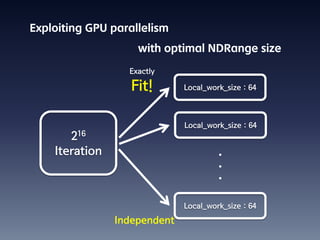
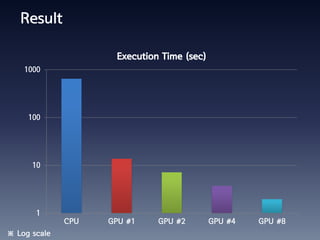
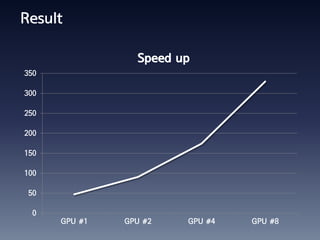
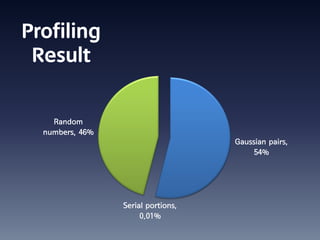
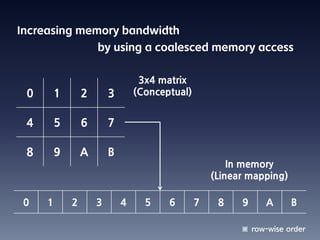
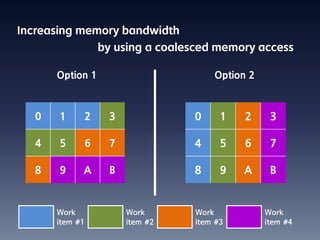
This document summarizes random number generation using OpenCL. It discusses the Marsaglia polar method for generating random numbers and Gaussian pairs. It presents pseudocode for the Gaussian pair generation algorithm. Profiling results show that 54% of time is spent generating Gaussian pairs while 46% is for random numbers. The document also discusses optimization techniques like using local memory, coalesced global memory access, and choosing an optimal work group size. Performance results show near linear speedup from 1 to 8 GPUs.











![Lowering memory access latency
by using local memory
Unoptimized Optimized
__kernel EP(...) { __kernel local_EP(...) {
... ...
for (i = 0; i < NK; i++) lq[] = q[];
{ for (i = 0; i < NK; i++) {
... ...
q[l] = q[l] + 1.0; lq[l] = lq[l] + 1.0;
// array q[] fits into // array q[] fits into
local memory local memory
... Hot ...
} spot }
q[] = lq[];
} }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/npbep-110824115535-phpapp01/85/NAS-EP-Algorithm-15-320.jpg)