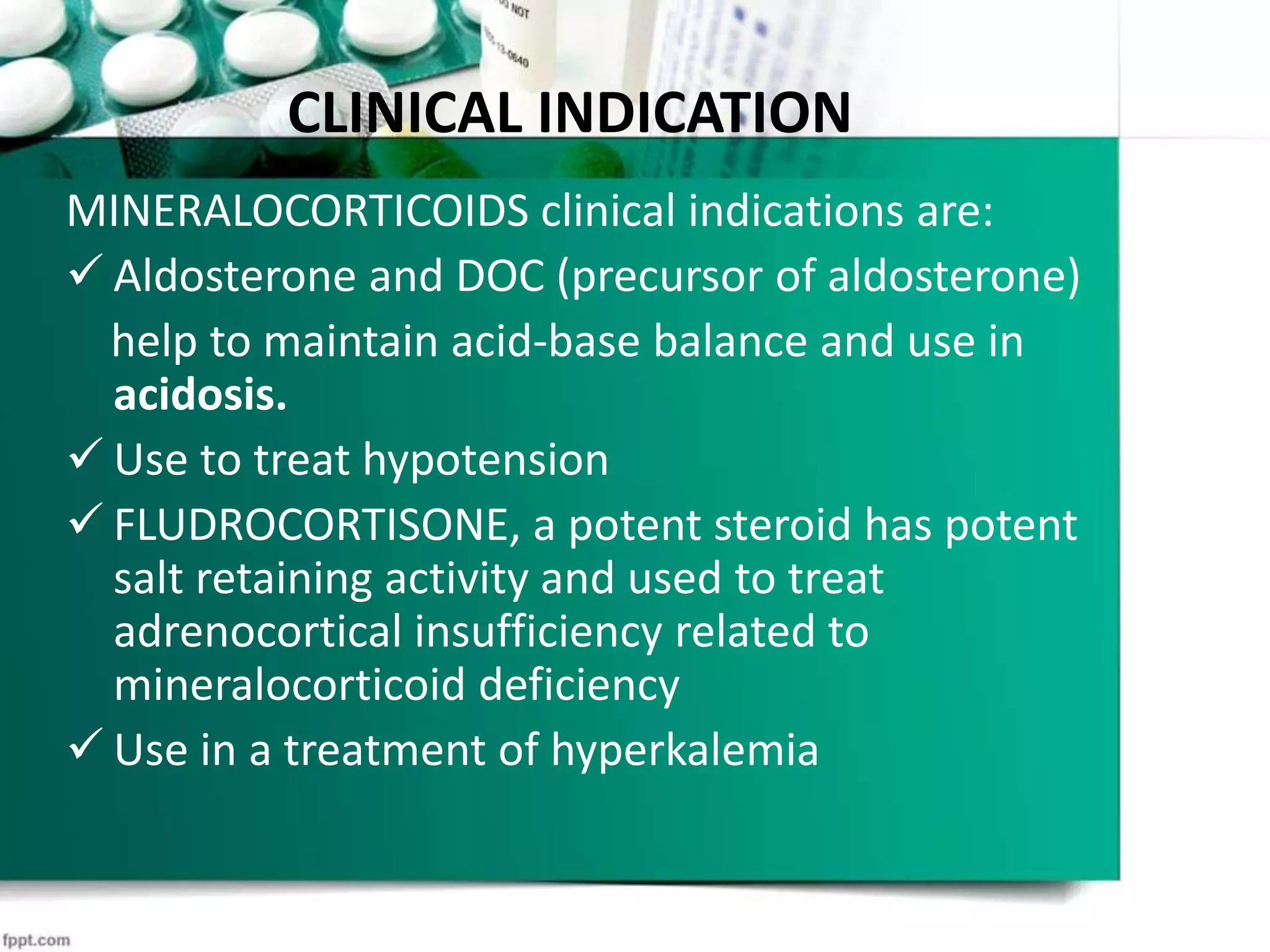
1. Mineralocorticoids such as aldosterone act on minerals like sodium and potassium, regulating their levels in the body.
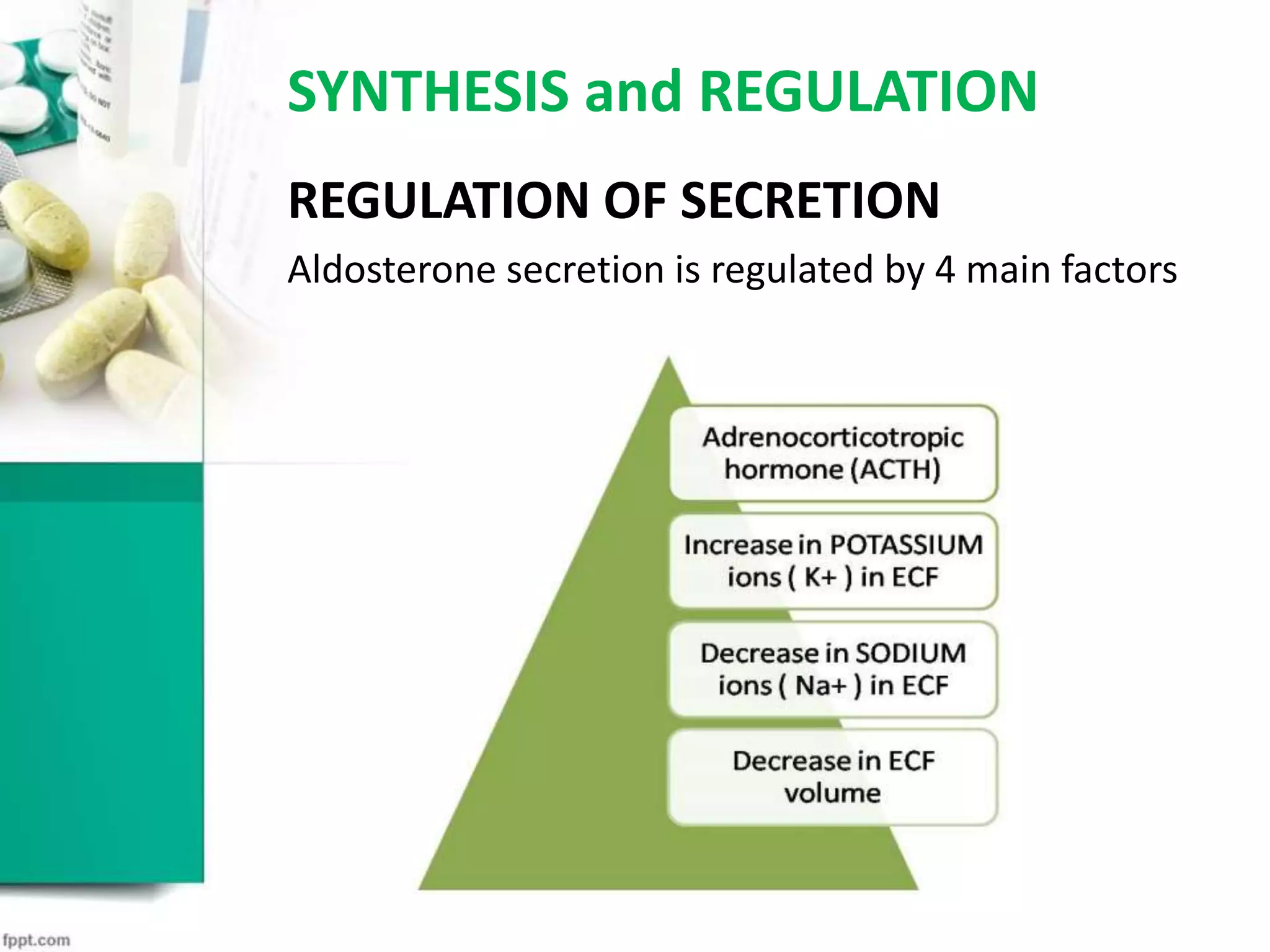
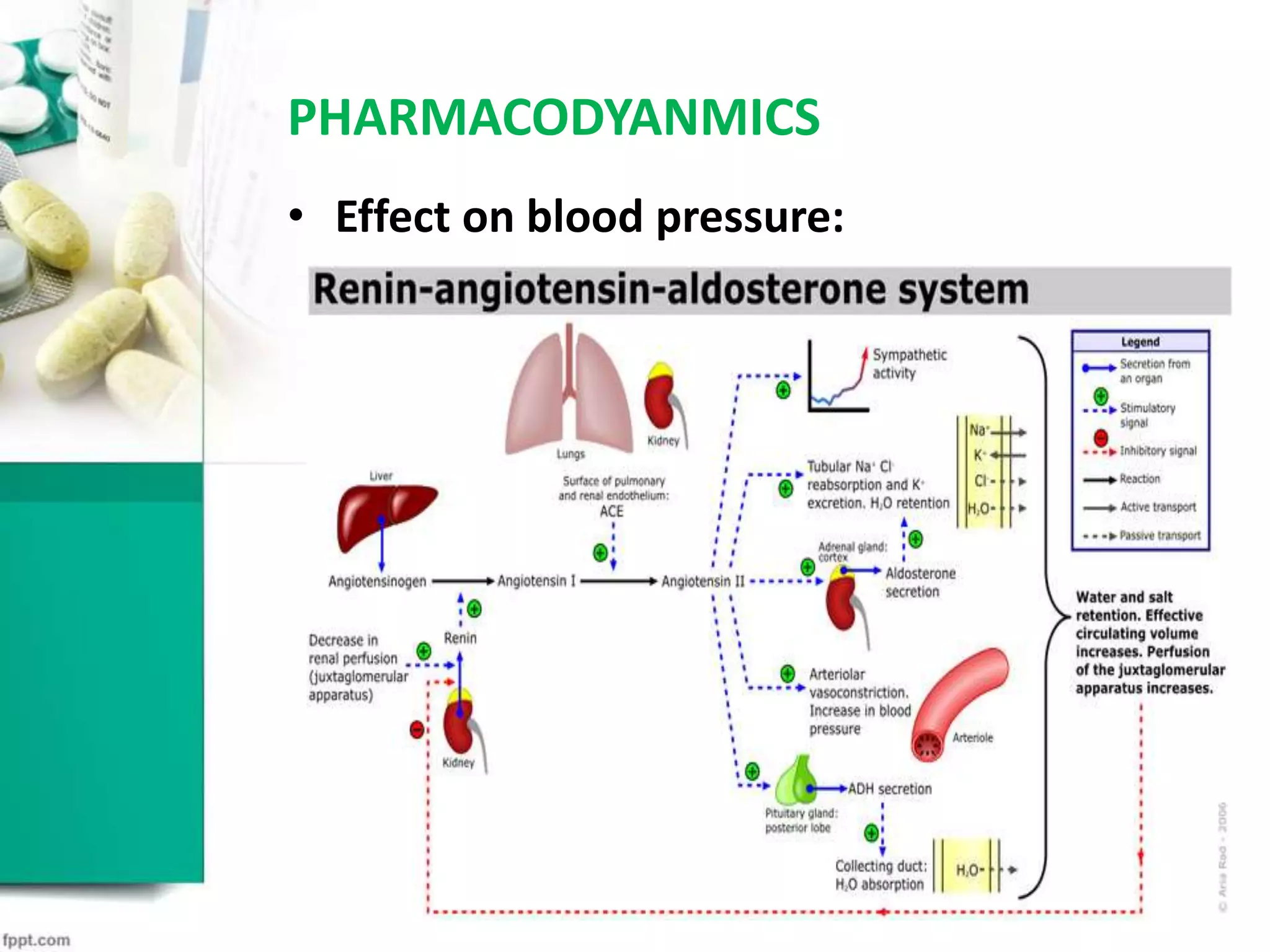
2. Aldosterone is synthesized in and released from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, regulated by factors like angiotensin.
3. It increases sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion, maintaining fluid volume and blood pressure levels. Imbalances can cause issues like hypokalemia or hypertension.